Bleomycins
The bleomycins are a group of structurally closely related antibiotic and cytostatic effective glycopeptide derived from the bacterium Streptomyces verticillus be formed.
Structure and properties
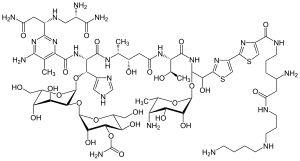
The basic structure of bleomycins is bleomycic acid, a glycopeptide. The peptide part is made up of ten building blocks and linked glycosidically with a disaccharide consisting of L - gulose and 3 - O - carbamoyl - D - mannose . One of the characteristic features is the dithiazole ring system formed from two cysteine units.
The bleomycins are the amides of bleomycin acid, 16 natural representatives are known.
| Biogenic and semi-synthetic bleomycins | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic structure of the bleomycins | |||||||||
| Surname | −R | CAS number | PubChem | Molecular formula | Molar mass | ||||
|
−OH | 37364-66-2 | 2410 | C 50 H 72 N 16 O 22 S 2 | 1313.33 g mol −1 | ||||
|

|
58995-26-9 | 84060 | C 54 H 81 N 17 O 22 S 3 | 1416.52 g mol −1 | ||||
|

|
11116-31-7 | 5460769 | C 55 H 84 N 17 O 21 S 3 + | 1415.55 g mol −1 | ||||
|
|
C 54 H 81 N 17 O 21 S 3 | 1400.52 g mol −1 | ||||||
|
|
11116-32-8 | 84046 | C 57 H 89 N 19 O 21 S 2 | 1440.56 g mol −1 | |||||
|
37293-17-7 | 5483658 | C 60 H 96 N 20 O 21 S 2 | 1497.66 g mol −1 | |||||
|
−NH 2 | 41138-54-9 | 84052 | C 50 H 73 N 17 O 21 S 2 | 1312.35 g mol −1 | ||||
|

|
9060-10-0 | 5496540 | C 55 H 84 N 20 O 21 S 2 | 1425.51 g mol −1 | ||||
|

|
9060-11-1 | 84043 | C 68 H 110 N 22 O 27 S 2 | 1731.86 g mol −1 | ||||

|
68247-85-8 | 6852373 | C 61 H 88 N 18 O 21 S 2 | 1473.56 g mol −1 | |||||
| 88266-67-5 | 16130954 | C 99 H 125 N 19 O 25 S 2 | 2045.29 g mol −1 | ||||||
Under the generic name Bleomycin , a type mixture produced by fermentation is used as a medicinal substance for the treatment of cancer diseases. It consists of at least 85% bleomycin A 2 + B 2 .
Peplomycin and liblomycin are two semisynthetic bleomycin derivatives that are not used therapeutically. Structurally related to the bleomycins are the cleomycins , talisomycins , phleomycins and zorbamycins .
Individual evidence
- ^ Theo Dingermann , Karl Hiller, Georg Schneider, Ilse Zündorf: Schneider drug drugs. 5th edition. Elsevier, Munich 2004, p. 488. ISBN 3-8274-1481-4 .