Demographics of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
| Demographics of Democratic Republic of the Congo | |
|---|---|
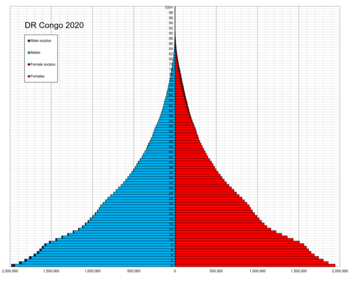 Population pyramid of the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 2020 | |
| Population | 95,894,118 (2021 est.) |
| Growth rate | 3.14% (2022 est.) |
| Birth rate | 40.08 births/1,000 population (2022 est.) |
| Death rate | 7.94 deaths/1,000 population (2022 est.) |
| Life expectancy | 61.83 years |
| • male | 60.03 years |
| • female | 63.69 years |
| Fertility rate | 5.63 children born/woman (2022 est.) |
| Infant mortality rate | 60.85 deaths/1,000 live births |
| Net migration rate | -0.71 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2022 est.) |
| Age structure | |
| 0–14 years | 46.38% |
| 65 and over | 2.47% |
| Sex ratio | |
| Total | 1 male(s)/female (2022 est.) |
| At birth | 1.03 male(s)/female |
| Under 15 | 1.01 male(s)/female |
| 65 and over | 0.6 male(s)/female |
| Nationality | |
| Nationality | Congolese |
| Language | |
| Official | French |

This article is about the demographic features of the population of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, including ethnicity, education level, health, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
As many as 250 ethnic groups have been distinguished and named. The most numerous people are the Luba, Mongo, and Bakongo.
Although 700 local languages and dialects are spoken, the linguistic variety is bridged both by the use of French, and the intermediary languages Kikongo ya leta, Tshiluba, Swahili, and Lingala.
Population

The CIA World Factbook estimated the population to be over 105 million as of 2022 (the exact number being 108,407,721), now exceeding that of Vietnam (with 98,721,275 inhabitants as of 2020) and ascending the country to the rank of 14th most populous in the world.[1] The proportion of children below the age of 14 in 2020 was 46.38%, 51.15% of the population was between 15 and 65 years of age, while 2.47% was 65 years or older.[1][2]
| Total population[1] | Population aged 0–14 (%) | Population aged 15–64 (%) | Population aged 65+ (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 12 184 000 | 43.7 | 52.5 | 3.8 |
| 1955 | 13 580 000 | 43.8 | 53.1 | 3.1 |
| 1960 | 15 368 000 | 43.8 | 53.3 | 2.9 |
| 1965 | 17 543 000 | 43.9 | 53.2 | 2.8 |
| 1970 | 20 267 000 | 44.4 | 52.8 | 2.8 |
| 1975 | 23 317 000 | 44.9 | 52.3 | 2.8 |
| 1980 | 27 019 000 | 45.4 | 51.8 | 2.8 |
| 1985 | 31 044 000 | 46.1 | 51.1 | 2.8 |
| 1990 | 36 406 000 | 47.0 | 50.2 | 2.8 |
| 1995 | 44 067 000 | 47.9 | 49.4 | 2.7 |
| 2000 | 49 626 000 | 48.0 | 49.4 | 2.7 |
