XT bus architecture
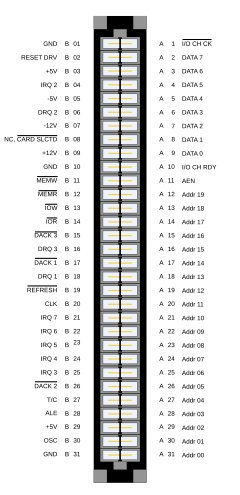
The XT bus architecture is an 8- bit bus architecture that was used in the Intel 8086 and in the Intel 8088 in IBM PCs and IBM PC XTs in the early to mid-1980s. The slot concept was essentially copied from the Apple II .
| Bus width | 8 bit |
| Insertable plug-in cards | 8 bit ISA |
| Pins | 62 |
| Pitch | 2.54 mm |
| Operating voltages | +5 V, −5 V, +12 V, −12 V |
| Bus cycle | 4.77 MHz |
| Theoretical data throughput |
0.96 MByte / s (1 W / S) |
The XT architecture is a direct predecessor of the 16-bit ISA architecture used in IBM PC-AT computers until the mid-1990s . The ISA bus, also known as AT bus, is backwards compatible with the XT bus; Most XT bus expansion cards also work in ISA bus computers, whereby they only occupy the first of the two sections of the ISA slot.
There are three DMA channels and five interrupt channels on the XT bus . Of these three, two are usually occupied by standard cards (floppy disk and hard disk controllers).
| channel | available on the bus ? |
Standard function |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | No | DRAM refresh |
| 1 | Yes | free for expansion cards |
| 2 | Floppy disk controller | |
| 3 | Hard disk controller |
| channel | available on the bus ? |
Standard function |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | No | timer |
| 1 | keyboard | |
| 2 | Video | |
| 3 | Yes | RS-232 : Port 2 (shared: 4) |
| 4th | RS-232: Port 1 (shared: 3) | |
| 5 |
IEEE 1284 : Port 2 (shared: 3) or sound card |
|
| 6th | Floppy disk controller | |
| 7th | IEEE 1284: Port 1 |
literature
- Intel ISA Bus Specification 2.01. 1989, accessed May 6, 2015 .