Alkenyl group
| Alkenyl group ( marked blue ) |
|
Vinyl group in vinyl chloride . The vinyl group is marked in blue . |
 Vinyl group in styrene . The vinyl group is marked in blue . |
|
Allyl group in allyl alcohol . The allyl group is marked in blue . |
 Mesomeric stabilized allyl radical. The allyl group is marked in blue . |
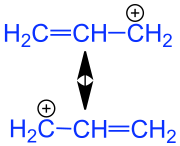 Mesomeric stabilized allyl cation. The allyl group is marked in blue . |
|
1-butenyl group in 1-butenyl chloride. The 1-butenyl group is marked in blue . |
In organic chemistry, an alkenyl radical or alkenyl group is a substituent that contains a carbon-carbon double bond ( ethylenic structural element). Formally, an alkenyl radical is derived from an alkene in which an H atom has been removed. In analogy to alkyl residues , the carbon atom to be linked to another molecule (residue) (with the so-called free valence , “yl”) is given the number “1”. From here you count and number up to the end of the longest carbon chain that contains the double bond. There are also alkenyl radicals and alkenyl cations, which are principally mesomeric stabilized .
The simplest alkenyl radical is logically derived from the C 2 hydrocarbon ethene ( ethylene ); It is therefore called “ethenyl”, but is usually called a vinyl residue . From the C 3 hydrocarbon propene there are isomeric alkenyl residues , depending on the position of the double bond .
literature
- H. Grünewald (Ed.): International rules for chemical nomenclature and terminology . German edition, Vol. 1, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim 1975.
Individual evidence
- ^ Hans Beyer and Wolfgang Walter : Organische Chemie , 20th edition, S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart 1984, ISBN 3-7776-0406-2 , p. 63.