Cat Scream Syndrome
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| Q93.4 | Deletion of the short arm of chromosome 5 - cat cry syndrome |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
The cat-cry syndrome or cri-du-chat syndrome (CDC syndrome or CCS for short) was first described from a scientific point of view in 1963 by the French geneticist and pediatrician Jérôme Lejeune . He named it after the cat-like screams ( French : cri du chat = "cat scream ") of the affected children in early childhood.
Cat cry syndrome is also known as Lejeune syndrome or, according to its cause, 5p syndrome (chromosome 5p syndrome).
root cause
The cause of the CDC syndrome is a structural chromosome aberration (not numerical) with partial deletion (= loss of pieces) on the short arm of chromosome 5 (= partial monosomy ). The loss usually occurs randomly and according to current knowledge without any particular external influences during the period of the last cell division of the egg cell .
In 15% of the cases, the CDC syndrome is triggered by an unbalanced chromosome translocation , whereby in 10% of the children part of the corresponding chromosome arm has already broken off in one of the parents and has attached to another chromosome (= balanced translocation). This parent does not have a CDC syndrome because the translocation is balanced (= balanced) and the amount of genetic material has not changed. The likelihood of having a child with CDC syndrome whose mother or father has a corresponding balanced translocation is 25%.
Frequency of occurrence
It is estimated that one in 50,000 children has CDC syndrome, and it is likely that the syndrome is often not recognized or diagnosed as such .
In a ratio of 5: 1, more girls than boys are affected by this chromosomal feature (= gynecotropy ).
features
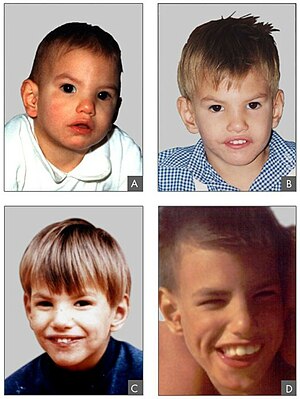
Most children with CDC syndrome have various features that can indicate the chromosome peculiarity. None of the features appear in any child or the symptoms are not the same in all children. A reliable diagnosis is therefore only possible through a chromosome analysis .
Common symptoms in people with CDC syndrome include:
- Cat-cry-like, high-pitched and shrill sounds in early childhood, which, however, disappear over time and are attributed to a malformation of the larynx ( laryngomalacia )
- Growth disorders ( short stature / below average height and below average body weight )
- Muscle weakness ( hypotonia )
- a comparatively small head ( microcephaly ) that is often elongated
- round face
- often deep-seated and specially shaped (dysplastic) ears
- a narrow chin , micrognathia
- a widened and flattened bridge of the nose
- eyes that are comparatively far apart ( hypertelorism )
- a small sickle-shaped fold of skin at the inner corner of the eye ( epicanthus medialis )
- outward sloping eyelid axes (the outer corners of the eyelid are lower than the inner ones )
- Difficulty sucking and swallowing (therefore often breastfeeding difficulties )
- often chronic constipation
- frequent infections of the ear and upper respiratory tract
- seldom malformations of the internal organs , but if present, the heart is predominantly affected
- Eye problems (e.g. optical atrophy , strabismus / strabismus , often alternating bilaterally in older people)
- Increase and broadening of the reflexes (= hyperreflexia )
- Curvature of the spine ( scoliosis ), often at an advanced age
- short metacarpal and / or metatarsal bones
- Flat feet
- Dental problems
- Four-finger furrow (not always)
- usually severe retardation of motor development
- usually strong delay in the development of the spoken language
- cognitive disabilities with individually varying degrees of severity
- sometimes renal agenesis
Life expectancy
In the absence of serious medical problems, the life expectancy of people with CDC syndrome does not appear to be significantly reduced, although long-term studies are not yet available. However, the emerging tendency supports the assumption.
diagnosis
It is possible to diagnose a CDC syndrome as part of prenatal diagnosis using amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling , or through the chromosome analysis that follows these examinations before birth.
Postnatal diagnosis can be made by examining the child's blood . If the child has a translocation , the parents should be examined for a balanced translocation. This can be used to estimate the likelihood of having another child with the syndrome in subsequent pregnancies . The relevant region for the symptoms of CDC syndrome is in 5p15.3-p15.2.
therapy
There is no causal cure for CDC syndrome. So far, only the symptoms have been more or less successfully influenced by medical and therapeutic treatment and social support.
It is impossible to predict with certainty the personal development of an individual child, although it has been established that most children who experience encouragement and encouragement develop better than the others.
The most common support methods that have a positive effect on the development of children are early support , physiotherapy , occupational therapy and speech therapy (speech therapy, often combined or supported with methods of supported communication ).
Early preventive treatment of dental problems is also important .
literature
- Paola Cerruti Mainardi: Cri du Chat syndrome. In: Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases. 1, 2006, doi : 10.1186 / 1750-1172-1-33 . (Review)
- Kurt Kallenbach (ed.): Children with special needs. Selected clinical pictures and forms of disability. ISBN 3-89166-208-4
Web links
Further med. Information (CDC Association)