Bipolar nerve cell
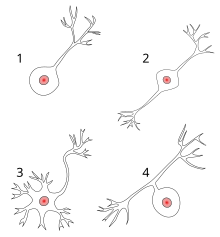
1 unipolar nerve cell
2 bipolar nerve cell
3 multipolar nerve cell
4 pseudounipolar nerve cell
A bipolar neuron or bipolar cell is a neuron with two at opposite poles of the cell formed projections , a dendrite and an neurites . If both are structured very similarly, one also speaks of a dendritic or neuritic axon .
As highly specialized sensor neurons, bipolar cells represent the receptor cells of the sense of smell ( olfactory cells ) and the sense of sight ( photoreceptors ). Other bipolar nerve cells convey the signals of the receptor cells as part of the sensory information transmission, including the sense of taste , touch , hearing and balance .
Overall, they occur most frequently as the second neuron of the retina (see bipolar cells of the retina ) or in the ganglia of the vestibulocochlear nerve (auditory balance nerve ). In the absence of specific information, the term usually refers to the cells that make up the retina.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Clemens Cherry: Biopsychologie from A to Z . Springer textbook, ISBN 3540396039 , p. 37 Lemma “ Bipolar cells”.
- ↑ Benninghoff: Macroscopic and microscopic anatomy of humans, Vol. 3. Nervous system, skin and sensory organs , Verlag Urban & Schwarzenberg, 1985, ISBN 3-541-00264-6 , p. 4.
- ↑ Hans G Liebich: Functional histology of domestic mammals and birds, textbook and color atlas for study and practice + histology online: the image database with the plus , Schattauer; Edition: 5th, completely revised. 2009 edition (October 20, 2009), page 111.
