Wyoming
| Wyoming | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
| List of states | |||||
| Capital: | Cheyenne | ||||
| State motto: | Equal rights (dt. Equal Rights) | ||||
| Official language : | English | ||||
| Surface: | 253,336 km² | ||||
| Residents: | 579,315 (2017 estimate) (2.3 U / km²) | ||||
| Member since: | July 10, 1890 | ||||
| Time zone: | Mountain : UTC − 7 / −6 | ||||
| The highest point: | 4207 m ( Gannett Peak ) | ||||
| Average Height: | 2040 m | ||||
| Deepest point: | 945 m ( Belle Fourche River ) | ||||
| Governor : | Mark Gordon ( R ) | ||||
| Post / Office / ISO | WY / Wyo. / US-WY | ||||
| Map of Wyoming | |||||
| Wyoming Geographic Map | |||||
Wyoming ( English pronunciation [ wai̯ˈoʊ̯mɪŋ ] ) is with 579,315 inhabitants (2017) the least populous state in the United States and, after Alaska , the state with the second lowest population density. It is located in the western United States and rises from the Great Plains of Eastern Wyomings to the Rocky Mountains .
The name comes from the language of the Algonquin - Indians and means "Great Plains". It was taken from the poetic short story Gertrude of Wyoming , written by Thomas Campbell in 1809.
The largest place is the capital Cheyenne . The nickname is Equality State according to the motto of the state: "Equal Rights" (German: equal rights).
Geography, flora and fauna
General
With its 253,336 km² Wyoming is the tenth largest state in the USA by area. After Colorado, it is also the second highest state in the country on average at 2044 m. It is located in the western center of the US state and therefore belongs to the legendary so-called (Wild) West (hence the nickname Cowboy State ) due to its location (as well as its culture ).
Wyoming extends for 450 km between approximately 41 ° N and 45 ° N and a length of 550 to 580 km between approximately 104 ° W and 111 ° W and belongs to the states along with its southern and western neighbors Colorado and Utah whose boundaries were defined almost exclusively according to geographical latitude and longitude. The demarcation corresponds (on a corresponding map network design , such as the Mercator projection ) to a rectangle with minor deviations.
Basically, the Wyoming area is a wide, broken plateau from which various ridges of the Rocky Mountains rise. Seen from a cross-sectional perspective, this plateau is in an inclined position that merges from a higher west to a lower east. This slope also describes the transition from the wide eastern plains of the prairies over central basin landscapes to the rocky mountains to the west. Wyoming is a state that connects the great cultural landscapes of the Great Plains and the Rocky Mountains - a position it shares only with three of the 50 other states: Montana in the north and Colorado and New Mexico in the south.
Another geographical significance is Wyoming's location on the Great Continental Divide , the great continental divide of the North American continent, which runs through the state area in a north-west-south-east direction. It runs along the Absaroka Range and Wind River Ranges and continues in the Great Divide Basin , and later the Park Range (mostly in Colorado). All rivers that arise east of this line drain eastward and at some point all flow into the Missouri River , which flows into the Mississippi River and finally into the Atlantic Ocean (Gulf of Mexico). Those rivers that begin their course west of the watershed end in the Pacific (either in the open ocean if they follow the Columbia River west, or in the Gulf of California if they drain south into the Green River and later the Colorado River ).
Wyoming can be broken down into three major geographic areas, each roughly one third of the state: the Great Plains , the Intermountain Basins, and the Rocky Mountains .
Great Plains
The eastern part of Wyoming is occupied by the Great Plains, vast prairies that stretch from southern Canada through the center of the United States down to the Mexican border and form an essential, world-famous cultural landscape. They also gave the state its name, which is taken from the Cheyenne language and means great plains .
The prairies of Wyoming are characterized on the one hand by completely flat stretches of land, on the other hand by the predominant, gently rolling hills. The majority of this area is characterized by largely treeless steppe landscapes overgrown with short grass. Some of them are interspersed with poplars and bushes. Agriculture (most likely wheat) is hardly possible in these windy, dry expanses, instead extensive grazing is practiced.