| 2005 | 57 421 000 | 47.5 | 49.9 | 2.7 |
| 2010 | 65 966 000 | 46.3 | 51.1 | 2.7 |
| 2020 | 101 780 263 | 46.4 | 51.2 | 2.5 |
Population Estimates by Sex and Age Group (01.VII.2020):[3]
| Age Group | Male | Female | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 50 286 000 | 51 472 000 | 101 758 000 | 100 |
| 0–4 | 9 956 000 | 9 780 000 | 19 736 000 | 19.40 |
| 5–9 | 8 046 000 | 7 978 000 | 16 024 000 | 15.75 |
| 10–14 | 6 638 000 | 6 588 000 | 13 226 000 | 13.00 |
| 15–19 | 5 280 000 | 5 250 000 | 10 530 000 | 10.35 |
| 20–24 | 4 224 000 | 4 272 000 | 8 496 000 | 8.35 |
| 25–29 | 3 621 000 | 3 603 000 | 7 224 000 | 7.10 |
| 30–34 | 3 017 000 | 3 037 000 | 6 054 000 | 5.95 |
| 35–39 | 2 565 000 | 2 728 000 | 5 293 000 | 5.20 |
| 40–44 | 2 011 000 | 2 059 000 | 4 070 000 | 4.00 |
| 45–49 | 1 307 000 | 1 493 000 | 2 800 000 | 2.75 |
| 50–54 | 1 056 000 | 1 287 000 | 2 343 000 | 2.30 |
| 55–59 | 704 000 | 926 000 | 1 630 000 | 1.60 |
| 60–64 | 704 000 | 926 000 | 1 630 000 | 1.60 |
| 65-69 | 553 000 | 721 000 | 1 274 000 | 1.25 |
| 70-74 | 302 000 | 412 000 | 714 000 | 0.70 |
| 75+ | 302 000 | 412 000 | 714 000 | 0.70 |
| Age group | Male | Female | Total | Percent |
| 0–14 | 24 640 000 | 24 346 000 | 48 986 000 | 48.14 |
| 15–64 | 24 489 000 | 25 581 000 | 50 070 000 | 49.20 |
| 65+ | 1 157 000 | 1 545 000 | 2 702 000 | 2.66 |
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. There is more info on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. There is more info on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. There is more info on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Census
The first and so far only census conducted in DR Congo dates from 1984.[4]
Vital statistics
Registration of vital events in the Democratic Republic of the Congo is incomplete. The Population Department of the United Nations prepared the following estimates. [5]
| Period | Live births per year | Deaths per year | Natural change per year | CBR* | CDR* | NC* | TFR* | IMR* | Life expectancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 566 000 | 326 000 | 239 000 | 46.0 | 19.5 | 26.6 | 5.97 | 179.9 | 38.31 |
| 1951 | 579 000 | 328 000 | 251 000 | 46.1 | 20.0 | 26.2 | 5.97 | 178.5 | 38.44 |
| 1952 | 592 000 | 327 000 | 264 000 | 46.2 | 20.6 | 25.6 | 5.97 | 175.8 | 38.85 |
| 1953 | 607 000 | 329 000 | 278 000 | 46.4 | 21.2 | 25.1 | 5.98 | 173.3 | 39.14 |
| 1954 | 619 000 | 330 000 | 289 000 | 46.3 | 21.6 | 24.7 | 5.98 | 171.0 | 39.47 |
| 1955 | 632 000 | 333 000 | 299 000 | 46.3 | 21.9 | 24.4 | 5.98 | 168.8 | 39.72 |
| 1956 | 646 000 | 336 000 | 311 000 | 46.4 | 22.3 | 24.1 | 5.99 | 166.7 | 39.98 |
| 1957 | 663 000 | 338 000 | 325 000 | 46.5 | 22.8 | 23.7 | 6.01 | 164.7 | 40.32 |
