Eastern Borneo Gibbon
| Eastern Borneo Gibbon | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Female of the Eastern Borneo Gibbon in the Tabin Wildlife Reserve in Sabah |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Hylobates funereus | ||||||||||||
| Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire , 1850 |
The Eastern Bornean Gibbon ( Hylobates funereus ) is an on Borneo endemic primate species from the family of gibbons (Hylobatidae).
distribution
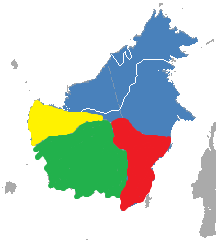
Blue - Eastern Borneo gibbon,
yellow - Western Borneo gibbon ,
red - Müller gibbon ,
green - white beard gibbon
It occurs in the north and northeast of the island; the distribution area extends in the southwest to the Kapuas Mountains and in the middle east of the island to the Mahakam River and thus includes the Malaysian state of Sabah and most of Sarawak , Brunei and the Indonesian province of Kalimantan Utara and the northern half of Kalimantan Timur .
features
The tailless Eastern Borneo gibbon reaches a head-torso length of 47 to 49 cm and a weight of 5 to 6.4 kg. It is deeply dark brown or gray in color. The hair on the top of the head runs in a fan shape from the forehead to the back and is significantly longer above the ears. The eyebrows that have grown together are whitish. The hands and feet are no darker than the legs, but sometimes they are lighter.
Habitat and way of life
The monkey species lives in primary and secondary deciduous forests and tropical evergreen forests, often with high populations of wing fruit plants . It can also survive in selectively cleared forests, provided there are enough fruit-bearing trees left. In the mountains of Sarawak it occurs up to an altitude of 1700 meters - with decreasing population density at higher altitudes. In the Kutai National Park the average area size is 36 hectares. Eastern Borneo gibbons can be found in the middle and upper tree regions 25 to 30 meters above the ground. They are usually active 8 to 10 hours a day, wake up at dawn and go to rest on the tops of their sleeping trees in the late afternoon before sunset.
Like all gibbons, Eastern Borneo gibbons feed mainly on ripe fruits, especially figs (24%). Fruits make up about 65% (27–90% depending on the season) of their diet, the proportion of leaves is 32% (8–73% depending on the season) that of the flowers is 4% and animal food has a proportion of around 2%.
A group usually consists of 3–4 animals, a female, a male and their offspring. The monkeys breed all year round. As a rule, 36 months elapse between two births. The young animals are usually looked after by the mother, although the father and older young animals help. The male spends more time with the young, playing and grooming each other. At the age of 6, the young animals reach the height of their parents, but remain with them until they reach sexual maturity at 8–9 years. The interval between births is 36 months and life expectancy is up to 47 years.
literature
- David J. Chivers, Martina V. Anandam, Colin P. Groves, Sanjay Molur, Benjamin M. Rawson, Matthew C. Richardson, Christian Roos & Danielle Whittaker: Family Hylobatidae (Gibbons). Pp. 784-785 in Russell A. Mittermeier , Anthony B. Rylands & Don E. Wilson : Handbook of the Mammals of the World: Volume 3. Primates. Lynx Editions, 2013, ISBN 978-84-96553-89-7