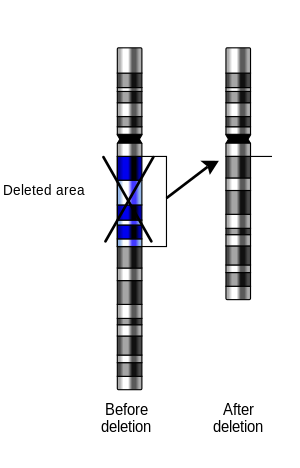
Deletion
A deletion ( engl. Delete "delete" from the Latin delere "destroy Destroy"), even gene deletion is in the genetics a variant of the gene mutation or chromosomal mutation (and thus a chromosomal aberration ) in which a nucleotide sequence or part of a nucleotide sequence is missing. A deletion is always a loss of genetic material. The number of nucleobases deleted is not fixed; it can range from the loss of a single base to the entire chromosome .
A distinction is made between the interstitial and the terminal deletion. The former describes a loss within the chromosome, the latter a loss of an end section, i.e. a part of the telomer range .
Effects of the Deletion
As a consequence of the deletion, a faulty protein can arise after translation of the mRNA created from the DNA . This is because the deletion of base pairs can cause a reading frame shift mutation if a number of base pairs has been removed that is not a whole number divisible by three.
If, however, a whole codon / base triplet is removed, a faulty protein is most likely created - since an amino acid is missing - but the reading frame is not shifted. It can also happen that the resulting protein is still partially functional and causes a weaker phenotype . A null mutation, on the other hand, would be the complete loss of gene function.
Of microdeletions is when the pieces losses of chromosomes are so small that they are microscopic only by special techniques (eg. As FISH test can be detected). There are numerous changes known as microdeletion syndromes . When microdeletions damage several adjacent genes and thus trigger independent phenotypic effects, this is called a contiguous gene syndrome .
Numerous deletions are also found in phenotypically normal (i.e., healthy) individuals. Such polymorphisms are also referred to as copy number variants (or, in general, structural variants ). An extensive catalog of such variants was published in 2010 and 2011 by the 1000 Genome Project .
Indel
The introduction of additional sequences ( insertion ) has similar effects as the deletion of nucleotide sequences . The combination of deletion and insertion of nucleotide sequences is in some cases not resolvable into the parts of deletion or insertion and is referred to as indel in these cases .
example
- Chondrodysplasia punctata due to X-linked deletion
- Nablus mask-like facial syndrome , microdeletion 8q22.1
- Partial deletion: cat cry syndrome
See also
Web links
literature
- James E. Darnell , Harvey Lodish, David Baltimore : Molecular Cell Biology . de Gruyter, Berlin et al. 1993, ISBN 3-11-011934-X (4th edition. Harvey Lodish: Molecular Cell Biology. Spectrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg et al. 2001, ISBN 3-8274-1077-0 ).
- Benjamin Lewin: Molecular Biology of Genes . Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg et al. 1998, ISBN 3-8274-0234-4 .
- William S. Klug, Michael R. Cummings, Charlotte A. Spencer: Genetics . 8th, updated edition 2007, ISBN 978-3-8273-7247-5 .