Sterol 26 hydroxylase
| Sterol 26 hydroxylase | ||
|---|---|---|
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 498 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Membrane protein (mit.) | |
| Cofactor | Hamm | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | CYP27A1 | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 1.14.13.15 , monooxygenase | |
| Response type | Hydroxylation | |
| Substrate | 3α, 7α, 12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholestane + NADPH / H + + O 2 | |
| Products | 3α, 7α, 12α, 26-tetrahydroxy-5β-cholestane + NADP + + H 2 O | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Parent taxon | Animals, mushrooms | |
The sterol-26-hydroxylase (CYP27) (also cholestanetriol-26-monooxygenase or cytochrome P450 27/25 ) is a mitochondrial enzyme, which is important for the breakdown of cholesterol into bile acids and together with cytochrome P450 2R1 the vitamin D 3 to 25 (OH) Vitamin D 3 hydroxylates (it has the enzyme function vitamin D 3 25-hydroxylase ). Mutations in CYP27A1 - gene are for a particular form of cholesterosis responsible.
Catalyzed reactions
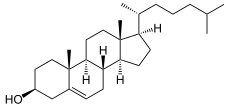 + NADP H / H + + O 2 ⇒
+ NADP H / H + + O 2 ⇒  + NADP + + H 2 O
+ NADP + + H 2 O
In addition to reverse cholesterol transport , the most important form of cholesterol transport out of the cells is the oxidation of cholesterol to 27-hydroxycholesterol and release into the blood plasma. But also the hydroxylation of other cholesterols and vitamin D3 is accomplished by CYP27.
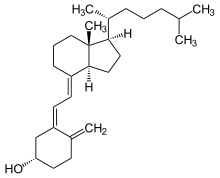 + NADP H / H + + O 2 ⇒
+ NADP H / H + + O 2 ⇒  + NADP + + H 2 O
+ NADP + + H 2 O
Individual evidence
Web links
- OrphaNet: Xanthomatosis cerebrotendinous
- Jassal / reactome: Cholesterol is hydroxylated to 27-hydroxycholesterol by CYP27
- Jassal / reactome: Synthesis of bile acids and bile salts via 7alpha-hydroxycholesterol
- D'Eustachio / reactome: Synthesis of bile acids and bile salts via 24alpha-hydroxycholesterol