On the prairie in northeast Wyoming, the Belle Fourche River is the deepest point in the entire state at 945 m. However, this does not exclude larger elevations in the same region: the Wyoming prairies have about a third share of the Black Hills , the sacred mountains of the Sioux and Cheyenne peoples, who they call Pahá Sapá ( Lakota ) or Mo'ōhta-vo'honáaeva (Cheyenne / Algonkin ) name. The partly densely covered island mountains with Ponderosa pines reach heights of just over 2000 m in Wyoming and are home to a well-known natural monument: the Devils Tower National Monument , a monumental volcanic monolith that rises 386 m above the Belle Fourche River and a height of 1558 m reached. This mountain is sacred to the Sioux and Cheyenne as well as other First Nations and is called Mato Tipila (hut of the bear) in Lakota .
Rocky mountains
Mainly in the north-west of the state and partly also in the south-east there are huge mountain ranges, which are all part of the Rocky Mountains. The rocky mountains in Wyoming are divided into various mountain ridges, which usually extend in a north-south or north-west-south-east direction. The Bighorn and Laramie Mountains limit the prairies and mark the transition into extensive basin landscapes, which are framed by the mountain ranges.
The most impressive folds of the Rocky Mountains in Wyoming are the Absaroka , Teton , Wind River and Wyoming Ranges , as well as the Big Horn Mountains in the northwest, which are juxtaposed with the lower and less spectacular Laramie and Medicine Bow Mountains in the southeast. The Wind River Range , where nine four-thousand-meter peaks soar into the sky, is particularly high and rugged . Wyoming's highest elevation is also located here: Gannett Peak , which, depending on the measurement, reaches 4202 m, 4207 m or 4210 m.
The Teton Range with its 4196 m high Grand Teton Peak , the second highest mountain in the state, on the edge of the national park of the same name south of the Yellowstone National Park, is a very valued photo opportunity and symbol of mighty, untouched nature .
Due to their relatively abundant rainfall, the mountain ranges of the Rocky Mountains are densely forested. Because of the altitude and the harshness of the climate, conifers predominate, with which the timber industry achieves a profitable business. In addition, valuable raw materials such as oil shale , hard coal , iron ore and uranium lie beneath the rock . Mountain tourism (hiking, climbing, canoeing and rafting in summer, skiing in winter) is also important.
Intermountain Basins (mountain basins)
The third large geographical area is represented by extensive basins , which are mainly in the center and southwest and are bordered by the mountain ranges, e.g. B. the Bighorn, Great Divide, Green River and Wind River Basins . These basins are located relatively high (1000–2000 m), but flat and mostly covered with short grass or low bushes. There are hardly any trees. Since they are located directly in the lee of the large mountain ranges, these basin landscapes have very little precipitation and therefore sometimes have a semi-desert character. Nevertheless, together with the Great Plains, they are the core area of the population and agriculture. However, arable farming (especially wheat and sugar beets) is hardly possible here without irrigation.
A special feature is the Great Divide Basin , which is a semi-desert with no inflow or outflow directly on the continental divide. Here is the so-called Red Desert , a semi-desert and desert area of around 24,000 km², which is known for its sand dunes, which are among the most powerful in the USA. To the southwest of it, bizarre canyons join, such as the colorful Flaming Gorge , which are already reminiscent of the Canyonlands in Utah and Arizona , which are further south-west .
rivers and lakes
As a fairly dry patch of America, Wyoming naturally has no large wetlands or lake landscapes. Only 0.7% of the state's area is covered by water. This puts Wyoming in tenth place among the American states, together with other states in the Midwest and Southwest (Arizona, Colorado, Kansas , Nebraska etc.).
