Azines (hydrazine)
| Azines (hydrazines) |
|---|
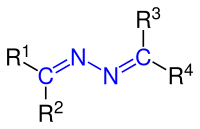
|
| General structure of azines (hydrazine derivatives) with the azine group marked in blue . The radicals R 1 to R 4 can be aliphatic , cyclic or aromatic groups or else a hydrogen atom. |
Azines are a group of chemical compounds which are derived from hydrazine and which can be described as double derivatives of hydrazine. Azines have the general structure R 1 R 2 C = N − N = CR 3 R 4 , with a symmetrical arrangement of the radicals R 1 to R 4 . Aldehydes form aldazines , ketones corresponding to ketazines . Azines are polar, mostly poorly water-soluble solids. Some dyes and drugs are azines.
education
Azines are formed when one equivalent of hydrazine reacts with two equivalents of a carbonyl compound ( aldehydes or ketones ) in a condensation reaction with the escape of water.
use
Azines are used as starting materials for the synthesis of heterocycles (see e.g. the Piloty-Robinson pyrrole synthesis ) as well as for the production of metal complexes.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b entry on azines. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 16, 2013.
