Azo coupling
The azo coupling is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction in which aryldiazonium salts ( diazo component ) are reacted ("coupled") with activated aromatics (= coupling component ), β-dicarbonyl compounds, pyrazoles and 2-pyridinones. Due to the low electrophilicity of the diazonium ion , the coupling can only take place as a second substitution with a strong + M first substituent and this preferably in the para position due to the + M effect .
General reaction equation:
where X - mostly Cl - is.
Azo couplings are carried out in the temperature range from 0 ° C to 5 ° C, since the diazonium salts used are subject to faster decomposition at higher temperatures. Depending on the starting material, the work is carried out in the weakly acidic to moderately basic range.
This reaction is characterized by the formation of an azo bond (Ar-N = N-Ar ', derivatives of diazene , H-N = N-H). The resulting azo compounds have pronounced absorption bands in the visible light range and are therefore dyes . Many of them have a wide range of uses as so-called azo dyes .
Reaction mechanism
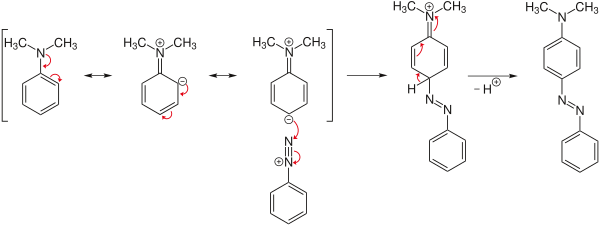
The azo coupling is illustrated below using the example of the reaction of N , N -dimethylaniline as an activated aromatic with a diazotized benzene derivative to form butter yellow :
literature
- Author collective: Organikum . Barth Verlagsgesellschaft, Leipzig, Berlin a. Heidelberg, 1993, p. 568 ff.
- KPC Vollhardt and NE Schore: Organic Chemistry. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2000, p. 1116 f.