Almost a quarter of the entire water area of Wyoming is taken up by Yellowstone Lake in the national park of the same name, which extends over 352 km² within the park boundaries. It is located at an altitude of 2376 m, has 177 km of shore length and, with an average water depth of 42 m, measures 118 m at its deepest point. Its position as the largest freshwater lake over 2000 m in all of North America is outstanding. However, Yellowstone Lake only has a liquid surface about half of the year (and rarely warmer than 15 ° C), as it freezes over in normal winters from early December to late May or early June. The ice layer is up to a meter thick in many places, but there are areas in which shallow water close to the shore lies over warm springs that prevent ice formation in these areas.
The second largest lake is not far south and also over 2000 m above sea level. It is the 103 km² Jackson Lake in Grand Teton National Park , which is 134 m even deeper than Yellowstone Lake. Originally smaller, the water area was enlarged by a dam. Jackson Lake is also frozen over for six months and rarely measures above 15 ° C, even in hot summers.
Apart from these two large lakes there are still a few minor, but almost all go back to Flussaufstauungen, such as the reservoirs Bighorn, Boysen, Buffalo Bill, Flaming Gorge, Fontenelle, Glendo, keyhole, Pathfinder and Seminoe reservoirs , all of supporting Are important for agriculture and the water supply of cities. The Wyoming rivers have their origins on the slopes of the mountain ranges that form the continental divide. The longest river in Wyoming's state is the North Platte River in the southeast, over 500 km in length. It is also of special importance in that it is home to three of the most water-rich reservoirs. The Green River , with almost 400 km the third longest river, is dammed into two large reservoirs, the Fontenelle Reservoir and the Flaming Gorge Reservoir , which stretches into neighboring Utah. On the Wind / Bighorn River, the second longest in Wyoming (around 500 km), are the Bighorn and Boysen Reservoirs, on which the yield of agriculture in the Bighorn Basin depends. Other rivers of importance are the Snake River , the Belle Fourche and the Powder Rivers , which cross the prairie in the northeast, the Sweetwater and Laramie Rivers in the southeast, both of which feed the North Platte, the southwestern Black Fork , Hams Fork and Sandy Rivers ( Big Sandy River , Little Sandy River ) that flow into the Green River, as well as the smaller tributaries of the Wind or Bighorn River in the Bighorn Basin: Greybull , Gooseberry , Nowood and Shoshone .
fauna
Wyoming's high-lying plains are home to hares , prairie dogs , coyotes , pronghorn , rattlesnakes , hawks , grouse, and pheasants . Both bison and pronghorn were almost extinct in the plains at the end of the 19th century due to excessive hunting, but their populations were able to stabilize thanks to extensive protective measures. After the pronghorns were placed under protection, they reproduced again from around 5000 animals in 1903 to more than half a million today. This means that Wyoming has at least as many pronghorns as there are people. Wyoming also has the highest pronghorn population in the United States and in the Red Desert also has the largest contiguous herd of these animals in the United States with 40,000–50,000 specimens. The bison, of which in Columbus ' time between 30 and 70 million were estimated to roam the North American continent in huge herds, had been decimated to less than 1000 by the end of the 19th century. On the one hand, the massive animals lost large parts of their habitat and were prevented from migrating due to the increasing population, on the other hand they were hunted to a far exaggerated extent, especially after it had become obvious that many Indian tribes would perish with the bison. One of the last small bison herds was given a secure refuge in Yellowstone National Park. Their population was able to stabilize there and in 2007 was 4700 animals. This is the largest wild herd in the entire United States. In addition, in Wyoming, as in many other states, there are flourishing bison ranches where thousands of animals are bred in Wyoming alone. The demand for bison meat and leather is substantial.
In contrast to the Plains, the Rocky Mountains in Wyoming are partially forested. Pumas , bobcats and mule deer live in the lower areas of the Rockies , and bighorn sheep and mountain goats in the higher areas . Furthermore, can be found in the mountains mammals like gray squirrels , chipmunks , raccoons , porcupines and skunks in the Yellowstone region also elk , moose , wolves , black and grizzly bears . Beavers were widespread in the Wyoming Mountains until the early 19th century . They were almost exterminated because of their furs. Today they are protected and their population is slowly recovering.
