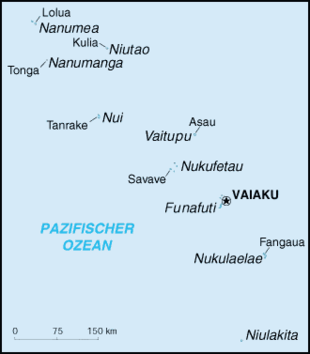
Tuvalu
| Tuvalu | |||||
|
|||||
|
Motto : Tuvalu mo te Atua
( Tuvaluan for "Eight Islands for the Almighty") |
|||||
| Official language | Tuvaluan and English | ||||
| Capital | Funafuti | ||||
| Form of government | Parliamentary monarchy | ||||
| Head of state |
Queen Elizabeth II represented by Governor General Iakoba Italeli |
||||
| Head of government | Cause Natano | ||||
| surface | 26 km² | ||||
| population | 10,640 (2012) | ||||
| Population density | 409 ( 20th , based on the year 2009) inhabitants per km² | ||||
gross domestic product
|
2017 | ||||
| currency |
Australian dollar (AUD) Tuvaluan dollar (TVD) |
||||
| independence | October 1, 1978 (from the UK ) |
||||
| National anthem |
Tuvalu mo te Atua royal hymn : God Save the Queen |
||||
| Time zone | UTC +12 | ||||
| License Plate | TUV | ||||
| ISO 3166 | TV , TUV, 798 | ||||
| Internet TLD | .tv | ||||
| Telephone code | +688 | ||||
Tuvalu ([ tuˈvaːlu ], Tuvaluan Fakavae Aliki-Malo i Tuvalu 'Constitutional Monarchy Tuvalu' ) is an island nation in the Pacific Ocean . It is organized as a parliamentary monarchy and a member of the Commonwealth of Nations . The capital is the Funafuti atoll and the seat of government is the village of Vaiaku located on this atoll .
Until independence on October 1, 1978, the territory was called Ellice Islands .
With a GDP of $ 40 million in 2017, Tuvalu had the smallest economy in the world.
geography
Tuvalu is located in the southwest of the Pacific Ocean , east of Papua New Guinea and north of New Zealand . The surrounding islands include the Solomon Islands , Nauru , Kiribati , Tokelau , Samoa , Wallis and Futuna , Fiji and Vanuatu .
With an area of 25.66 square kilometers (km²) Tuvalu is the fourth smallest state in the world after Vatican City with 0.44 km², Monaco with 2.02 km² and Nauru with 21 km². Funafuti , Nanumea , Nui , Nukufetau , Nukulaelae and Vaitupu are atolls , ring-shaped coral reefs with sometimes tiny reef islands that enclose a lagoon whose area, except in the case of Vaitupu, is much larger than the respective land area. There is even a freshwater pond on Nanumea, which is extremely rare for atolls. Vaitupu has two lagoons that are almost completely surrounded by land and are only connected to the sea through narrow channels. The other islands Nanumanga , Niutao and Niulakita are also atolls, but with smaller and closed lagoons, i.e. pure inland waters with no connection to the sea.
At their highest point, the islands are only five meters above sea level . As the sea level due to global warming increases , it was feared the islands would be flooded in the near future. The government has already tried to apply for asylum for its people in New Zealand and Australia on this basis . Originally around 300 people were supposed to emigrate each year (around 4,000 Tuvalu citizens already live in New Zealand). New Zealand and Australia refused. In 2014, however, the New Zealand Immigration Tribunal first considered the consequences of climate change in a case in which a family of four from Tuvalu was granted asylum.
The scientist Don Kennedy, who originally came from Tuvalu, suggested in early 2006 that the population should be resettled in the future on the Fiji island of Kioa. The associated costs should be borne by the industrialized countries as the cause of global warming: "If the culture of our island state is to live on, the 9,000 Tuvaluans must move to Kioa together" .
Tuvalu's then Prime Minister Maatia Toafa and all Tuvalu political groups criticized this proposal. The evacuation is currently a low priority project, as no demise is expected in the next 30 years. Toafa also prefers to acquire land in New Zealand or Australia and not to relocate to an island without adequate infrastructure.