| 1958 | 681 000 | 343 000 | 338 000 | 46.7 | 23.2 | 23.5 | 6.04 | 162.9 | 40.50 |
| 1959 | 698 000 | 348 000 | 349 000 | 46.8 | 23.4 | 23.4 | 6.07 | 161.2 | 40.64 |
| 1960 | 716 000 | 354 000 | 362 000 | 46.9 | 23.7 | 23.2 | 6.08 | 159.8 | 40.86 |
| 1961 | 738 000 | 370 000 | 368 000 | 47.1 | 23.5 | 23.6 | 6.11 | 159.6 | 40.24 |
| 1962 | 761 000 | 378 000 | 383 000 | 47.4 | 23.8 | 23.5 | 6.13 | 158.1 | 40.34 |
| 1963 | 785 000 | 385 000 | 400 000 | 47.5 | 24.2 | 23.3 | 6.16 | 156.5 | 40.60 |
| 1964 | 808 000 | 403 000 | 406 000 | 47.7 | 24.0 | 23.8 | 6.18 | 155.7 | 40.05 |
| 1965 | 833 000 | 404 000 | 429 000 | 47.9 | 24.7 | 23.2 | 6.21 | 153.1 | 40.70 |
| 1966 | 859 000 | 397 000 | 462 000 | 47.9 | 25.8 | 22.1 | 6.24 | 149.5 | 42.05 |
| 1967 | 885 000 | 405 000 | 480 000 | 48.0 | 26.0 | 21.9 | 6.27 | 147.3 | 42.31 |
| 1968 | 910 000 | 411 000 | 500 000 | 47.9 | 26.3 | 21.6 | 6.30 | 145.1 | 42.71 |
| 1969 | 935 000 | 418 000 | 517 000 | 47.8 | 26.4 | 21.4 | 6.32 | 142.7 | 42.98 |
| 1970 | 959 000 | 425 000 | 534 000 | 47.6 | 26.5 | 21.1 | 6.34 | 140.5 | 43.28 |
| 1971 | 985 000 | 431 000 | 554 000 | 47.5 | 26.8 | 20.8 | 6.38 | 138.3 | 43.66 |
| 1972 | 1 006 000 | 437 000 | 569 000 | 47.3 | 26.8 | 20.5 | 6.40 | 136.4 | 43.93 |
| 1973 | 1 026 000 | 445 000 | 582 000 | 47.0 | 26.6 | 20.4 | 6.41 | 134.7 | 44.10 |
| 1974 | 1 047 000 | 451 000 | 597 000 | 46.7 | 26.6 | 20.1 | 6.42 | 133.3 | 44.41 |
| 1975 | 1 070 000 | 460 000 | 610 000 | 46.4 | 26.4 | 20.0 | 6.42 | 132.1 | 44.47 |
| 1976 | 1 091 000 | 468 000 | 623 000 | 46.1 | 26.3 | 19.8 | 6.43 | 130.9 | 44.66 |
| 1977 | 1 111 000 | 476 000 | 634 000 | 45.8 | 26.1 | 19.6 | 6.43 | 129.8 | 44.76 |
| 1978 | 1 134 000 | 491 000 | 643 000 | 45.6 | 25.8 | 19.7 | 6.44 | 129.1 | 44.54 |
| 1979 | 1 184 000 | 496 000 | 688 000 | 45.9 | 26.7 | 19.2 | 6.46 | 126.9 | 45.21 |
| 1980 | 1 227 000 | 507 000 | 720 000 | 46.0 | 27.0 | 19.0 | 6.47 | 125.1 | 45.47 |
| 1981 | 1 260 000 | 517 000 | 744 000 | 45.9 | 27.1 | 18.8 | 6.49 | 123.5 | 45.72 |
| 1982 | 1 293 000 | 526 000 | 766 000 | 45.8 | 27.2 | 18.6 | 6.50 | 121.9 | 45.92 |
| 1983 | 1 333 000 | 535 000 | 798 000 | 45.9 | 27.5 | 18.5 | 6.55 | 120.3 | 46.18 |
| 1984 | 1 377 000 | 545 000 | 832 000 | 46.2 | 27.9 | 18.3 | 6.60 | 118.7 | 46.45 |
| 1985 | 1 433 000 | 559 000 | 873 000 | 46.5 | 28.4 | 18.2 | 6.65 | 117.4 | 46.62 |
| 1986 | 1 480 000 | 571 000 | 910 000 | 46.7 | 28.7 | 18.0 | 6.69 | 116.1 | 46.91 |
| 1987 | 1 529 000 | 579 000 | 950 000 | 46.8 | 29.1 | 17.7 | 6.74 | 114.9 | 47.34 |
| 1988 | 1 568 000 | 588 000 | 980 000 | 46.5 | 29.1 | 17.4 | 6.73 | 113.7 | 47.77 |