Among the species of deer are wapiti (the name comes from the language of the Blackfoot -Indianer meaning white rump , in English they are called elk (not to be confused with elk ( moose )) referred and mule deer ( mule deer )) is the best-known representatives. In Wyoming there are about 106,000 elk herd (as of 2001) and the largest desert elk herd in the world in the Red Desert. The number of mule deer is likely to be in the hundreds of thousands, with 40,000–50,000 specimens to be found in the Red Desert alone.
The still endangered grizzly bears are mainly found in the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem , where the largest population in the USA lives with 500 to 600 animals (a total of around 1,400 in Montana , Idaho , Washington and Wyoming as opposed to 50,000-100,000 before the discovery of North America or its settlement by Europeans).
The number of bighorn sheep is around 6000 (as of 2004) and that of mountain goats around 100 to 200 specimens. The mountain goats, which predominantly live in and around Yellowstone National Park, pose a problem in that they were not originally native to Wyoming. According to the Yellowstone Park Administration, however, they have settled in here well and threaten the authenticity of the fauna in the region.
Extension of the national territory
Wyoming extends for 450 km between 41 ° N to 45 ° N and a length of 580 km between 104 ° 3 'W to 111 ° 3' W.
Neighbore states
Wyoming is bordered by Montana to the north, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Colorado to the south, and Utah and Idaho to the west . In addition to Colorado, Wyoming is one of only two US states that are bounded exclusively by two degrees of latitude and two degrees of longitude.
Counties
climate
Wyoming has a semi-arid , continental climate that can come up with all kinds of extremes. It is shaped by several geographic factors, which are reflected in different ways in the climatic conditions.
overview
The location of the state in the heart of the North American continent, far away from any large bodies of water that could have a balancing effect on the climate, ensures a strictly continental climate, which is characterized by hot summers, cold winters and low rainfall. The relatively high location of large parts of the country (there are hardly any areas that are less than 1000 m above sea level), paired with southern location (roughly between the 41st and 45th parallel, which in Europe corresponds to the height of central Italy, southern France and northern Spain) and dry air, causes strong temperature fluctuations between day and night. In addition, the Rocky Mountains have a decisive effect : On the one hand, they represent a veritable barrier that shields humid and rainy air masses from the Pacific and thus ensures semi-arid conditions in their rain shadow . On the other hand, their unfolding in a north-south direction enables a more or less unhindered exchange of air masses in parallel. This means that sudden polar cold air inrushes can occur all year round. Thirdly, the mountains also allow exactly the opposite effect: warm downward winds - known as chinooks (comparable to the alpine foehn) - can cause unusually mild temperatures, especially in winter. After all, the location near the jet stream as well as wide, hilly prairie landscapes and plateaus cause rather windy conditions.
detail
Two local climate types can be identified in detail: On the one hand, the extensive prairies, plateaus and basins in the center, east and southwest of Wyoming have a continental steppe climate - such as the Powder River Basin , Bighorn Basin , Great Divide Basin and Green River Basin , which are linked to the largest places ( Casper , Cheyenne , Gillette , Green River , Rawlins , Rock Springs and Sheridan ) also unite a bulk of the population. On the other hand, there is a mountain climate in the mountain ranges and high valleys above 1900 m - this concerns z. B. the Absaroka Range , the Bighorn Mountains , Laramie Mountains , Wind River Range and Wyoming Range , which run in a north-south direction through the state and have several peaks over 4000 m; The entire world-famous Yellowstone National Park, which is consistently over 2000 m, and the south adjoining area of Jackson Hole , which is famous for its winter sports , also fall into this climate range .
Steppe climate
The steppe climate of the prairies is characterized by extremely cold but very dry winters. December, January and February are the driest months of the year; Temperatures drop to an average of −13 to −8 ° C at night, while the maximum daytime values are usually around freezing point or in the slight plus range (typically −1 to +4 ° C) despite the freezing morning frost. Cold waves , which can fall unhindered from the north, occasionally cause significant temperature drops and severe frosts: Then it can cool down to below −30 ° C at night, and temperatures often do not rise above −15 ° C during the day either. Blizzards can also trigger sudden, heavy snowfalls that can paralyze public life. On the other hand, when the warm chinook downwind hits the basins and plains, it can easily reach +15 ° C (even at night); on peak days up to +20 ° C are possible.
