Antigua and Barbuda
| Antigua and Barbuda | |||||
| Antigua and Barbuda | |||||
|
|||||
|
Motto : Each Endeavoring, All Achieving ( eng. , "Everyone tries hard, everyone succeeds") |
|||||
| Official language | English | ||||
| Capital | Saint John's | ||||
| Form of government | Constitutional - parliamentary monarchy | ||||
| Head of state | Queen Elizabeth II represented by |
||||
| Head of government | Prime Minister Gaston Browne | ||||
| surface | 442 km² Antigua: 281 km² Barbuda: 161 km² |
||||
| population | 94,731 estimate July 2017 | ||||
| Population density | 214 inhabitants per km² | ||||
gross domestic product
|
2016 | ||||
| Human Development Index | 0.783 (58.) | ||||
| currency | East Caribbean Dollar (XCD) | ||||
| independence | November 1, 1981 (from the UK ) |
||||
| National anthem |
Fair Antigua, We Salute Thee |
||||
| National holiday | November 1st | ||||
| Time zone | UTC − 4 | ||||
| License Plate | AG | ||||
| ISO 3166 | AG , ATG, 028 | ||||
| Internet TLD | .ag | ||||
| Telephone code | +1 (268) see NANP | ||||
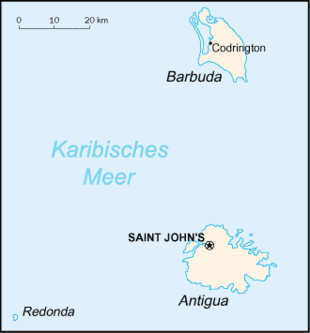
Antigua and Barbuda ( English Antigua and Barbuda ) is an independent state within the Commonwealth , which was formed from the islands of Antigua and Barbuda . The island state belonging to the Eastern Caribbean , which also includes the uninhabited remote island of Redonda , is located between the North Atlantic and the Caribbean , southeast of Puerto Rico .
geography
location
The Antillean state of Antigua and Barbuda is one of the so-called Leeward Islands . It is located between the Caribbean and the Atlantic Ocean , approx. 650 km southeast of Puerto Rico . The total area of 442.6 km² - located on land - includes two main and a few smaller islands. The largest is the 280 km² island of Antigua , on which the capital Saint John’s is also located. Barbuda covers 161 km² and is 48 km north of Antigua. 56 km southwest of Antigua is the only 1.6 km² large uninhabited rock island of Redonda . Other islands over 1 km in length are Long Island , Guinea Island and Green Island off the coast of Antigua, as well as the spit 11 Mile Beach on Barbuda.
Geology and geomorphology
Even if the main island of Antigua is mainly made up of limestone formations , it goes back to a submarine volcano that erupted in the southwest of the island about 34 million years ago. With the growth of hard corals , calcium deposits spread to the northeast. The highest point of the island and at the same time of the island state is the 402 m high Mount Obama , formerly Boggy Peak . It is the remainder of the volcanic crater in southwest Antigua. Barbuda is the surface of a large coral reef. The highest point of the still largely untouched and natural coral island rises only 44.5 m from the sea. The coastlines of the two main islands are extremely richly structured. They have a number of beaches, lagoons and numerous natural harbors (bays). The islands are surrounded by a number of coral reefs and shallows . The small rock island Redonda is the remainder of a 296 m high extinct volcano.
climate
The climate is tropical . Average monthly temperatures range from 22 (December to February) to 30 ° C (June to September). With an average annual precipitation of 900 to 1000 mm, it is relatively dry by Caribbean standards. Most of the precipitation falls between September and November. In summer (July to October) there is a risk of tropical cyclones .
population
State and development
In 2017, 94,731 people lived there. A large part of the population lives on Antigua, Barbuda only has about 1600 inhabitants (as of 2011), Redonda is uninhabited. The population development has been almost entirely positive over the past 50 years. Between 1961 and 1969 the population grew from 55,000 to 65,000. After that, it stagnated at around 63,000 until the early 1990s. From 1993 onwards there was a renewed increase to the current level. The fertility rate (TFR) is 2.0 (Germany 1.46) just above the conservation level and causes low natural growth. In contrast, however, the infant mortality rate is four times as high as in Germany. The migration balance is also negative; In 2005 alone, 420 people left the island nation. In 2017, 28.1% of the population was born abroad.
structure
According to the 2011 Census, the population consisted of 44,581 women and 40,986 men. The age pyramid is very regular. Just under a quarter of the population is 14 years of age and younger, while around 6.9 percent are 65 years of age and older. With an average age of 32.5 years, the population is very young.