| 1989 | 1 610 000 | 596 000 | 1 014 000 | 46.3 | 29.1 | 17.1 | 6.74 | 112.6 | 48.17 |
| 1990 | 1 652 000 | 604 000 | 1 047 000 | 46.0 | 29.2 | 16.8 | 6.70 | 111.3 | 48.60 |
| 1991 | 1 713 000 | 617 000 | 1 097 000 | 46.1 | 29.5 | 16.6 | 6.69 | 110.1 | 48.95 |
| 1992 | 1 761 000 | 629 000 | 1 132 000 | 45.9 | 29.5 | 16.4 | 6.67 | 108.9 | 49.24 |
| 1993 | 1 804 000 | 638 000 | 1 165 000 | 45.7 | 29.5 | 16.2 | 6.64 | 108.1 | 49.55 |
| 1994 | 1 878 000 | 653 000 | 1 225 000 | 45.9 | 29.9 | 16.0 | 6.67 | 107.0 | 49.88 |
| 1995 | 2 046 000 | 682 000 | 1 364 000 | 47.1 | 31.4 | 15.7 | 6.71 | 105.7 | 50.41 |
| 1996 | 2 083 000 | 730 000 | 1 353 000 | 46.8 | 30.4 | 16.4 | 6.72 | 106.4 | 49.31 |
| 1997 | 2 067 000 | 707 000 | 1 360 000 | 45.8 | 30.2 | 15.7 | 6.73 | 103.7 | 50.40 |
| 1998 | 2 071 000 | 729 000 | 1 342 000 | 45.1 | 29.2 | 15.9 | 6.73 | 101.5 | 49.70 |
| 1999 | 2 128 000 | 739 000 | 1 389 000 | 45.0 | 29.4 | 15.6 | 6.72 | 99.5 | 49.95 |
| 2000 | 2 189 000 | 712 000 | 1 477 000 | 45.0 | 30.4 | 14.6 | 6.72 | 97.3 | 51.78 |
| 2001 | 2 245 000 | 721 000 | 1 525 000 | 44.8 | 30.4 | 14.4 | 6.70 | 95.0 | 52.12 |
| 2002 | 2 310 000 | 733 000 | 1 577 000 | 44.7 | 30.5 | 14.2 | 6.67 | 92.6 | 52.33 |
| 2003 | 2 372 000 | 738 000 | 1 634 000 | 44.5 | 30.7 | 13.9 | 6.64 | 89.9 | 52.83 |
| 2004 | 2 426 000 | 738 000 | 1 688 000 | 44.3 | 30.8 | 13.5 | 6.62 | 87.2 | 53.43 |
| 2005 | 2 499 000 | 743 000 | 1 757 000 | 44.2 | 31.1 | 13.1 | 6.60 | 84.6 | 53.93 |
| 2006 | 2 592 000 | 746 000 | 1 846 000 | 44.4 | 31.6 | 12.8 | 6.59 | 82.0 | 54.53 |
| 2007 | 2 675 000 | 756 000 | 1 920 000 | 44.4 | 31.8 | 12.5 | 6.58 | 79.4 | 54.92 |
| 2008 | 2 767 000 | 764 000 | 2 003 000 | 44.4 | 32.2 | 12.3 | 6.58 | 77.0 | 55.34 |
| 2009 | 2 867 000 | 771 000 | 2 096 000 | 44.6 | 32.6 | 12.0 | 6.59 | 74.5 | 55.84 |
| 2010 | 2 957 000 | 774 000 | 2 183 000 | 44.5 | 32.9 | 11.7 | 6.59 | 72.2 | 56.42 |
| 2011 | 3 069 000 | 776 000 | 2 293 000 | 44.7 | 33.4 | 11.3 | 6.58 | 70.0 | 57.07 |
| 2012 | 3 171 000 | 793 000 | 2 378 000 | 44.6 | 33.5 | 11.2 | 6.56 | 68.0 | 57.25 |
| 2013 | 3 247 000 | 797 000 | 2 450 000 | 44.2 | 33.4 | 10.9 | 6.53 | 65.9 | 57.76 |
| 2014 | 3 345 000 | 802 000 | 2 543 000 | 44.0 | 33.4 | 10.6 | 6.48 | 64.0 | 58.30 |
| 2015 | 3 433 000 | 818 000 | 2 615 000 | 43.6 | 33.2 | 10.4 | 6.44 | 62.2 | 58.49 |
| 2016 | 3 532 000 | 820 000 | 2 712 000 | 43.4 | 33.3 | 10.1 | 6.39 | 60.4 | 59.07 |
| 2017 | 3 647 000 | 832 000 | 2 815 000 | 43.3 | 33.4 | 9.9 | 6.35 | 58.6 | 59.41 |
| 2018 | 3 748 000 | 835 000 | 2 913 000 | 43.0 | 33.4 | 9.6 | 6.30 | 56.9 | 59.94 |
| 2019 | 3 839 000 | 844 000 | 2 995 000 | 42.7 | 33.3 | 9.4 | 6.25 | 55.5 | 60.28 |
| 2020 | 3 930 000 | 886 000 | 3 044 000 | 42.3 | 32.8 | 9.5 | 6.21 | 53.9 | 59.74 |
