Complanin
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
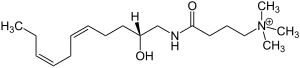
|
|||||||||||||
| Counterion not shown | |||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Complanin | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 18 H 35 N 2 O 2 + | ||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 311 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Complanine is a natural substance that from the marine polychaete Eurythoe complanata was isolated.
Occurrence
The marine poly-bristle Eurythoe complanata is known for its dangerousness towards animals. In humans, it can cause skin inflammation due to its small bristles. Complanin was isolated from these animals as an inflammatory agent. A total synthesis confirmed the structure and the absolute configuration.
Chemical structure
The natural product is a doubly unsaturated hydrocarbon chain with a double cis configuration that is common in such structures . An ammonium salt of a γ-amino acid is bound via an amide bond. Complanin is also a chiral secondary alcohol that occurs enantiomerically pure in nature .
Biological importance
The substance probably serves to ward off predators.
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Kazuhiko Nakamura, Yu Tachikawa, Makoto Kitamura, Osamu Ohno, Masami Suganuma and Daisuke Uemura: Complanine, an inflammation-inducing substance isolated from the marine fireworm Eurythoe complanata. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008 , 6 , 2058-2060.
- ↑ Kazuhiko Nakamura, Yu Tachikawa, Daisuke Uemura: (-) - Complanine, an inflammatory substance of marine fireworm: a synthetic study. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2009 , 5 , No. 12.
