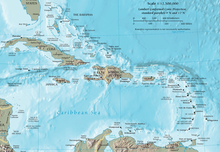
Caribbean
The Caribbean is a region in the western, tropical part of the Atlantic Ocean north of the equator . As part of the Central American sub-continent it consists of the on and in the Caribbean Sea located islands and island groups and the marine area between them. At the western end, the Caribbean extends into the Gulf of Mexico .
The Caribbean is named after the people of the Caribs that the Spanish conquerors found in the Lesser Antilles (lat. Ante ilium , "offshore islands"). It was or is also called the West India , because when it was discovered it was believed to be a direct sea route to India .
Geography and population


According to the delimitation of the International Hydrographic Organization , the arched islands of the Caribbean lie within the Caribbean Sea. From the Yucatán peninsula to northern South America, this forms a rectangle. In addition, the second largest reef system on earth is located off the Belizean coast : the Belize Barrier Reef . The highest point in the Caribbean is the Pico Duarte with 3,098 m in the Dominican Republic . The largest waterfalls are the Mt. Carmel Falls .
Around 40 million people of different origins live in the Caribbean region on a total area of around 220,000 km² (see below). In addition to the very few remaining indigenous inhabitants, mainly people of African and European origin, Creoles as well as Indians (mainly in Trinidad and Tobago) and Chinese live on the various islands of the Caribbean. Spanish with about 70% and English with about 24% are the main languages of the Caribbean, in addition to French (particularly in Haiti ), Dutch and various forms of Creole or Caribischen speaking (especially in everyday life ).
The life expectancy was in 2013 with an average of 72 years and 26% of the population were among the under-15s, while 9% were over 65 years old. It wandered Although more people from as immigrated, but that is the population density of 180 inhabitants per square kilometer compared globally relatively high.
Important Caribbean educational institutions are the " University of the West Indies " and the "Center for Hotel and Tourism Management". Tourism is one of the most important sources of income for the Caribbean states. There are also many tax havens in the financial services sector , above all on the Cayman Islands .
The soccer caribbean championship is a biennial sporting event .
In the Caribbean cuisine , fish, pulses and spices are used in particular.
geology
The Caribbean Sea is in turn part of the American Mediterranean and reaches a depth of 7,680 m in the Cayman Trench. It is mainly located on the Caribbean plate , only the northwest part beyond the deep-sea trench is on the North American plate . Earthquakes and occasional volcanic eruptions occur repeatedly due to tectonic activities at the plate boundaries . In 1995, after several eruptions of the Soufrière, the capital of Montserrat, Plymouth , had to be abandoned after around 8,000 people had fled. The last major quake occurred in 2010 in Haiti , killing an estimated 300,000 people.
Nature and climate
In general, there is a tropical rainforest climate and thus a time of day climate with average temperatures above 20 ° C. In the summer months from June to September the probability of rain is around 30–50%. The winter months between November and April, on the other hand, are the driest months of the year with five to nine rainy days. In addition, the Gulf Stream , which drifts into Europe , has its origin in the Bahamas . The designation above / below the wind of the Antilles indicates the influence of the northeast trade winds . Another natural phenomenon are emerging or passing hurricanes , which regularly damage z. B. caused by flooding.
Resident animal species include the Caribbean manatee , the Caribbean lobster and iguanas . Other species such as the Caribbean shrews have already become extinct due to anthropogenic influences. Due to the export-oriented cultivation of cash crops (traditionally e.g. sugar cane ) on monoculture plantations , native plant species such as the mangroves have been strongly pushed back. Many of the soils are of volcanic origin and have different fertility.
Great Blue Hole off Belize
History and Discovery of the Caribbean
Before the discoveries in the 1st millennium BC Chr. Were Arawak -Indianer coming from Venezuela to the Caribbean islands. They spread north over Trinidad . They were followed around 1500 years later by the warlike Caribs , who slowly drove the Arawak from the Lesser Antilles . At the time of Christopher Columbus' voyages of discovery , the Arawak settled the islands of Cuba , Hispaniola and the Bahamas , while the Caribs inhabited the Lesser Antilles.
When Columbus landed on San Salvador (Bahamas) on behalf of the Spanish crown in 1492 , he was primarily looking for gold and other riches. But the Arawak paid no attention to what Europeans viewed as wealth. So the Caribbean was settled, but the conquistadors soon moved to the American continent . Little by little the English , Dutch and French also settled. Even Denmark , Sweden and Courland owned some colonies. St. Barthélemy was z. B. almost a century under Swedish rule . Most of the native Indians eventually fell victim to diseases or slavery that were brought in.
