1,4-α-glucan branching enzyme
| 1,4-α-glucan branching enzyme | ||
|---|---|---|
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 702 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Monomer | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | GBE1 | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 2.4.1.18 , glycosyl transferase | |
| Response type | Transfer of glucose | |
| Substrate | 1,4-glycogen / amylose | |
| Products | branched glycogen / amylopectin | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Parent taxon | Creature | |
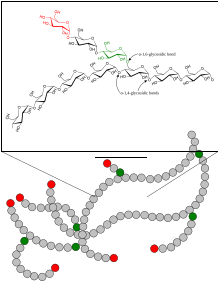
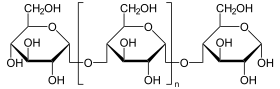
The 1,4-α-glucan-branching enzyme (GBE) is the enzyme that adds poly- glucose chains to long-chain polysaccharides , but not at the end of the chain, but in a branching manner, approximately at a distance of 10 to 14 glucose units from the next Branching (see fig.). This reaction (along with chain elongation) is the final step in building glycogen . The branches are necessary in order to increase the solubility of the glycogen and thus prevent the osmotic pressure in the cell from becoming too high. GBE occurs in most living things, the plant enzyme has the name amylopectin-branching enzyme or Q-enzyme . In humans, it is particularly localized in the liver and muscles . Mutations at GBE1 - gene can for Glycogen Storage Disease Type IV ( Glycogen storage disease type IV ) or Polyglucosankörper disease adults lead.
Catalyzed reaction
The linear glycogen chain is branched (analogous in plants: amylose is converted to amylopectin ).
Individual evidence
- ↑ UniProt Q04446
- ^ Lossos et al .: Adult polyglucosan body disease in Ashkenazi Jewish patients carrying the Tyr329Ser mutation in the glycogen-branching enzyme gene. Ann Neurol. 1998; 44 (6): 867-72. PMID 9851430