Diabetic angiopathy
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| E10-E14 | Diabetes mellitus |
| .2+ N08.3 * |
With kidney complications - diabetic nephropathy glomerular diseases in diabetes mellitus |
| .3+ H36.0 * |
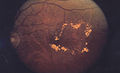
With eye complications - diabetic retinopathy Retinopathia diabetica |
| .4+ G99.0 * G59.0 * G63.2 * |
With neurological complications Autonomic neuropathy in endocrine and metabolic diseases Diabetic mononeuropathy Diabetic polyneuropathy |
| .5+ I79.2 * |
With peripheral vascular complications, Diabetic Peripheral Angiopathy. Peripheral Angiopathy in Diseases Classified Elsewhere - Diabetic Peripheral Angiopathy |
| I70 | Atherosclerosis |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
Vascular damage that occurs as a late complication in diabetes mellitus is referred to as diabetic angiopathy .
Changes in the capillaries ( microangiopathy ) cause various forms of diabetic microangiopathy : in particular diabetic nephropathy (kidney disease), diabetic retinopathy (eye disease) and autonomic neuropathy (disease of the peripheral nervous system).
Although macroangiopathy is not diabetic-specific, it occurs more quickly and more strongly than in non-diabetics, which is why the term diabetic macroangiopathy is common. It leads to atherosclerotic changes in medium and large arteries. It is responsible for the high risk of heart attack , stroke and gangrene in diabetes.
The main factors that promote the development of micro- and macroangiopathy in diabetics are hyperglycemia , hyperlipoproteinemia , insulin resistance, and various vasoactive hormones , cytokines, and growth factors .
swell
- Alvin C. Powers (for the German edition: Elke Austenat and Sabine Semmler). Diabetes mellitus. In: Harrison's Internal Medicine. German Edition of the 15th edition, ABW-Wissenschaftsverl., Berlin 2003, ISBN 3-936072-10-8