View (representation)

In an architectural drawing or technical drawing, the two-dimensional representations of a three-dimensional body from different sides are referred to as a view .
In mechanical engineering , for example, the body can be a component , in architecture and construction, for example, a building .
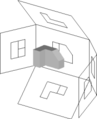
Views in the three-panel projection
In the three-panel projection , the views are drawn from three angles at right angles to each other.
In general, you can use two known views to construct any further perspective, i.e. view, even non-orthogonal. The prerequisite for this, however, is that it is not the counter position, e.g. B. Right view and left view. Views are often defined as: " top view " DS, "front" VS, "side left" SL, "side right" SR, "rear view" RA, or "view from below" AU. Views can be displayed with and without invisible edges. Frequently given views are the top view and the front view. The right and left views can be constructed directly from these two.
The selection of the displayed views is important, as it must be possible to read the shape of the displayed body unequivocally.
Body to be represented in the projection cuboid