The Caribbean was particularly active in the 17th and early 18th centuries for buccaneers and pirates (the so-called golden age of piracy ). The small islands offered the pirates, some of whom were freebooters on behalf of a king, numerous hiding places and the Spanish treasure fleets were a good and worthwhile target. Port Royal in Jamaica and the French settlement on Tortuga were downright pirate settlements .
Street in the largest city, Havana (Cuba)
Bob Marley statue in Kingston (Jamaica)
Castries Cathedral (St. Lucia)
National Museum in Port of Spain
Caribbean islands and territories
In the Caribbean there are both independent states and islands that are mainly dependent on European states (clockwise):
| region | Island (group) | Membership or year of independence | Member Community |
currency | Official language | Area (km²) |
Population (2013) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| open Atlantic North | 14,436 | 366.785 | |||||
|
|
1973 |
|
B $ |
English ( Bahamas Creole ) |
13,939 | 319.031 | |
|
|
|
$ | English (Creole) | 497 | 47,754 | ||
| Greater Antilles | 206,583 | 37,784,549 | |||||
|
|
1902 |
|
Cub $ | Spanish | 109,884 | 11,061,886 | |
| Guantanamo Bay |
|
118 | Military personnel 1 | ||||
|
|
|
CI $ | English | 264 | 53,737 | ||
|
|
1962 |
|
J $ | English ( Jamaican ) |
10,991 | 2,909,714 | |
|
|
|
5 | uninhabited 2 | ||||
|
|
1804 |
|
HTG |
Haitian , French |
27,750 | 9,893,934 | |
|
|
1844 |
|
RD $ | Spanish | 48,730 | 10,219,630 | |
|
|
|
$ | Spanish, English | 8,959 | 3,645,648 | ||
| Lesser Antilles | 9,235 | 2,613,961 | |||||
| Above the wind |
|
|
$ | English (Creole) | 346 | 104,737 | |
|
|
|
$ | English (Creole) | 153 | 31,912 | ||
|
|
|
EC $ | English (Creole) | 96 | 15,754 | ||
|
|
|
part |
€ | French | 53 | 31,264 | |
|
|
|
part |
CMf |
Dutch , English |
34 | 39,689 | |
|
|
|
€ | French ( Patwa ) | 21st | 7,298 | ||
|
|
|
part |
$ | Dutch (English) | 13 | 1,991 3 | |
|
|
|
part |
$ | Dutch (English) | 21st | 4,020 3 | |
|
|
1983 |
|
EC $ | English (Creole) | 269 | 51.134 | |
|
|
1981 |
|
EC $ | English (Antigua Creole) |
442 | 90.156 | |
|
|
|
EC $ | English | 102 | 5,189 | ||
|
|
|
€ | French ( Guadeloupe Creole ) | 1,628 | 403,355 3 | ||
|
|
1978 |
|
EC $ | English (Patwa) | 746 | 73.286 | |
|
|
|
€ | French (Martinique Creole) |
1,128 | 394,173 3 | ||
|
|
1979 |
|
EC $ | English (Patwa) | 616 | 162,781 | |
|
|
1966 |
|
BDS $ | English | 430 | 288.725 | |
|
|
1979 |
|
EC $ | English | 389 | 103.220 | |
|
|
1974 |
|
EC $ | English (Grenada Creole) |
344 | 107,850 | |
| Under the wind |
|
|
|
BsF | Spanish | 1,150 | 426,337 3 |
|
|
|
|
BsF | Spanish | 342 | 3,100 3 | |
|
|
|
part |
$ | Dutch ( Papiamentu ) | 288 | 13,389 3 | |
|
|
|
part |
CMf | Papiamentu, Dutch, English | 444 | 146.836 | |
|
|
|
part |
Afl | Papiamentu, Dutch | 180 | 109,153 | |
| open Atlantic-South |
|
1962 |
|
C $ (TTD) | English (Creole) | 5,128 | 1,225,225 |
| western caribbean | 796 | 186.176 | |||||
|
|
|
|
$ (COP) | Spanish | 44 | 70,554 3 | |
| Corn Islands |
|
|
C $ (NOK) | Spanish | 13 | 7,429 3 | |
| Islas de la Bahía |
|
|
L. | Spanish | 261 | 35,000 3 | |
| Cozumel |
|
Mex $ | Spanish | 478 | 73,193 3 | ||
| total | 221.993 | 42.176.696 |
Legend:
CELAC ,
CARICOM ,
ALBA ,
SICA ,
OECS ,
EU ,
UNASUR . 1 military personnel resident.
