Cast (medicine)
A cast bandage (called cast or synthetic plaster of paris ) is a sedative bandage that can be used as an alternative to plaster bandages, e.g. B. is created as part of bone fracture treatment. The designation Cast (English cast ) is intended to illustrate the good Anmodellierbarkeit. The term is a pseudo-Anglicism , since in English the word cast is used for all sedative bandages (i.e. cast and plaster bandage). The stretchable carrier fabric consists of glass fibers or polyester coated with a synthetic resin , which is activated by immersion in water (analogous to plaster of paris bandages). Depending on the water temperature and the diving time, more or less time is now available to apply and model the bandage. There is also the variant that the bandage is applied dry and then activated by misting with water. As a rule, cast bandages are cured after 30 minutes and can therefore be fully loaded. In the first phase of conservative bone fracture treatment, conventional plaster casts are usually applied, which are split lengthways immediately after hardening (split plaster) in order to allow further swelling of the immobilized extremity, which would otherwise not be possible with a circularly closed bandage. After the swelling has subsided, a circular cast can be applied; therefore cast associations are often referred to as secondary associations. Colloquially, cast bandages are often referred to as plaster of paris, as this name has become common for immobilizing bandages.
Advantages over plaster casts
- lower weight
- faster curing and therefore very early loading capacity
- higher strength, which means fewer repairs if worn for long periods of time
- Insensitivity to water; With special upholstery and underlay material, you can even shower and bathe.
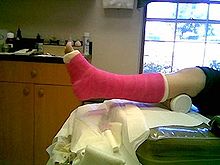
- Cast bandages are available in many bright colors and z. Sometimes also available with motif prints, which is intended to promote acceptance of the treatment, especially among children.
Disadvantages compared to plaster casts
- higher costs, therefore unprofitable for associations that have to be renewed frequently or are only to be worn for a few days
- poorer shelf life
- Disposal more problematic
- rough surface (damage to clothing)
- possibly allergenic substances; therefore especially long-term exposure to nursing staff is problematic
There are no differences in terms of medical effectiveness. The adverse effects of immobilization (This means that for physician and patient immobilisation ) must be observed. These include risk of thrombosis , circulatory disorders , joint stiffening, muscle atrophy .