Pseudounipolar nerve cell
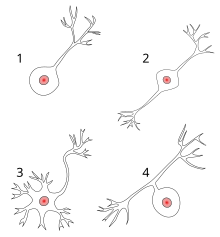
1 unipolar nerve cell
2 bipolar nerve cell
3 multipolar nerve cell
4 pseudounipolar nerve cell
Pseudounipolar nerve cells are nerve cells that consist of a perikaryon , an axon and an axon-like dendrite and are typically found in the somatosensory system (e.g. sense of touch , proprioception ). In these nerve cells, the axon near the perikaryon divides into 2 branches, one branch (the dendrite) extending to the periphery (e.g. skin and muscles) and another branch to the central nervous system . The perikarya of the somatosensory neurons is located in the spinal ganglia and the trigeminal nucleus. The axon-like dendrite located in the periphery receives information in the form of stimuli and forwards this to the initial segment generating the action potential. This is typically located near the peripheral, receptive (stimulus receiving) areas. The action potential is now conducted over the entire axon until it hits a synaptic terminal.
literature
- Robert F. Schmidt , Gerhard Thews , Florian Lang (eds.): Physiology of humans (= Springer textbook ). 28th edition. Springer, Berlin 2000, ISBN 3-540-66733-4 , pp. 199-206 .
- Eric Kandel (Ed.): Principals of Neural Science . 4th edition. McGrawHill, Cambridge 2000, ISBN 0-8385-7701-6 .