Selected demographic indicators
The following figures show the status of 2017 (excluding tourists).
- age structure
- 0-14 years: 23.09%
- 15–24 years: 16.83%
- 25–54 years: 42.19%
- 55-64 years: 9.83%
- over 65 years: 8.06%
- Average age: 31.6 years
- Birth rate: 15.7 / 1000 inhabitants
- Death rate: 5.7 / 1000 people
- Growth rate: 1.2%
- Fertility rate: 2
- Net migration rate: −2.2 / 1000 inhabitants
- Life expectancy
- Men: 74.4 years
- Women: 78.8 years
Languages and ethnic groups
Common languages are English (the official language) and a Creole language based on it . Ethnically, the population consists of 87.3% black Africans and 4.7% mixed race. There are also Europeans and Asians.
religion
Nominal members of religious communities:
- 76.5% Christians
- 68.3% Protestants
- 17.6% Anglicans
- 12.4% Seventh-day Adventists
- 12.2% Pentecostal movement
- 8.3% Moravian people
- 5.6% Methodists
- 4.5% Wesleyan Holiness
- 4.1% Church of God
- 3.6% Baptists
- 8.2% Catholics ( Diocese of St. John's-Basseterre )
- 68.3% Protestants
- 12.2% other
- 5.5% not specified
- 5.9% without confession
history
From around 10,000 BC. Indians from the Siboney tribe ("stone people") settled the islands. By 1200, the Arawak Indians displaced the Siboney from the Orinoco region . Subsequently, Caribs invaded from South America and spread in the area.
In 1493, Christopher Columbus landed in Antigua. In the following years, the Indians living on the islands were deported to Hispaniola and other Spanish colonies by the Spaniards for slave labor . A large part of the Indians died within a short time as a result of work or illness. After 1500 the Spaniards, French and British tried alternately, each unsuccessfully, to settle the islands permanently and to bring them into their possession. Pirates used the islands as retreats at that time.
Barbuda (1628) came into British possession over 100 years later. However, efforts on the part of the government to colonize the area failed. Four years later, Antigua was colonized by British settlers from St. Kitts and Nevis . The settlers first grew tobacco there. The first settlers from England arrived there in 1663. The first permanent settlement was also built on Barbuda in 1666.
In 1680 large parts of Barbuda became the property of the Codrington family, who established the place named after them as an administrative center. Five years later, sugar cane plantations were set up on the islands , most of which were managed by African slaves.

Admiral Horatio Nelson built a British naval base on Antigua in 1784 . Due to the storm-proof port, English Harbor was expanded to become the headquarters of the fleet stationed in the Antilles. The fleet presence drove away the last of the pirates. The slavery was abolished in 1834, making the plantations , the economic base was lost, ushering in a difficult period of economic downturn and restructuring. In 1860 Antigua and Barbuda were united; the name of the colony was just Antigua.
Under the leadership of the future Prime Minister Vere Cornwall Bird, an independence movement formed from 1940. Six years later, the islands received their own parliament. The women's suffrage was introduced in the 1951st Antigua and Barbuda received the status of an independent colony in 1956. From 1958 to 1962 the islands belonged to the province of the West Indian Federation .
The islands joined the West Indies Associated States group in 1967 . This gave them complete domestic political autonomy; foreign policy issues were taken care of by Great Britain. In May 1968 the state became a member of the Caribbean Free Trade Association (CARIFTA). The sugar cane industry, which had dominated for centuries, was discontinued in 1972. On November 1, 1981, the islands gained independence from Great Britain under the new name of Antigua and Barbuda.
politics
Political system
The state has been a constitutional monarchy belonging to the Commonwealth of Nations since 1981 . The structure of the political system is based on the British model. Antigua and Barbuda is a member of CARICOM , the OECS and the OAS and is one of the sponsors of the University of the West Indies .
Executive: The head of state is the monarch of the United Kingdom , represented by a governor-general . This office has been held by Rodney Williams since August 14, 2014 . The real government power rests with the Prime Minister , who relies on the majority of the MPs in the House of Representatives . The office of prime minister was between 1967 and 1971 and 1976 and 1994 Vere Cornwall Bird and his son Lester Bird between 1994 and 2004 . He was followed by Baldwin Spencer , who served from 2004 to 2014. Gaston Browne has been acting Prime Minister since 2014 . The Prime Minister appoints the members of his government from among the ranks of parliament. As of 2018, the cabinet comprised 13 ministers. Unlike the United Kingdom, Antigua and Barbuda has a written constitution.
