gangrene

| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| R02 | gangrene |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
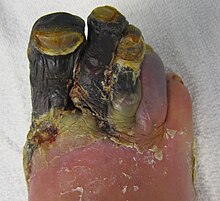
As a gangrene (rarely gangrene ; plural: "the gangrene" or "gangrene", Greek γάγγραινα gángraina literally "the Wegfressende") refers to a tissue necrosis , usually due to blood deficiency , in which the affected tissue by decomposition and autolysis (Self-digestion) breaks down and changes color as a result of hemoglobin breakdown. In the past one also spoke of a dry fire or a wet fire or gangrene . The term gas fire is still in use today for an infected gangrene with gas-forming clostridia .
The definitions and morphological classifications differ slightly depending on the literature. The following structure is based on that of the Pschyrembel .
morphology
A distinction is made between a) dry, b) wet gangrene and c) gas fire . The first shows shrinkage and leather-like drying ( mummification ) due to water loss , while the second is characterized by bacterial contamination and has a fluid and fine consistency. In gas gangrene, on the other hand, the bacteria in the dead or dying tissue form bubbles under the skin, causing the tissue to peel off quickly.
Since bacteria are usually present in gangrene, the resulting infection often contributes to the rapid spread of cell death - within hours or a few days. If the bacteria enter the bloodstream, the condition becomes critical ( septic blood poisoning ) and, if not treated immediately with appropriate antibiotics , death is common.
Occurrence
Gangrene occurs primarily in the extremities , for example as a result of peripheral arterial occlusive disease or diabetic microangiopathy . The feet are more often affected than the hands, in this case one also speaks of a foot burn . In lung abscesses and as a result of aspiration pneumonia may for pulmonary gangrene ( gangrene pulmonis come). As a result of a mesenteric infarction or an ileus (intestinal obstruction), the affected section of the intestine, the small or large intestinal gangrene, can die. In dentistry , gangrene is an infection-related necrosis of the pulp , i.e. the nerve-supplied part of a tooth.
Older pathological differentiations are
- Gangraena arteriosclerotica -gangrene causedby arteriosclerosis (compare arterial occlusive disease )
- Gangraena senilis - so-called old age burn or old age burn, also due to arteriosclerotic changes
- Gangraena emphysematosa - gas burn or intoxicating burn with edema caused by clostridia , mostly of the muscles, mainly as a result of tears
- Gangraena congelationis - gangrene in frostbite (as the third degree of severity)
- Gangraena acuta genitalium - gangrenous inflammation of the genitals
- Gangraena nosocomialis - so-called hospital fire
therapy
Resection if possible; Maggot therapy ; antiseptic measures; Immobilization of the affected limb; finally also necrectomy (removal of dead tissue); Amputation ; Diet change in gangrene as a result of peripheral arterial disease.
Complications
See also
Web links
- Hospital fire in Meyer's Konversations-Lexikon from 1885
Individual evidence
- ↑ Duden - The foreign dictionary . 8th edition. Bibliographical Institute, Mannheim 2003
- ↑ On the etymology cf. gangrene . etymonline.com (English)
- ↑ Wilhelm Fabry : Thorough report of the hot and cold fire, which is called Gangraena et Sphacelus or S. Antonii- and Martialis fire. After the second German edition published in 1603, edited and edited. by Erich Hintzsche , Bern and Stuttgart 1965 (= Huber's classics of medicine and natural sciences , 4).
- ^ Greger: Heart Disease Starts in Childhood . Nutritionfacts.org
- ^ YM Hong: Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Beginning in Childhood . An Open Access Biomedical Image Search Engine