Growth curve
The growth curve is a controlling instrument and is used to reveal potential for cost savings .
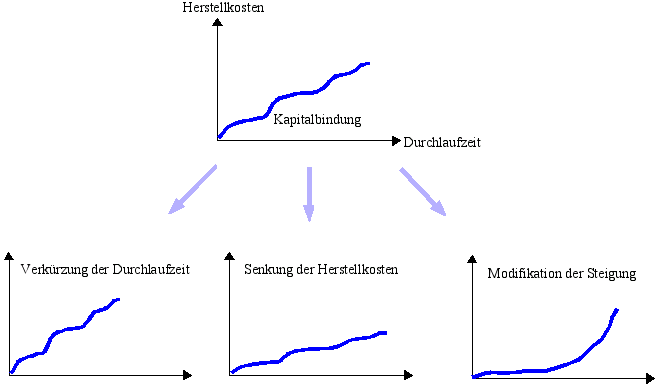
The value growth curve shows the cost of added value in the manufacture of a product. The representation takes place in a right-angled coordinate system . The production time is shown on the (horizontal) x-axis and the production costs accrued up to the respective time are shown on the (vertical) y-axis. The area under the curve shows the capital tied up during production and thus becomes the benchmark for the costs of capital tied up.
The slope of the curve reflects the efficiency of the manufacturing process. The curve should be as flat as possible at the start of production and only rise at the end; the most capital-intensive work should therefore be carried out last.
The possibility of lowering costs arises through a reduction in capital commitment. Various measures can be carried out for this purpose. The throughput time can be shortened, for example, by reducing and standardizing the parts required; the synchronization and parallelization of the individual production stages reduces the throughput time of the product. Manufacturing costs can be reduced primarily through automation and just-in-time procurement.
See also
literature
- Carl-Christian Freidank, Stefan Müller, Inge Wulf: Controlling and accounting: current developments in science and practice . Springer-Verlag, 2008, ISBN 978-3-8349-9718-0 , pp. 123 ff . ( Digitized version [accessed on January 22, 2016]).
- Frank Balsliemke: The value growth curve . In: Cost-oriented value stream planning (= essentials ). Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden, 2015, ISBN 978-3-658-08698-5 , p. 15-17 , doi : 10.1007 / 978-3-658-08699-2_4 ( abstract [accessed January 22, 2016]).
- Value growth curve analysis. In: Florian Klug: Concepts for production segment planning with special consideration of cost aspects. Dissertation. University of Linz. Utz, Munich 2000, ISBN 3-89675-677-X , p. 58 f. ( limited preview in Google Book search)
- Growth curve. In: Carl-Christian Freidank, Uwe Götze, Burkhard Huch, Jürgen Weber (eds.): Cost management: current concepts and applications. Springer, Berlin a. a. 1994, ISBN 978-3-642-63831-2 , pp. 217-219 ( limited preview in Google book search).