| 2021 | 4 035 000 | 931 000 | 3 104 000 | 42.0 | 32.3 | 9.7 | 6.16 | 52.3 | 59.19 |
| *CBR = crude birth rate (per 1000 people); CDR = crude death rate (per 1000 people); NC = natural change (per 1000 people), also equals CBR minus CDR; IMR = infant mortality rate per 1000 births; TFR = total fertility rate (number of children per woman) | |||||||||
Fertility and Births
Total Fertility Rate (TFR) (Wanted Fertility Rate) and Crude Birth Rate (CBR) for urban and rural areas:[6]
The Wanted Fertility Rate is an estimate of what the fertility rate would be if all unwanted births were avoided.[7]
| Year | CBR (Total) | TFR (Total) | CBR (Urban) | TFR (Urban) | CBR (Rural) | TFR (Rural) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 44,1 | 6,3 (5,6) | 40,4 | 5,4 (4,8) | 46,8 | 7,0 (6,2) |
| 2013-14 | 44,1 | 6,6 (5,7) | 40,5 | 5,4 (4,6) | 45,9 | 7,3 (6,5) |
Fertility data per province, as of 2014:[8]
| Province | Total fertility rate | Percentage of women age 15-49 currently pregnant | Mean number of children ever born to women age 40-49 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kinshasa | 4.2 | 5.7 | 4.8 |
| Bas-Congo | 6.0 | 12.6 | 6.5 |
| Bandundu | 6.3 | 12.1 | 6.1 |
| Équateur | 7.0 | 14.3 | 6.5 |
| Orientale | 5.9 | 11.6 | 5.3 |
| Nord-Kivu | 6.5 | 9.7 | 6.7 |
| Sud-Kivu | 7.7 | 12.5 | 7.4 |
| Maniema | 6.9 | 14.8 | 7.0 |
| Katanga | 7.8 | 12.8 | 7.3 |
| Kasaï Oriental | 7.3 | 12.4 | 7.5 |
| Kasaï Occidental | 8.2 | 14.2 | 7.5 |
Life expectancy

| Period | Life expectancy in Years[9] |
|---|---|
| 1950–1955 | 39.06 |
| 1955–1960 | |
| 1960–1965 | |
| 1965–1970 | |
| 1970–1975 | |
| 1975–1980 | |
| 1980–1985 | |
| 1985–1990 | |
| 1990–1995 | |
| 1995–2000 | |
| 2000–2005 | |
| 2005–2010 | |
| 2010–2015 |
Ethnic groups
More than 250 ethnic groups have been identified and named, of which the majority are Bantu. The four largest groups - Mongo, Luba, Kongo (all Bantu), and the Mangbetu-Azande collectively make up about 45% of the population. 5,000 people from Belgium and 5,000 people from Greece currently live in DR Congo.[10]

Bantu peoples (80%):
- Luba (18%), Mongo (17%), Kongo (12%)[citation needed]
- Others:[citation needed] Ambala, Ambuun, Angba, Babindi, Baboma, Baholo, Balunda, Bangala, Bango, Batsamba, Bazombe, Bemba, Bembe, Bira, Bowa, Dikidiki, Dzing, Fuliru, Havu, Hema, Hima, Hunde, Iboko, Kanioka, Kaonde, Kuba, Kumu, Kwango, Lengola, Lokele, Lupu, Lwalwa, Mbala, Mbole, Mbuza (Budja), Nande, Ngoli, Bangoli, Ngombe, Nkumu, Nyanga, Pende, Popoi, Poto, Sango, Shi, Songo, Sukus, Tabwa, Chokwe, Téké, Tembo, Tetela, Topoke, Ungana, Vira, Wakuti, Yaka, Yakoma, Yanzi, Yéké, Yela etc.
