Diffusion stress
The diffusion voltage , seldom also called anti- diffusion voltage , is the potential difference ( electrical voltage ) across a space charge zone that counteracts the diffusion of charge carriers ( electrons and holes ) . It depends on the material and is ≈ 0.7 V for silicon and ≈ 0.3 V for germanium .
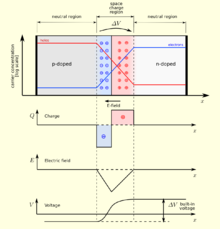
A semiconductor diode with a pn junction is considered : At the boundary between p- and n-doped semiconductors , the concentration gradient causes diffusion of charge carriers, i.e. H. Free electrons from the n-area migrate into the p-area ( diffusion current ), analogous to this the holes (defect electrons) migrate from the p- to the n-area.
This movement of charge carriers creates an opposing electric field between the space charges inside the crystal . This counteracts the further diffusion of mobile charge carriers, as it generates an opposite drift current .
The voltage generated by the counter electric field is called diffusion voltage (hence the name anti diffusion voltage ):
With
- the temperature stress
- the Boltzmann constant
- the absolute temperature
- the elementary charge
- the number of acceptors
- the number of donors
- the intrinsic charge carrier density .