According to evaluations of current satellite images, the islands and the associated coral reefs have become larger in the last 60 years. According to this, the rise in sea levels is currently more than offset by alluvial deposits and sedimentation, although some beaches are being used as sand pits for the increasing construction of roads and buildings. However, it is uncertain whether the sedimentation rate can keep up with the accelerated sea level rise - by 18 to 59 cm, as is forecast for the next 90 years up to 2100 (IPCC 2007). In addition, the shape of the islands is changed, while in some places land is lost, the islands grow in others. According to Naomi Biribo, this represents a great challenge. Measures against flooding caused by seaquakes and hurricanes are also necessary.
history
Linguists consider a settlement about 2000 years ago to be likely, which was mainly from the islands of Tokelau and Samoa by Polynesians .
The first European explorer was Álvaro de Mendaña de Neyra from Spain. In 1567/68 he sailed westwards across the Pacific, sighted the island of Nui and called it Isla de Jesús at that time . In the period that followed, the islands of Tuvalu were discovered by chance and were not taken into account by those who discovered them. In 1819 the American Arent de Peyster , captain of a British merchant ship, discovered the island of Funafuti and named it Ellice Island in honor of the merchant and owner of the cargo, Edward Ellice. The term Ellice Islands was later used for the entire chain of islands.
In the decades that followed, more and more Europeans came to Tuvalu, mainly for whaling and the slave trade . In the 1860s, 400 people were deported from Tuvalu to Peru as workers . Others were taken to plantations on the surrounding islands. Many residents also died from introduced diseases.
Christianization began in 1861 with the first missionary on the islands. The German company JC Godeffroy & Sohn from Hamburg established the first trading relationships with the residents. In 1877 Tuvalu came under British administration under the then name Ellice Islands and in 1892 became part of the British Protectorate of the Gilbert and Ellice Islands . In 1915 the islands officially became a colony of the British Empire.
During the Second World War , the Japanese conquered the Pacific as far as Kiribati ; however, the Americans landed first on Tuvalu. They built airfields and defensive bunkers on the islands of Funafuti, Nukufetau and Nanumea. All three islands were bombed by the Japanese, but without major damage. After the end of the war, the British formed the colony of Gilbert and Ellice Islands again with Tuvalu and the islands of Kiribati, which were conquered by the Japanese .
In the 1950s, Niulakita was incorporated into Tuvalu.
Under British administration, active and passive women's suffrage was introduced on January 1, 1967 . With independence in 1978 this right was confirmed.
In 1974 the British planned to give the colony independence by installing its own government. But soon afterwards the Tuvaluans pushed for independence in order not to end up under Kiribati administration. The British initiated a referendum, with 92% of Tuvaluans voting for the Tuvalu Islands to form their own state.
On October 1, 1978, the former Ellica Islands under the new name Tuvalu became a sovereign state with a parliamentary monarchy and at the same time a member of the Commonwealth of Nations , the Gilbert Islands followed a year later and in 1979 merged with other islands to form the independent island state of Kiribati .
Tuvalu joined the United Nations in 2000 .
Administrative division
Tuvalu consists of six atolls and three islands. Tuvalu means "eight islands" because originally only eight islands were inhabited. The ninth (and southernmost) island, Niulakita , was not settled with residents of the overpopulated island of Niutao until 1949 , but continues to form a joint administrative unit with it.
The largest town in Tuvalu is the capital, Funafuti .
climate
All islands have a hot tropical climate with an average temperature of 30 degrees Celsius. The rains are heavy and usually set in between November and February. Occasionally, Tuvalu is hit by cyclones .
In October 2011, the rising sea level, which penetrates the groundwater reserves, and an unusual period of drought led to an acute shortage of drinking water (→ “ salt water intrusion ”). Tokelau faces the same problem . Experts fear that the drinking water shortage could spread to other islands throughout the South Pacific . New Zealand and Australia are currently helping the islands with seawater desalination plants.
population
Tuvalu has 11,097 inhabitants (as of 2016). About 96 percent of the population are Polynesians , the other four percent are Micronesians .
29 percent of the population are up to 14 years old, 65 percent between 15 and 64 years old, over 64 years are only 5.5 percent of the population. Population growth is 0.8 percent per year, with the birth rate per 1000 inhabitants at 23.7 and the death rate at 8.7 per 1000 inhabitants. Infant mortality is three percent. The life expectancy of the population is 66 years (men 64 years, women 68 years). (all as of 2015)
| year | population |
|---|---|
| 1960 | 6.104 |
| 1970 | 7,303 |
| 1980 | 8,052 |
| 1990 | 9.003 |
| 2000 | 9,420 |
| 2016 | 11.097 |
languages
The official languages are Tuvaluan and English , both of which are represented on all islands. In addition, Samoan and Kiribati (Gilbertian) are spoken in the Nui- Atoll .