In spring and early summer, the temperature increases, so does the humidity. Precipitation can fall on up to ten days a month (this results in between 30 and 65 mm of precipitation, which is rarely achieved in large parts of Central Europe, even in the driest months!). In summer the rain often falls in the form of violent thunderstorms, which discharge over the heated prairies and often bring devastating hail, storms or lightning strikes. In midsummer it gets drier again and temperatures rise to an average maximum of 27 to 33 ° C during the day. At night, however, in most areas it cools down considerably due to altitude, drought and high pressure zones (9-14 ° C); morning frost can occur everywhere except in July and August. On the other hand, heat waves of over 35 ° C are not uncommon, in many places more than 40 ° C have already been measured; this is often accompanied by periods of drought in which there is no precipitation for weeks. In autumn there is again a slight increase in moisture before very dry conditions prevail again with the frost in winter.
Some valleys get so little rainfall in the rain shadow of the Rockies that they can be described as semi-deserts. B. the Bighorn Basin, in which only 130-200 mm of precipitation fall per year.
Mountain climate
In the mountains it is generally cooler and more humid. In the mountain ranges and high valleys, especially in the mountainous and high north-west of the state (with Yellowstone and Jackson Hole), permafrost prevails from early December to late February (e.g. Jackson : night −18, day −4 ° C; to below −40 ° C possible). In contrast to the plains, there is a maximum of precipitation in the winter half of the year, which falls abundantly and mostly in the form of snow. Snow-reliable ski areas in Jackson Hole and the surrounding area benefit from this, as they can accommodate up to 8 m of snow per year. This is due to frequent cloud jams caused by the west wind drift, which shovels humid air masses from the Pacific towards the Rocky Mountains, where they unload their wet cargo.
Until late May, winter and spring fight in the mountain regions, chasing down rain showers, sun and snowstorms. Only in midsummer does drier and warmer weather prevail.
In principle, however, it can snow in locations above 2000 m at any time of the year, including July. The summers are generally very different: sometimes the mountain valleys are constantly hit by violent thunderstorms, including hail, storms, lightning and heavy rain, then again it is very dry and sunny; in some years the summer is very cool (in the town of Jackson there are summers in which temperatures never exceed 25 ° C), in others it is almost hot (in Jackson, for example, up to 36 ° C were measured). There is morning frost practically every summer.
Weather extremes
The strongly continental character of Wyoming's climate, coupled with local conditions, leads to frequent weather extremes. In the winter months, these are mainly blizzards that fall from the north and can paralyze public life through freezing rain and heavy snowfall. Except in midsummer, there is always a risk of blizzards. Opposite the blizzards are the extremes of summer: Weeks of shimmering heat and without any precipitation regularly hit agriculture heavily, as do the violent (hail) thunderstorms that come down in large numbers. The southeast of the state is also in the catchment area of tornadoes , which occur significantly less frequently and destructively than in the prairies further south, but still sweep across the country again and again. A weather phenomenon that occurs regardless of the season is considerable temperature drops. While the day and night fluctuations can be considerable (up to 30 ° C), air mass changes or other wind phenomena (blizzards, chinook ) cause temperatures to rise or fall enormously within a few hours. Temperature fluctuations of up to 40 ° C within 24 hours have already been observed.