2 Temporarily inhabited by Haitian fishermen.
3 (Missing) numbers taken from the country pages.![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
States included in the Caribbean
The following states belong geographically to the American mainland, but are often included in the Caribbean due to their colonial history and their economic, transport and linguistic relationships:
| region | Country | Membership or year of independence |
membership | currency | Official language | Area (km²) |
Population (2013) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central America |
|
1981 |
|
Bz $ | English (Belize Creole) | 22,966 | 334.297 |
| South America | 462.324 | 1,535,789 | |||||
|
|
1966 |
|
G $ | English ( Hindi ) | 214,970 | 739.903 | |
|
|
1975 |
|
$ (SRD) | Dutch ( Sranantongo ) | 163,820 | 566,846 | |
|
|
|
€ | French ( Creole ) | 83,534 | 229,040 3 |
3 Number taken from the country's website.
Caribbean neighbors
The following states border the Caribbean (from northwest to southeast):
-
North America : United States , Mexico


- Central America: Belize , Guatemala , Honduras , Nicaragua , Costa Rica , Panama






- South America: Colombia , Venezuela , Guyana , Suriname , French Guiana





Island divisions and common archipelagos
The following islands are administered by several states:
- Hispaniola : Haiti and Dominican Republic
- St. Martin (island) : Dependent on France and the Netherlands
The following islands are grouped together:
- British West Indies : Anglophones of the Lesser Antilles linked by institutions and events.
- French West Indies : Francophone Lesser Antilles.
- Virgin Islands : Spanish (west), American (central) and British (east).
- Leeward Islands : Northern and Southwest Lesser Antilles, leeward .
- Windward Islands : Southern Lesser Antilles, facing the wind .
- ABC islands : Aruba, Bonaire, Curaçao are geographically next to each other.
- BES Islands : Bonaire, St. Eustatius, Saba are special parishes of the Netherlands.
The following archipelagos were dissolved:
- The Danish West Indies existed until April 1, 1917 and have formed the US Virgin Islands since then.
-
 West Indian Federation existed until May 31, 1962.
West Indian Federation existed until May 31, 1962. -
 Netherlands Antilles existed until October 10, 2010.
Netherlands Antilles existed until October 10, 2010. - Arrondissement Saint-Martin-Saint-Barthélemy existed until February 22, 2007.
See also
literature
- Ottmar Ette : Of islands, borders and vectors. Attempt on the fractal island world of the Caribbean . In: Marianne Braig u. a. (Ed.): Limits of Power - Power of Limits. Latin America in a global context . Vervuert, Frankfurt am Main 2005, pp. 135-180.
- Heinrich Hasebeck, Andreas Venzke (eds.): Gasparan or the last journey of Francis Drake , Benziger-Verlag, Zurich 1996, ISBN 3-545-36531-X .
- Bernd Hausberger , Gerhard Pfeisinger (Ed.): The Caribbean. History and Society 1492–2000. Promedia, Vienna 2005, ISBN 3-85371-236-3 .
- Holger Henke: Modern Political Culture in the Caribbean . The University of the West Indies Press, Kingston 2003, ISBN 976-640-135-7 .
- Holger Henke: Between Self-Determination and Dependency: Jamaica's Foreign Relations, 1972–1989. The University of the West Indies Press, Kingston 2000.
- Barry William Higman: A concise history of the Caribbean . Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 2011, ISBN 978-0-521-88854-7 .
- Gabriele Knauer, Ineke Phaf-Rheinberger (eds.): Caribbean worlds - Mundos caribeños - Mondes caribéens . Vervuert, Frankfurt am Main 2020, ISBN 978-84-9192-106-6 .
- Matthew Mulcahy: Hurricanes and society in the British Greater Caribbean, 1624-1783. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore 2006, 257 pp., ISBN 0-8018-8223-0 .
- Edith Oppens: Caribbean. Mediterranean of the New World . Prestel, Munich, 2nd complete Edition 1981, ISBN 3-7913-0431-3 .
Web links
- Database of indexed literature on the social, political and economic situation in the Caribbean
- Thematic website on the Caribbean and Latin America (journalists' initiative)
- Spektrum .de: Deforestation in the Amazon is suffocating the Caribbean in algae August 27, 2019
Individual evidence
- ^ International Hydrographic Organization: Limits of Oceans and Seas. 3rd Edition 1953, Monte Carlo 27.- Caribbean Sea
- ↑ Country database , accessed March 6, 2014
- ↑ Addition of climatic conditions. Retrieved March 18, 2019 .
- ↑ World Factbook , accessed March 6, 2014
Coordinates: 14 ° 31 ′ 48 ″ N , 75 ° 49 ′ 12 ″ W.