More than 600,000 pygmies (around 1% of the total population) are believed to live in DR Congo, mainly in forests, where they survive by hunting wild animals and gathering fruits.[11]
Languages
The four major languages in the DRC are French (official, from colonization), Lingala (a lingua franca, or trade language), Kingwana (a dialect of Swahili), Kikongo ya leta, and Tshiluba. In total, there are over 200 ethnic languages.
French is generally the language of instruction in schools. English is taught as a compulsory foreign language in Secondary and High Schools around the country. It is a required subject in the Faculty of Economics at major universities around the country and there are numerous language schools in the country that teach it. Former President Kabila himself is fluent in both English and French, as was his father.
Religions
A survey conducted by the Demographic and Health Surveys program in 2013-2014 indicated that Christians constituted 93.7% of the population (Catholics 29.7%, Protestants 26.8%, and other Christians 37.2%). An indigenous religion, Kimbanguism, was practiced by 2.8% of the population, while Muslims make up 1.2%.[12]
Another estimate (by the Pew Research Center in 2010) found Christianity was followed by 95.8% of the population.[13]
The CIA The World Factbook gives the following percentages: Roman Catholic 29.9%, Protestant 26.7%, Kimbanguist 2.8%, Other Christian 36.5%, Islam 1.3%, Other (includes Syncretic Sects and Indigenous beliefs) 2.7%.[14]
The Joshua Project, a Christian missionary organisation, gives the following percentages: Roman Catholic 43.9%, Protestant 24.8%, Other Christian 23.7%, Muslim 1.6%, Non-religious 0.6%, Hindu 0.1% other syncretic sects and indigenous beliefs 5.3%.[15]
Other demographic statistics


These are some other demographic statistics according to the World Population Review in 2022.[16]
- One birth every 9 seconds
- One death every 38 seconds
- One net migrant every 111 minutes
- Net gain of one person every 11 seconds
The following demographic statistics are from the CIA World Factbook.[17]
Population
- 108,407,721 (2022 est.)
- 85,281,024 (July 2018 est.)
- Note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population and growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and gender than would otherwise be expected (July 2017 est.)
Religions
Roman Catholic 29.9%, Protestant 26.7%, other Christian 36.5%, Kimbanguist 2.8%, Muslim 1.3%, other (includes syncretic sects and indigenous beliefs) 1.2%, none 1.3%, unspecified 0.2% (2014 est.)
Age structure
- 0-14 years: 46.38% (male 23,757,297/female 23,449,057)
- 15-24 years: 19.42% (male 9,908,686/female 9,856,841)
- 25-54 years: 28.38% (male 14,459,453/female 14,422,912)
- 55-64 years: 3.36% (male 1,647,267/female 1,769,429)
- 65 years and over: 2.47% (male 1,085,539/female 1,423,782) (2020 est.)
- 0-14 years: 41.25% (male 17,735,697 /female 17,446,866)
- 15-24 years: 21.46% (male 9,184,871 /female 9,117,462)
- 25-54 years: 30.96% (male 13,176,714 /female 13,225,429)
- 55-64 years: 3.63% (male 1,472,758 /female 1,625,637)
- 65 years and over: 2.69% (male 974,293 /female 1,321,297) (2018 est.)
Median age
- total: 16.7 years. Country comparison to the world: 222nd
- male: 16.5 years
- female: 16.8 years (2020 est.)
- total: 18.8 years. Country comparison to the world: 206th
- male: 18.6 years
- female: 19 years (2018 est.)
Birth rate
- 40.08 births/1,000 population (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 7th
- 40.1 births/1,000 population (2020 est.)
Death rate
- 7.94 deaths/1,000 population (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 95th
- 9.1 deaths/1,000 population (2020 est.)
Total fertility rate
- 5.63 children born/woman (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 3rd
- 5.7 children born/woman (2020 est.)
Population growth rate
- 3.14% (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 9th
- 2.33% (2018 est.) Country comparison to the world: 31st
- 2.42% (2016)
Mother's mean age at first birth
- 19.9 years (2013/14 est.)