Legislature: The parliament, which has existed since 1946, consists of two chambers : a House of Representatives and a Senate with 17 seats each. While the members of the Senate are appointed by the Governor General, the members of the House of Representatives are determined in elections that take place every five years. The last parliamentary elections took place as early elections on March 21, 2018. With 59.39% of votes won the Labor Party (Antigua Labor Party, ALP) election. It received 15 seats and continues to provide the Prime Minister. A seat was accounted for by the United Progressive Party ( United Progressive Party , UPP) and a seat to the People's Movement of Barbuda ( Barbuda People's Movement ).
Active and passive women's suffrage has existed since 1951.
Foreign policy
The state has been a member of the United Nations since 1981, a member of the WTO since 1995 , a member of AOSIS , Group of 77 , CELAC and is a signatory to the ICC . Antigua and Barbuda is a member of the Bolivarian Alliance for America . But it also has good relations with the United States .
Security policy
Administrative division
The state is divided into six administrative districts ( Parishes ) and the two secondary areas ( Dependencies ) Barbuda and Redonda .
| No. | Administrative unit | Area in km² | Total population | Inhabitants per km² |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Saint George | 24.1 | 7,976 | 331 |
| 2 | Saint John | 73.8 | 51.129 | 693 |
| 3 | Saint Mary | 57.0 | 7,331 | 129 |
| 4th | Saint Paul | 47.9 | 8,116 | 169 |
| 5 | Saint Peter | 32.9 | 5,317 | 162 |
| 6th | Saint Phillip | 44.0 | 3,322 | 76 |
| Barbuda | 160.6 | 1,625 | 10 | |
| Redonda | 1.3 | 0 | 0 | |
| Antigua and Barbuda | 441.6 | 84,816 | 192 |
economy
State budget
The state budget in 2000 comprised expenditures of the equivalent of 145.9 million US dollars , which was offset by income of the equivalent of 123.7 million US dollars. This results in a budget deficit of 3.6% of GDP . The national debt in 2009 was about one billion US dollars or about 90% of GDP.
The share of government expenditure (in% of GDP) in the following areas was:
Infrastructure
Transportation
There is no regular rail network on Antigua and Barbuda. However, there is a 77 km long narrow-gauge network that is used to transport sugar cane . It includes lines with a gauge of 760 mm (64 km) and 610 mm (13 km).
The main burden of transportation is on road traffic. In 2011, the road network was 1,170 km long. Of that, only 386 km were paved. There are no motorways at all. Overland traffic is handled by some bus routes. In 2013, almost 30,000 vehicles were registered in the island state.
The international airport VC Bird International ( IATA airport code: ANU) is located in the northeast of the island of Antigua, about eight kilometers northeast of the capital Saint John's. It was laid out as an American military base during World War II and today has a 2744 m long runway. From there flights to North America and Europe are offered. There are flights to Puerto Rico (one hour), Miami (three hours), New York (four hours), Baltimore (four hours), Toronto (four hours), London (eight hours), Paris (eight hours) and Frankfurt am Main (nine hours). The airport is the home base of Caribbean Airlines , which flies to destinations in the Lesser Antilles and South America from Antigua . The following airlines also fly daily to weekly to St. John's on Antigua: Air Canada , American Airlines , Continental Airlines , Delta Airlines and US Airways . Other airlines offer their flight services to Europe: British Airways , Virgin Atlantic , Sunsail Airways and Condor Flugdienst . LIAT , Air St.Kitts / Nevis , Carib Aviation , Caribbean Airlines, Montserratt Airways and Caribbean Star Airlines Ltd connect St. John's with most of the islands in the Caribbean.
The overseas port is also located in Saint John's and is used by cruise ships, among others. In 2005 a total of 981 ships with a size of over seven million gross tons were registered under the flag of the island state . But underneath seized 953 ships, the flag of Antigua and Barbuda as a flag of convenience . 1094 of the flagged ships came from Germany.
Culture
- National Day: November 1st
Others
- According to the 2006 Guinness Book of Records , the state is the country with the most marriages and the country with the lowest suicide rate .
- Antigua there are antique stone monuments, the coordinates are 17 ° 4 '29.1 " N , 61 ° 51' 2.7" W .
literature
- Christian Cwik, Verena Muth: Antigua and Barbuda. In: Wolfgang Gieler , Markus Porsche-Ludwig (Hrsg.): State dictionary America: Geography, history, culture, politics and economy. Peter Lang, Berlin 2018, ISBN 978-3-631-77017-7 , pp. 15-26.
