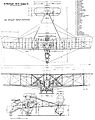
Breguet Michelin types
| Breguet Michelin | |
|---|---|
| Type: | Bomber, scout |
| Design country: | |
| Manufacturer: | |
| First flight: |
1914 |
| Commissioning: |
1915 |
| Production time: |
1915-1916 |
| Number of pieces: |
approx. 460 |
The Breguet-Michelin-types were French military aircraft in the First World War .
Development and use
BrM.2 / 4
With the BU-3 , the French aeronautical engineer Louis Breguet had designed a pusher propeller aircraft in 1914, in which the observer placed in the nose of the fuselage had much better observation and aiming possibilities. This prototype went into series production at the Michelin works in Clermont-Ferrand and was therefore called "Breguet-Michelin" . This first series consisted of 100 pieces, which were initially supplied to the Aéronautique Militaire in four variants with 200 HP Canton-Unné, then with 220 HP Renault - V-engine
- BUM (military designation BrM2B.2, with Canton-Unné engine) and
- BLM (military designation BrM4B.2, with Renault engine) as a bomber, as well
- BUC (with Canton-Unné engine) and
- BLC (with Renault engine) as a fighter / escort fighter (C = "Chasse")
Breguet also produced 17 BLC equipped with 225 HP Sunbeam Mohawk engines as "Breguet de Chasse" for the British naval aviators of the Royal Naval Air Service .
BrM.5
After the French military administration announced the construction of a bomber with a load capacity of 300 kg bombs and a range of 600 kilometers for attacks on the Ruhr area in 1915 , Louis Breguet revised the design and created the SN3 with wings of different spans and modified landing gear. The aircraft was accepted at the competition in October 1915 and was also produced in series as a bomber and a fighter aircraft versions at Michelin and Breguet. The two-tailed bomber carried bomb suspensions attached to the lower wing for up to 40 7.5 kg bombs, the dropping of which could be triggered from the cockpit, the fighter aircraft was armed with a 3.7 cm cannon for escort protection. A second machine gun that fires backwards over the upper wing was also attached as defensive armament. The Aviation Militaire gave the aircraft the military designations 5B.2 and 5Ca.2. and took it into service in early 1916.
The British Naval Aviation (RNAS) procured 20 - 30 aircraft and had another 10 piece of Grahame-White with 250 hp Rolls-Royce Eagle I-motors as Grahame-White GW19 build under license.
BrM.6
The BrM.5 was followed in 1916 by the slightly more powerful BrM.6 with a Canton-Unné DF-9 engine, which was also produced as a bomber and escort fighter version .
commitment
The Breguet-Michelin proved their worth because of their large bomb load and range, but required a long runway because of their weight, and they were slow and difficult to land. They had at least five squadrons of the Aéronautique Militaire in their inventory, including the Groupe de Bombardement (GB) 5 for their strategic long-range missions. After a loss-making bomb flight on Oberndorf am Neckar in November 1916, in which seven out of eight aircraft did not return from action, the remaining aircraft were withdrawn, fitted with searchlights and again under the name Breguet Bre.12 as a night fighter and night bomber until at least January 1918 until they were replaced by Breguet 14 . Some Breguet Michelin were also used in Romania , for example in the attack on Brăila on March 31, 1917, in which one ship was sunk and others were damaged.
The British planes were u. a. from Wing 3 on the Aegean and on the western front from Wing No. 5 used in Dunkerque together with Caudron G.IV for long-distance missions, but withdrawn from June 1916 due to unsatisfactory performance. One aircraft was tested by the Imperial Russian Air Fleet , but not taken over.
Technical specifications
| Parameter | Breguet BrM.2 (BUM, BUC) | Breguet BrM.4 (BLM, BLC) | Breguet BrM. 5 | Grahame-White type XIX | Breguet BrM. 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crew | 2 | ||||
| length | 9.90 m | 7.94 m | |||
| span | 16.40 m | 18.80 m | 17.58 m | ||
| height | 3.70 m | 3.90 m | 3.82 m | ||
| Wing area | 54 m² | 66.8 m² | 58.7 m² | ||
| Empty mass | 1315 kg | 1435 kg | |||
| Takeoff mass | 2115 kg | 2112 kg | 2150 kg | ||
| Standard engine | Canton-Unné | Renault | Rolls Royce Eagle I. | Salmson | |
| Starting power | 220 hp | 220-240 hp | 250 hp | ||
| Maximum speed (NN) | 124 km / h | 135 km / h | 138 km / h | ||
| Range | 730 km | 675 km | 700 km | ||
| Rate of climb 2000 m | 40 min | 22 min | |||
| Summit height | 3900 m | 4300 m | |||
| Flight duration | 3:30 h | ||||
| Armament | 1 MG, approx. 100 kg bombs | 1 MG, 1 on-board cannon, approx. 300 kg bombs | 1 MG, 1 on-board cannon | 2 MG, approx. 300 kg bombs | |
photos
Maintenance of a Breguet Michelin 5 of the Escadrille V.21 in Saint-Etienne-au-Temple on the Marne in 1916
See also
literature
- Enzo Angelucci, Paolo Matricardi: The planes. From the beginning to the First World War. Falken-Verlag, Wiesbaden 1976, ISBN 3-8068-0391-9 , ( Falken manual in color )
- Kenneth Munson: Bomber 1914-1918 , Orell, Füssli Verlag, Zurich
- Karlheinz Kens, Hanns Müller: The aircraft of the First World War 1914-1918 , Heyne-Verlag, Munich 1980, ISBN 3-453-00404-3
- Heinz Nowarra: The Development of Airplanes 1914-1918 , Munich 1959
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ data according to Kenneth Munson: Bomber 1914-1918 , Orell, Füssli Verlag, Zurich