- note: median age at first birth among women 25-29
Contraceptive prevalence rate
- 28.1% (2017/18)
- 20.4% (2013/14)
Net migration rate
- -0.71 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 131st
- -0.1 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2018 est.) Country comparison to the world: 105th
- -0.54 migrant(s)/1,000 population
note: fighting between the Congolese Government and Uganda- and Rwanda-backed Congolese rebels spawned a regional war in DRC in August 1998, which left 2.33 million Congolese internally displaced and caused 412,000 Congolese refugees to flee to surrounding countries (2011 est.)
Given the situation in the country and the condition of state structures, it is extremely difficult to obtain reliable data however evidence suggests that DRC continues to be a destination country for immigrants in spite of recent declines. Immigration is seen to be very diverse in nature, with refugees and asylum-seekers - products of the numerous and violent conflicts in the Great Lakes Region - constituting an important subset of the population in the country.[18]
Additionally, the country's large mine operations attract migrant workers from Africa and beyond and there is considerable migration for commercial activities from other African countries and the rest of the world, but these movements are not well studied. Transit migration towards South Africa and Europe also plays a role. Immigration in the DRC has decreased steadily over the past two decades, most likely as a result of the armed violence that the country has experienced.[18]
According to the International Organization for Migration, the number of immigrants in the DRC has declined from just over 1 million in 1960, to 754,000 in 1990, to 480,000 in 2005, to an estimated 445,000 in 2010. Valid figures are not available on migrant workers in particular, partly due to the predominance of the informal economy in the DRC. Data are also lacking on irregular immigrants, however given neighbouring country ethnic links to nationals of the DRC, irregular migration is assumed to be a significant phenomenon in the country.[18]
Figures on the number of Congolese nationals abroad vary greatly depending on the source, from 3 to 6 million. This discrepancy is due to a lack of official, reliable data. Emigrants from the DRC are above all long-term emigrants, the majority of which live within Africa and to a lesser extent in Europe; 79.7% and 15.3% respectively, according to estimates on 2000 data. Most Congolese emigrants however, remain in Africa, with new destination countries including South Africa and various points en route to Europe.[18]
In addition to being a host country, the DRC has also produced a considerable number of refugees and asylum-seekers located in the region and beyond. These numbers peaked in 2004 when, according to UNHCR, there were more than 460,000 refugees from the DRC; in 2008, Congolese refugees numbered 367,995 in total, 68% of which were living in other African countries.[18]
Religions
- Roman Catholic (55.8%), Other Christian (39.1%), Folk religion (2.5%), Islam (2.1%), None (0.5%)
Dependency ratios
- total dependency ratio: 97.5 (2015 est.)
- youth dependency ratio: 91.5 (2015 est.)
- elderly dependency ratio: 6 (2015 est.)
- potential support ratio: 16.8 (2015 est.)
Gender ratio
- At birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
- Under 15 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
- 15–64 years: 0.99 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over: 0.69 male(s)/female
- Total population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
- total population: 61.83 years. Country comparison to the world: 216th
- male: 60.03 years
- female: 63.69 years (2022 est.)
- total population: 58.1 years (2018 est.) Country comparison to the world: 213rd
- male: 56.5 years (2018 est.)
- female: 59.7 years (2018 est.)
- total population: 56.93 years
- male: 55.39 years
- female: 58.51 years (2015 est.)[19]
Urbanization
- urban population: 46.8% of total population (2022)
- rate of urbanization: 4.33% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
- urban population: 44.5% of total population (2018)
- rate of urbanization: 4.53% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)
HIV/AIDS
- Adult prevalence rate: 0.7% (2017 est.)
- People living with HIV/AIDS: 390,000 (2017 est.)
- Deaths: 17,000 (2017 est.)
Major infectious diseases
- Degree of risk: very high
- Food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, typhoid fever and ebola.
- Vectorborne diseases: malaria, plague, and African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) are high risks in some locations
- Water contact disease: schistosomiasis (2005)
Nationality
- Noun: Congolese (singular and plural)
- Adjective: Congolese or Congo
Literacy
- Definition: age 15 and over can read and write French, Lingala, Kingwana, or Tshiluba
- Total population: 77%
- Male: 88.5%
- Female: 66.5% (2016 est.)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
- total: 10 years (2013)
- male: 11 years (2013)
- female: 9 years (2013)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
- total: 8.7% (2012 est.) Country comparison to the world: 134th
- male: 11.3% (2012 est.)
