King attack
| King attack | |
|---|---|
| NASA satellite image | |
| Waters | Pacific Ocean |
| archipelago | Line Islands |
| Geographical location | 6 ° 24 ′ N , 162 ° 24 ′ W |
| Number of islands | 3 |
| Main island | unnamed |
| Land area | 1 ha |
| total area | 60 km² |
| Residents | uninhabited |
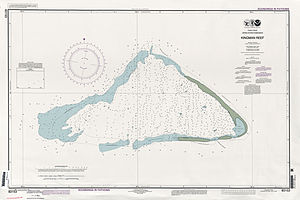
| Sea chart of the Kingman attack | |
The Kingman Reef ( English Kingman Reef , [ ˈkɪŋmən ]) is a coral reef in the North Pacific and belongs to the United States as a non-incorporated territory ( outer area ) . It is located 61 km northwest of Palmyra and 1,713 km southwest of Honolulu . Geographically, it belongs to the northern Line Islands .
history
The American captain Edmund Fanning discovered the Kingman attack on June 14, 1798 with his brig Betsey . In his book "Voyages and Travels" he reported how his ship almost ran aground on the reef and got stuck if he hadn't felt the danger and had stopped it in time. He described the reef as follows:
Coral reef, or sandbar, in the shape of a crescent moon, extending for six miles from north to south; under its lee, and within the area in the crescent, the water appears to be shallow and shallow. We have not seen a foot of earth, rock, or sand over the water where a boat might be pulled ashore.
On some nautical charts it was then noted as Danger Rock (German for "dangerous rock").
The reef was named after the naval officer WE Kingman , who paid him a visit on November 29, 1853 with the Shooting Star . He reported on the discovery in September 1855 in the Honolulu newspaper "The Friend". There he also pointed out the considerable threat that the reef would pose at night, especially in light winds and calm seas, as breakers could only be seen when the ship had already come dangerously close to the reef.
Under the name Danger or Danger Island , it was one of the islands that were claimed by the Americans in 1856 under the Guano Islands Act .
The US annexed it on May 10, 1922, and granted it naval reserve status twelve years later. Its protected lagoon of the airline served Pan Am 1937/1938 as a stopover for Boeing 314 - flying boats between Hawaii and American Samoa . Due to its particularly diverse marine flora and fauna - according to ecologists it is home to more than 225 different fish species and 205 coral species - it was declared a nature reserve Kingman Reef National Wildlife Refuge in 2001 , which together with six other American islands in the Pacific has been the Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument forms.
Geography and climate
The Kingman attack is largely under water, under favorable conditions 10,000 m² (0.01 km²) of dry land are visible, the coastline can be up to 3 km. The total area within the reef rim, which is constantly flooded in the west, is 60 km². Due to the small land area and frequent flooding of the triangular coral reef, neither land vegetation nor natural resources can be found; the soil is completely sterile. The highest point is one meter above sea level to the east . The climate is tropical , but it is significantly influenced by the prevailing winds.
administration
The United States counts the Kingman attack among the so-called United States Minor Outlying Islands . The United States Navy , which carries out its duties from Washington, DC, is responsible for all administrative tasks. The public is not granted access to the reef unless a special permit has been obtained. A visit would be possible either with a flying boat that lands in the deep inner lagoon, or a ship that berths at the coastal anchorage.
Radio amateur expeditions
The Kingman attack has rarely been visited since the 1940s. However, due to its special status as an independent unit ("Entity"), it was repeatedly the target of expeditions for radio amateurs. Between 1977 and 2000, several excursions to the Kingman attack were undertaken, sometimes with considerable financial outlay, in order to make this special spot accessible to radio amateurs. After the administration of the Kingman attack was transferred from the US Navy to the US Fish & Wildlife Service, the reef also belongs to the Palmyra / Jarvis Wildlife Refuge for radio amateurs and has lost its extraordinary rank with effect from March 29, 2016.
literature
- GAO / OGC-98-5: US Insular Areas - Application of the US Constitution . Report to the Chairman, Committee on Resources, House of Representatives. United States General Accounting Office (GAO), November 1997 (English, online at www.gao.gov [PDF; 863 kB ] with map of the Kingman attack).
Web links
- Kingman Reef National Wildlife Refuge. In: National Wildlife Refuge System. United States Fish and Wildlife Service (English).
- Kingman Reef. Depth images of the Kingman attack. Pacific Islands Benthic Habitat Mapping Center, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology, University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa (English).
- CIA World Factbook: United States Pacific Island Wildlife Refuges: Kingman Reef (English).
- Kingman Reef. In: Jane's Oceania Home Page. Jane Resture (English).
- Photo album Kingman Reef on Flickr
Individual evidence
- ↑ Wildlife & Habitat. Marine Life and Coral Communities Sections . In: Kingman Reef National Wildlife Refuge. United States Fish and Wildlife Service , accessed May 23, 2017 .
- ^ US Unincorporated Possessions. Kingman Reef. In: World Statesmen.org. Retrieved May 15, 2017 .
- ↑ Kingman Reef (KH5) Deleted from DXCC List. In: www.arrl.org/news. American Radio Relay League (ARRL), March 28, 2016, accessed May 15, 2017 .