Tuvaluan is a Polynesian language that is spoken in various island dialects and does not have a uniform written form. English was brought to the islands through British colonization.
Tuvalu means "eight belonging together" in Tuvaluan, referring to the eight islands that make up Tuvalu geographically. After Niulakita joined the island association in the 1950s, the name was no longer consistent. Therefore, there was often a discussion about renaming the country to “Tuiva”, where “iva” stands for nine.
religion
The state church in Tuvalu is the Ekalesia Kelisiano Tuvalu by law . These belong to between 91 and 97 percent of the population. This stands in the congregational tradition and has been independent since 1968. Small minorities are the Seventh-day Adventists (1.4–3 percent), Baha'i (1–3 percent), Jehovah's Witnesses (two percent) and Catholics (one percent).
politics
Political system
Tuvalu is a parliamentary monarchy . The head of state is the British monarch , currently Queen Elizabeth II. She bears the official title Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God Queen of Tuvalu and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth , Elizabeth the Second, by the grace of God Queen of Tuvalu and your other empires and territories, chief of the Commonwealth . A governor general represents the monarch on the islands, although he only has representative duties. Iakoba Italeli has been performing this role since his appointment by the Queen on April 16, 2010. The governor general is appointed on the recommendation of the prime minister.
The head of government is the prime minister who sets the guidelines for politics. He is elected by a unicameral parliament. The parliamentary elections on August 14, 2006 resulted in a government under Apisai Ielemia , who was replaced by Maatia Toafa on September 29, 2010 . After a vote of no confidence by his former Foreign Minister Willy Telavi, he took over government responsibility himself on December 24, 2010. On August 1, 2013, he was dismissed by the Governor General, followed by Enele Sopoaga on August 5, 2013 . The Cabinet of Ministers, consisting of a maximum of five parliamentarians, is appointed by the Governor General on the proposal of the Prime Minister. On September 19, 2019, Kausea Natano took over the office.
The parliament (Fale i Fono) has 16 seats. Each island has two members. Parliament is elected directly by the people at least every four years. Every citizen over the age of 18 is entitled to vote. Political parties do not exist in Tuvalu; instead, clan associations play a corresponding role.
In the 2008 referendum on the monarchy in Tuvalu , almost two-thirds of the voters who took part voted in favor of maintaining the monarchy , with a turnout of just over 20 percent.
Memberships
Tuvalu is a member of the following international organizations: ACP , AOSIS , AsEB , Commonwealth of Nations , ESCAP , ICAO , ITU , IMF , OPCW , PIF , Sparteca , SPC , UNESCO , UPU , United Nations , WHO , WTO
Tuvalu is not a member of any military alliance. It does not have its own armed forces. The territorial waters and the exclusive maritime economic zone are monitored by occasional reconnaissance flights by the New Zealand Air Force (without a contractual basis) and by a patrol boat supplied by Australia .
economy
Economic situation
The Tuvaluan economy is underdeveloped. The gross domestic product (GDP) in 2013 was 38.3 million US dollars . Annual economic growth is (as of 2013) around one percent. The service sector contributes 69.11 percent to GDP, industry 8.73 percent and agriculture 22.16 percent (all as of 2013). The main industries are fishing , tourism and the export of copra and coconuts . With an export volume of 600,000 US dollars (as of 2013), Tuvalu is one of the world's smallest exporting nations. Exports are compared to imports, especially fuel, food and machinery, amounting to 20 million US dollars (as of 2013).
Top-level domain
Tuvalu achieved international fame through the fact that the International Organization for Standardization has assigned the island nation the country code TV, which is also used as a top-level domain (TLD). The sale of these TLD rights to DotTV brought the island nation , in addition to global headlines, an urgently needed source of income. The company agreed to pay 50 million US dollars , payable in annual installments of 5 million US dollars. Tuvalu even honored the domain sale with its own stamp. Tuvalu's government used the money to procure IT infrastructure for the most important government institutions and paid the entry fee for the United Nations .
State budget
The state budget in 2006 included expenditures equivalent to US $ 23 million , which was offset by income equivalent to US $ 21.5 million. This results in a budget deficit of up to six percent of GDP . The Tuvalu Trust Fund , a fund set up by Australia, New Zealand and the United Kingdom and supported by Japan and South Korea, contributes several million US dollars to the national budget. In 2006 it was nine million US dollars.
tourism
Tuvalu was visited by 1232 tourists in 2011 . Tuvalu is one of the least visited independent states in the world.