- female: 6.8% (2012 est.)
Congolese diaspora
This article needs to be updated. (August 2016) |
The table below shows DRC born people who have emigrated abroad in selected Western countries (although it excludes their descendants).[20]
| Rank | Country | Region | Year | DRC born population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Europe | 2010 | 59,641 | |
| 2 | Europe | 2015 | 44,715 | |
| 3 | North America | 2011-13 | 20,410 | |
| 4 | North America | 2011 | 19,890 | |
| 5 | Europe | 2011 | 19,193 | |
| 6 | Europe | 2011 (foreign citizens) | 9,299 | |
| 7 | Europe | 2011 | 6,724 | |
| 8 | Europe | 2015 | 6,010 | |
| 9 | Europe | 2015 | 4,973 | |
| 10 | Europe | 2015 | 3,092 | |
| 11 | Oceania | 2011 | 2,576 | |
| 12 | Europe | 2015 | 2,210 | |
| 13 | South America | 2020 | 2,064 | |
| 14 | Europe | 2013 | 1,494 | |
| 15 | Europe | 2015 | 1,523 | |
| 16 | Europe | 2015 | 1,264 | |
| 17 | Europe | 2015 | 1,258 |
These are only estimates and do not account for Congolese migrants residing illegally in these and other countries. Among African countries, Congo's diaspora is second only to Nigeria in size.[citation needed]
See also
Congolese ethnic groups:
Other articles
References
- ^ a b c "Congo, Democratic Republic of the". 18 April 2022.
- ^ Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations Secretariat, World Population Prospects: The 2010 Revision Archived May 6, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "UNSD — Demographic and Social Statistics".
- ^ "Recensement scientifique de la population 1984. Résultats provisoires" (PDF).
- ^ "World Population Prospects - Population Division - United Nations". population.un.org. Retrieved 2022-07-13.
- ^ "Congo, Dem. Rep. - Enquête Démographique et de Santé 2007". microdata.worldbank.org.
- ^ "Fertility and wanted fertility". Our World in Data. Retrieved 2021-06-21.
- ^ "Democratic Republic of Congo" (PDF).
- ^ "World Population Prospects - Population Division - United Nations". esa.un.org. Retrieved 2018-08-26.
- ^ "Greeks Around the Globe". Archived from the original on 2006-06-19.
- ^ "BBC NEWS - Africa - DR Congo pygmies 'exterminated'". news.bbc.co.uk. 6 July 2004.
- ^ "Enquête Démographique et de Santé (EDS-RDC) 2013-2014" (PDF) (in French). Ministère du Plan et Suivi de la Mise en œuvre de la Révolution de la Modernité, Ministère de la Santé Publique. p. 36. Retrieved 20 April 2018.
- ^ "Global Religious Landscape". Pew Forum. 18 December 2012.
- ^ "Africa :: CONGO, DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE". CIA The World Factbook. 18 April 2022.
- ^ "Joshua Project - Congo, Democratic Republic of - Religions".
- ^ "DR Congo Population 2022", World Population Review
- ^ "The World FactBook - Congo, Democratic Republic of the", The World Factbook, July 12, 2018
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b c d e "Migration en République Démocratique du Congo: Profil national 2009". International Organization for Migration. 2009. Retrieved 2010-08-17.
- ^ CIA "The World Factbook": DR Congo 2015. Retrieved January 13, 2016.
- ^ Flahaux M.-L. and Schoumaker B. (2016), Democratic Republic of the Congo: A Migration History Marked by Crises and Restrictions, Migration Policy Institute Retrieved January 20, 2018.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook (2024 ed.). CIA. (Archived 2007 edition.)
This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook (2024 ed.). CIA. (Archived 2007 edition.)
External links
- "Mortality in the Democratic Republic of the Congo: An Ongoing Crisis" (PDF). (1.07 MB), International Rescue Committee, January 2008 (estimates 5.4 million excess deaths above sub-Saharan average from 1998 to 2007)
