Barton reaction
The Barton reaction is one of the name reactions in organic chemistry and is named after the British chemist Derek Harold Richard Barton (1918–1998), who first published it in 1960.
Overview reaction
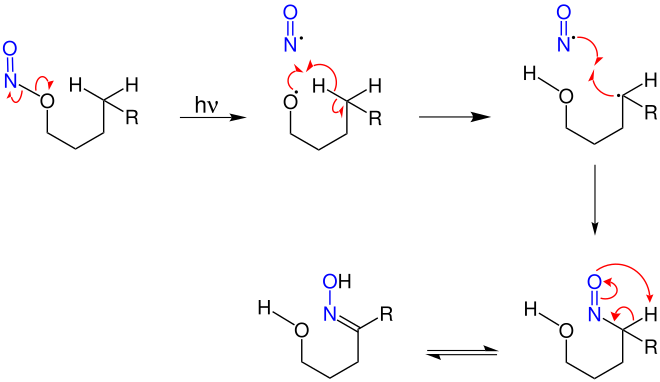
In the Barton reaction, a nitrous acid ester is photolytically converted into a δ-hydroxy-substituted oxime .
Since oximes to carbonyl compounds (R = H, aldehyde or R = Organylgruppe , ketone ) hydrolyze blank, are about this reaction sequence, ultimately, δ-hydroxy-substituted aldehydes or ketones accessible.
Reaction mechanism
By the action of ultraviolet light which decomposes nitrite and cleaves a nitric oxide - radical from, at the same time creates an alkoxy radical. The alkoxy radical abstracts a δ-hydrogen atom via a six-membered transition state, which creates a carbon radical. This recombines with the nitrogen monoxide radical to form δ-nitroso alcohol from which a δ-hydroxy-substituted oxime is formed through a 1,3-proton shift:
Optional subsequent reaction: The corresponding carbonyl compound δ-hydroxy-substituted aldehyde or ketone can be obtained by hydrolysis of the oxime . In this way, Barton was able to convert the methyl group in the 18-position of the corticosterone acetate into the required formyl group ( aldehyde ) in the synthesis of aldosterone .
Application (selection)
The δ- nitroso alcohols obtained in the Barton reaction are useful synthesis intermediates. In a multi-step partial natural product synthesis, T. Konoike and his co-workers used the Barton reaction for the targeted synthesis of an oxime in a key step :
The Barton reaction is also used in the synthesis of antibiotics . Cephalosporins are important antibiotics, but a number of pathogenic microorganisms with β-lactamase activity have developed resistance to these antibiotics. I. Chao and his colleagues therefore tried to produce a new antibiotic based on cephalosporins. They synthesized the β-lactam 2 , which is resistant to β-lactamase. An important step in the synthetic sequence was the Barton reaction. The isomeric oximes 1a and 1b were generated and converted into β-lactam 2 .
See also
- Barton-McCombie deoxygenation for the formal substitution of a functional hydroxyl group by a hydrogen atom.
Individual evidence
- ↑ DHR Barton, JM Beaton, LE Geller, MM Pechet: A New Photochemical Reaction. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society. 82, 1960, pp. 2640-2641, doi : 10.1021 / ja01495a061 .
- ^ DHR Barton: Invention of new reactions useful in the chemistry of natural products. In: Pure Appl. Chem. , 1968, Volume 58, Issue 5, pp. 675-684.
- ↑ Michael B. Smith: March's Advanced Organic Chemistry , Wiley & Sons, 7th Edition, 2013, p. 1077, ISBN 978-0-470-46259-1 .
- ↑ Entry on Barton reaction. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 12, 2014.
- ↑ a b László Kürti , Barbara Czakó: Strategic Applications of Named Reactions in Organic Synthesis , Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam 2005, ISBN 978-0-12-429785-2 , p. 42.