In addition to the philately office in Funafuti, the Funafuti Conservation Area (a marine reserve ) is one of the most popular tourist destinations. There are six hotels across Tuvalu .
traffic
Tuvalu has had 8 kilometers of asphalt roads since 2002, making it the country with the fewest kilometers of roads in the world. The remaining traffic routes are not asphalted. The connection between the individual atolls is ensured by a ferry service .
The Funafuti International Airport is served by Fiji regularly and once a week from Kiribati
The Tuvalus merchant navy has almost 50 ships with more than a thousand gross tons , including tank , cargo and container ships . The majority of the ships sail under the Tuvaluan flag , but have foreign owners.
Culture
The music of Tuvalu since the second half of the 19th century musical styles from Samoa embossed and by Western missionaries introduced European folk songs and polyphonic church hymns. The most popular dance style today is called fatele .
media
The Tuvalu Media Department (TMD) (from 2006 to 2008 Tuvalu Media Corporation (TMC)) broadcasts the radio station Radio Tuvalu on an AM frequency . The station has also had an FM studio since 2011 and can be heard on all nine atolls and islands. It is broadcast daily from 6:30 a.m. to 8 a.m., 11:25 a.m. to 1 p.m. and 6:25 p.m. to 10 p.m.; the rest of the time the British BBC is fed in. Programs are broadcast in English or Tuvaluan .
The only newspaper in the country "Sikuleo o Tuvalu - Tuvalu Ech" o (formerly "Tuvalu Echoes") was discontinued in 2012.
Currently (as of 2013), television reception via sky Pacific is only possible to a limited extent. The TMD is interested in setting up a Tuvaluan television station.
TMD is a member of the Pacific Islands News Association .
The top-level domain of Tuvalu, .tv , is often used for the Internet presence of television broadcasters (see also misappropriation of top-level domains ).
education
In addition to numerous elementary and secondary schools , Tuvalu runs the University of the South Pacific (USP; German University of the South Pacific ) together with eleven other Pacific countries . The university is spread across various locations in the South Pacific. The Tuvalu campus is located in the capital, Funafuti.
literature
- Martin Zinggl: Why not Mariazell? As an ethnologist in Tuvalu. Abera Verlag, Hamburg 2014, ISBN 3-939876-04-6 .
- Peter McQuarrie: A Floating World - Images of the Tuvalu Environment. Ellice Islands Press, Waltakere City 2008, ISBN 978-1-877479-15-1 .
- GEO (ed.): South Sea: Calm before the storm. In: GEO. March 2004, No. 3, Gruner & Jahr-Verlag, Hamburg 2004, ISSN 0342-8311 .
- Peter McQuarrie: Strategic Atolls, Tuvalu and the Second World War. MBC University of Canterbury & IPS University of the South Pacific, Christchurch 1994, ISBN 978-0-9583300-5-3 .
- Peter McQuarrie: TUVALU - A Celebration of 10 Years Independence. Government of Tuvalu, Funafuti 1988, OCLC 768631807 .
- Gerd Koch : The material culture of the Ellice Islands. Museum of Ethnology, Berlin 1961, OCLC 715059481 .
Movies
- 2003, Marianne Aschenbrenner, Bernd Niebügge: The Fall of Tuvalu. Documentation, Arte-TV, 90 minutes
- 2004, Christopher Horner , Gilliane Le Gallic: The Disappearing of Tuvalu: Trouble In Paradise . Documentation, 75 minutes
- 2005, Elizabeth Pollock: Tuvalu: That Sinking Feeling . Documentation, PBS Rough Cut, 16 minutes
- 2007, Ulli Weissbach, Werner Zeppenfeld: An island disappears. Report, Das Erste ( Weltspiegel ), January 21, 6 minutes
- 2011, Martin Zinggl: Toku Fenua. Documentation, 29 minutes
- 2015, Matthias von Gunten : ThuleTuvalu , documentation, approx. 96 minutes
Web links
- Official tourism website for Tuvalu (English)
- Information page about Tuvalu (English)
- Country information from the Federal Foreign Office on Tuvalu
Individual evidence
- ↑ PopGIS 2.0 Tuvalu , Census 2012, Secretariat of the Pacific Community, accessed July 9, 2016th
- ↑ [1] of the International Monetary Fund .
- ↑ Tuvalu is threatened with extinction: An atoll is broadcasting SOS ( Memento from November 3, 2008 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ https://www.nature.com/articles/440734a
- ↑ www.zeit.de/wissen/umwelt/2014-08/neuseeland-klimawandel-tuvalu-asyl
- ^ Move Tuvalu Population To A Fiji Island To Ensure Survival, Scientist Says. February 20, 2006, accessed February 11, 2015 .