- Natasha Lightfoot: Troubling Freedom: Antigua and the Aftermath of British Emancipation . Duke University, Durham 2015, ISBN 978-0-8223-5975-3
- Riva Berleant-Schiller, Susan Lowes & Milton Benjamin: Antigua and Barbuda (World bibliographical series, Volume 182). ABC-CLIO, Oxford 1995, ISBN 978-1-85109-228-4
Web links
- Review article
- Government Website (English)
- Country information from the Federal Foreign Office on Antigua and Barbuda
- Database of indexed literature on the social, political and economic situation in Antigua and Barbuda
- Information, among other things about history, culture, politics (Engl.)
- CIA World Factbook 2010 (Engl.)
- Politics / political system
- The Constitution of Antigua and Barbuda (Engl.)
- Information about the Parliament ( Memento of October 1, 2009 in the Internet Archive )
- Election results for the House of Representatives 1972-2004
- Antigua and Barbuda Defense Force: A Preliminary Look ( Memento January 17, 2006 in the Internet Archive )
- history
Notes and individual references
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Antigua and Barbuda. In: The World Factbook . Central Intelligence Agency , accessed September 7, 2017 .
- ↑ imf.org (PDF) International Monetary Fund
- ↑ Human development index (HDI) , United Nations Development Report 2015, United Nations Development Program Accessed October 27, 2016
- ↑ The boundaries of the maritime national territory, i.e. the territorial waters, are stipulated in the Maritime Areas Act , and include a zone 12 nautical miles off the coast, unless they touch the corresponding territory of a neighboring state (which is around Antigua compared to the United Kingdom at Montserrat in a small way Extent and around Redonda near Montserrat and opposite Saint Kitts and Nevis is the case to a large extent: there the sovereign border to the neighboring islands is around 5 nautical miles); in addition, the territories around Antigua and around Barbuda touch each other to a small extent. Maritime Areas Act, 1982 (No. 18 of 1982); (Brief description with link to text in the idF Cap. 260, pdf, faolex.fao.org). Further regulations also in the Territorial Waters Act, 1982 , 1982 (Act No. 18). (faolex.fao.org)
- ↑ a b Census 2011 Population and Housing Census - Book of Statistical Tables I , Antigua Observer Newspaper, PDF 6.4 MB, accessed September 9, 2017
- ↑ Migration Report 2017. UN, accessed on September 30, 2018 (English).
- ^ Walter Adolphe Roberts: The French in the West Indies . Bobbs-Merrill, Indianapolis 1942, pp. 35-36.
- ^ Jad Adams: Women and the Vote. A world history. Oxford University Press, Oxford 2014, ISBN 978-0-19-870684-7 , page 438
- ^ Antigua and Barbuda - The Governmental System. In: countrystudies.us. Retrieved October 16, 2019 .
- ^ Antigua - New 13-member cabinet sworn in. In: caribbeannewsservice.com. March 23, 2018, accessed November 20, 2018 .
- ↑ Our Constitution. In: ab.gov.ag. Accessed August 28, 2019 .
- ^ Antigua and Barbuda Election Center. Retrieved July 27, 2018 .
- ^ Berndt Hillebrands: Antigua and Barbuda. In: Dieter Nohlen (Ed.): Handbook of the election data of Latin America and the Caribbean (= political organization and representation in America. Volume 1). Leske + Budrich, Opladen 1993, ISBN 3-8100-1028-6 , pp. 21-27, p. 22.
- ^ Mart Martin: The Almanac of Women and Minorities in World Politics. Westview Press Boulder, Colorado, 2000, p. 9.
- ^ Der Fischer Weltalmanach 2008. Fischer Taschenbuch-Verlag, Frankfurt 2007, ISBN 978-3-596-72008-8 .
- ^ US Relations With Antigua and Barbuda. In: state.gov. United States Department of State , March 20, 2019, accessed April 10, 2019 .
- ↑ The population figures refer to the census of May 27, 2011 (source: https://statistics.gov.ag/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/Census-2011-Book-of-Statistical-Tables-I. pdf )
- ↑ Registered vehicles - Data by country. In: apps.who.int. November 30, 2015, archived from the original on April 12, 2019 ; accessed on April 12, 2019 (English, original page is continuously updated; information is based on archive version).
Coordinates: 17 ° N , 62 ° W