Digital Terrestrial Multimedia Broadcast
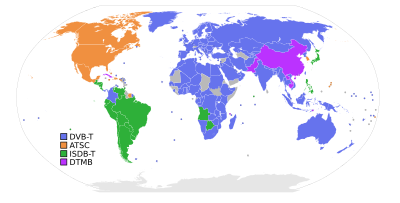
Digital Terrestrial Multimedia Broadcast , abbreviated DTMB , describes a terrestrial (earthbound) distribution of digital television signals , which is primarily used in the People's Republic of China . The area of application is comparable to the digital television transmission standards DVB-T and DVB-T2 for stationary and DVB-H for mobile television receptioncommon in Europe.
DTMB was developed in 2004 and emerged from the two precursor digital transmission methods ADTB-T , developed at Jiaotong University Shanghai , and the standard DMB-T / H , developed at Tsinghua University . It is standardized in the Chinese standard GB20600-2006. ( GB stands for guo biao = ”National Standard” in Chinese)
DTMB became the official standard in 2006 and replaced the analog television transmission technology previously used in China from 2008. The complete shutdown of analog television transmission is planned in China by 2018. [obsolete] In addition to China, DTMB is used in the Asian region in Hong Kong , which has been completely converted to DTMB since 2012, in Macau and in the Caribbean country Cuba .
description
DTMB is designed for mobile and stationary television reception and also supports the transmission of data services and multimedia applications. In addition to standard definition television (SDTV) resolutions, which are used in particular for mobile reception, DTMB is designed for the transmission of high definition television (HDTV). A bandwidth of 8 MHz is provided for each radio channel ; a single- frequency network is provided, in which several spatially distributed transmission towers broadcast the same program in the same radio channel.
Between 6 and a maximum of 15 SDTV programs and one or two HDTV programs can be transmitted independently of one another per channel. The bit rates occurring per radio channel can be dynamically changed by the transmitter and are in the range from 4.813 Mbit / s to 32.486 Mbit / s (gross). A time-synchronized orthogonal frequency division multiplex method (TDS-OFDM) is used for transmission . Low-density parity check codes (LDPC) are used as forward error correction . The digital transmission method is designed so that digital television reception is possible in mobile applications at relative speeds of around 200 km / h despite the Doppler shift .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Chinese standard GB20600-2006: 数字 电视 地面 广播 传输 系统 帧 结构 、 信 道 编码 和 调制 (Chinese) (English translation: Framing structure, channel coding and modulation for digital television terrestrial broadcasting system). AQSIQ, 2006, accessed April 25, 2014 .
- ↑ DTV status. Retrieved April 25, 2014 .
- ↑ Raj Karamchedu: Does China Have the Best Digital Television Standard on the Planet? IEEE Spectrum, May 4, 2009, accessed April 25, 2014 .