- ↑ Tuvalu: Evacuation Plans Due to Rising Sea Levels - Global Warming Will Make Atolls Uninhabitable in 30 Years , pressetext.at, February 20, 2006.
- ^ Arthur P. Webb, Paul S. Kench: The dynamic response of reef islands to sea level rise: evidence from multi-decadal analysis of island change in the central pacific. In: Global and Planetary Change doi : 10.1016 / j.gloplacha.2010.05.003 , May 3, 2010.
- ↑ 'Shape-shifting islands defy sea-level rise' by Wendy Zukerman, Newscientist (June 2, 2010)
- ↑ a b - New Parline: the IPU's Open Data Platform (beta). In: data.ipu.org. January 1, 1967, accessed October 7, 2018 .
- ^ Mart Martin: The Almanac of Women and Minorities in World Politics. Westview Press Boulder, Colorado, 2000, p. 390.
- ^ Dieter Nohlen, Florian Grotz, Christof Hartmann (eds.): South East Asia, East Asia and the South Pacific. (= Elections in Asia and the Pacific. A Data Handbook. Volume 2). Oxford University Press, New York 2002, ISBN 0-19-924959-8 , p. 825
- ^ Falekaupule Act. Government of Tuvalu, 1997, No. 8; 2008 revised edition, CAP. 4.08, Schedule 1, p. 56, accessed on July 29, 2014
- ↑ vgt. about this: http://english.aljazeera.net/news/asia-pacific/2011/10/201110364857797250.html and http://wetter.t-online.de/pazifik-suedseeparadiese-leiden-unter-trinkwassermangel/id_50323600/ index
- ↑ english.aljazeera.net
- ↑ a b c The World Factbook, Tuvalu. Central Intelligence Agency, last accessed June 1, 2016
- ↑ a b c d e f population, total | Data. Retrieved October 18, 2017 (American English).
- ^ State Church (Declaration) Act, 2008 Revised Edition, CAP. 54.20, p. 3. Government of Tuvalu, April 1, 1993. Retrieved July 28, 2014
- ↑ Country information from the Foreign Office on Tuvalu ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ See http://www.state.gov/g/drl/rls/irf/2003/24325.htm
- ↑ a b Country information from the Federal Foreign Office on Tuvalu
- ^ Royal Style and Titles Act, 2008 Revised Edition, CAP. 4.28. Government of Tuvalu, 2008. Retrieved July 28, 2014
- ^ The local government system in Tuvalu. Commonwealth Local Government Forum, unknown date , p. 229, accessed July 28, 2014
- ↑ World Bank country data for Tuvalu , accessed on September 30, 2015
- ↑ Economic data for Tuvalu ( Memento of the original from October 1, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. on Quandl Financial and Economic Data , accessed September 30, 2015
- ↑ Export data for Tuvalu ( Memento of the original from August 27, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. on Kushnir's World Macroeconomic Research , accessed September 30, 2015
- ↑ Import data for Tuvalu ( Memento of the original from August 27, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. on Kushnir's World Macroeconomic Research , accessed September 30, 2015
- ^ Announcement at heise.de: The island state of Tuvalu is taking off with .tv , September 4, 2000.
- ↑ Migration - Visitors summary. Tuvalu Central Statistics Division, 2011 retrieved July 23, 2014
- ↑ timelesstuvalu.com: Accommodation. (accessed on July 23, 2014)
- ^ The ten: ... longest road networks in the world. Spiegel Online , August 25, 2008, accessed May 31, 2012 .
- ↑ The largest road networks in the world. Statista , accessed September 8, 2010 .
- ^ Tuvalu Official Tourism Website
- ^ Air Kiribati Limited. Retrieved April 22, 2020 (English).
- ^ A b c Tuvalu State of Media and Communication Report 2013. Pacific Media Assistance Scheme, 2013, p. 3, accessed July 25, 2014
- ↑ Shuuichi Endou: New AM Radio Station in Funafuti . Tuvalu-News.TV. December 30, 2011. Retrieved July 24, 2014.
- ↑ About Tuvalu-News.TV . Archived from the original on March 26, 2012. Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved July 25, 2014.
- ^ Country profile - Tuvalu. PINA, date unknown retrieved July 25, 2014
- ^ Tuvalu campus. University of the South Pacific. Retrieved July 28, 2014
- ↑ FRONTLINE / WORLD. Rough cut. Tuvalu: That Sinking Feeling | PBS. Retrieved April 26, 2020 .
Coordinates: 7 ° S , 178 ° E