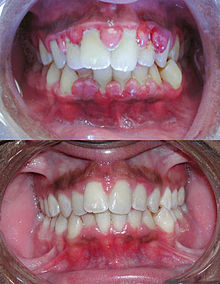
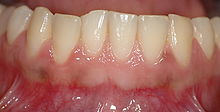
Bleeding gums
Bleeding gums are usually the result of an inflammatory disease of the gingiva ( gums ).
Signs
With bleeding gums, the gums react to various kinds of contact, e.g. B. Cleaning your teeth with a brush or floss, with bleeding. If the cause is inflammatory, the gingiva ( gums ) is more or less swollen and discolored red. Redness and swelling of the tissue are due to widening of the blood vessels. The blood flow is increased and the vessel walls become permeable. This causes blood plasma to escape into the neighboring tissue, and the gums swell. First the gingival papillae between the teeth swell, then in the other areas. in contrast, a healthy gingiva is pale pink in color. If a pale, not swollen gingiva is bleeding, the cause is not inflammatory, but is due to other reasons.
Possible causes
Gingivitis
In a poor oral hygiene for a period of more than 36 hours of bacterial forms on the teeth of dental plaque (plaque) . It contains leftovers, fats, emulsions, protein, sugar and bacteria . These excrete tooth-damaging acids and endotoxins as metabolic products . These are able to penetrate the gums and accumulate there. The immune system defends itself against this attack and acute inflammation develops . This inflammation is different. There are factors that prevent bleeding from occurring even with extremely unkempt teeth.
The gums bleed either from chemical, hormonal, bacterial, or mechanical stimuli.
If teeth are not adequately cared for, a film of plaque bacteria initially develops on the edge between the tooth neck and the gingiva (gums). A distinction is made between fixed (attached) and movable gingiva. The attached gingiva forms the “sulcus”, the small trench between the neck of the tooth and the gums. The "harmless" ubiquitous (ubiquitous) enterococci initially settle under the settling plaque. They form a so-called "sugar-protein matrix". If there is still no adequate oral hygiene, mobile lactic acid sticks and other bacteria, so-called anaerobes , which do not need oxygen to live , settle under this protective matrix . These include spirochetes , chlamydia , fungi and other microorganisms.
Among other things, they convert sulfur into hydrogen sulfide and thus produce bad breath . This form of gingivitis is called Schmutzgingivitis . At this stage a healthy condition can usually be restored by thoroughly removing the hard and soft coverings. If the plaque is not removed, it can develop a maximally harmful effect after a week at the latest.
Numerous factors promote plaque formation. These include a. Insufficient amount of saliva, narrow teeth, carious defects, protruding filling and crown margins, tartar and an improper diet that forces too little to chew. Of course, the type of germs that make up the plaque is also important. Minerals present in the saliva and fluid in the gum pockets cause the plaque to mineralize. Tartar forms, which greatly promotes the accumulation of plaque. Its removal is therefore important for the prevention and treatment of inflammation of the gums.
As gingivitis progresses, periodontitis can develop.
Periodontal disease
Periodontitis is an inflammation caused by bacteria, which manifests itself in a largely irreversible destruction of the periodontium and is accompanied by bleeding gums.
Anticoagulants - liver damage
If anticoagulant medication is taken for a longer period of time for therapeutic reasons , even minor injuries in the mouth, for example during tartar removal , can lead to prolonged bleeding. Before oral surgical interventions, the Quick or INR value is checked in order to avoid complications at an early stage. The same applies to bleeding in the event of liver damage. Various coagulation factors in the blood are not sufficiently produced and hemostasis is delayed.
Anti-epileptic drugs
Bleeding and growths are observed when taking antiepileptic drugs (elephantiasis gingivae).
Other causes
Other causes of bleeding gums include:
- Taking medication
- Hydantoin
- Cyclosporine A
- Nifedipine
- Vitamin C deficiency
- pregnancy
- Puberty gingivitis
- contraception
- Bleeding disorder ( haemophilia )
- leukemia
- Thrombocytopenia
- HIV
Bleeding gums can be an indication of systemic diseases, which should be clarified by a doctor.
therapy
Depending on the severity of the disease, professional teeth cleaning or periodontal treatment, possibly with subsequent full mouth disinfection, is carried out. In the case of cardiac diseases, antibiotic protection is indicated in order to prevent the consequences of bacteremia during therapy. Regular oral hygiene is a prerequisite for successful therapy.
forecast
With dirty gingivitis, the prognosis is very good. Professional teeth cleaning is the basis for quick healing. If periodontitis is present, the prognosis depends on the stage and the depth of the gingival pocket.
In the case of “pregnancy gingivitis”, which is caused by the hormonal changes, a healing of the gingival hyperplasia occurs as early as two months after the birth .
If you take anti-epileptic drugs, the prognosis is unfavorable because you cannot do without the drug.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b W. Bengel: Why the gums bleed - the gingivitis. In: KZBV, accessed on February 24, 2013.
- ↑ KZV Nordrhein, alarm signal bleeding gums ( Memento from December 19, 2015 in the Internet Archive )
Web links
- Chemical lexicon: Jodoform http://www.chemischemlexikon.de/cheminfo/0267-lex.htm