The lowest temperature ever recorded in Wyoming is −54.4 ° C (= −66 ° F ). This record comes from two places, Riverside (2177 m) in the south of the state and Moran (2057 m) in the northwest near Yellowstone Park, the coldest continuously inhabited place in Wyoming, and was measured on February 9, 1933. Since then, similarly low values have only been achieved in the Yellowstone area (−54 ° C). The highest temperature was registered in the town of Basin in the semi-desert Bighorn Basin in the northern center, which is generally known as hot and dry: it was 46.7 ° C (= 116 ° F) on August 8, 1983.
population
| Population development | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Residents | ± in% | |
| 1870 | 9.118 | - | |
| 1880 | 20.789 | 128% | |
| 1890 | 62.555 | 200.9% | |
| 1900 | 92.531 | 47.9% | |
| 1910 | 145.965 | 57.7% | |
| 1920 | 194,402 | 33.2% | |
| 1930 | 225.565 | 16% | |
| 1940 | 250.742 | 11.2% | |
| 1950 | 290.529 | 15.9% | |
| 1960 | 330.066 | 13.6% | |
| 1970 | 332,416 | 0.7% | |
| 1980 | 469,557 | 41.3% | |
| 1990 | 453,588 | -3.4% | |
| 2000 | 493.782 | 8.9% | |
| 2010 | 563.626 | 14.1% | |
| 2017 estimate | 579.315 | 2.8% | |
| Before 1900
1900-1990 2000 |
|||
Wyoming has been the least populous state in the United States since 1985, previously it was Alaska. In 2005 the population of Wyoming was estimated at 509,294. This would have increased the number by 3,407 people within one year, which corresponds to a population growth of 0.7 percent. Since the 2000 census , the population has risen by 12,165 due to a higher birth than death rate and 4,035 due to higher immigration than emigration. In 2004 the proportion of foreigners was 11,000 (2.2 percent).
In 2000, 88.9 percent of the population were white, 6.4 percent Hispanic , 2.3 percent Native American, 0.8 percent African American, 0.6 percent Asian, and 2.5 percent other. 1.8 percent belonged to multiple races . Over a quarter of the population (25.9 percent) had German ancestors, 15.9 percent English , 13.3 percent Irish , 6.5 percent American and 4.3 percent Norwegian .
The area was very sparsely populated even before the white immigrants, which is mainly due to unfavorable geographical and climatic factors. The currently around 12,000 Native Americans in Wyoming mainly belong to the two tribes of the Cheyenne and Arapaho . Almost the entire indigenous population lives in the state's only reservation in the western center, in the Wind River Indian Reservation , which is the seventh largest reservation in the USA with an area of 9148 km².
Religions
In 2014, a 2014 survey by the Pew Research Center in Wyoming revealed that 71% of residents were Christians. Christians are divided into Protestants (43%, of which 27% are evangelicals and 16% mainline Protestants ), Catholics (14%), Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints / Mormons (9%), Jehovah's Witnesses (3%) and smaller churches. Non-Christian denominations together belong to 3%, with only Buddhism above 1%. 26% said they had no faith, of which 3% each described themselves as atheists and agnostics . 20% did not assign themselves to any definition.
education
Wyoming has a total of eight colleges : Casper College , Central Wyoming College , Eastern Wyoming College , Laramie County Community College , Northwest College , Sheridan College , Western Wyoming Community College , Wyoming Technical Institute .
The University of Wyoming at Laramie is the only university in the state.
Biggest cities
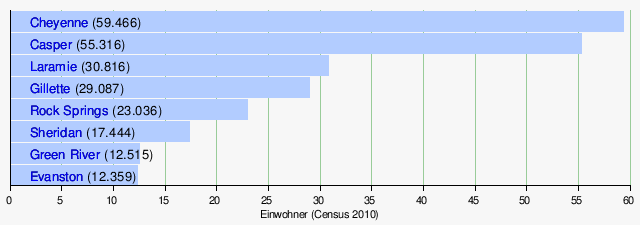
With Cheyenne and Laramie, two of the largest cities belong to the Front Range or Front Range Urban Corridor . This settlement band below the easternmost mountain range of the Rocky Mountains has its focus with Denver and Colorado Springs in the state of Colorado, but extends in the north to Cheyenne.
The small town of Cody is approximately 25 miles east of Yellowstone National Park. It houses a Buffalo Bill Museum, which is in memory of William Frederick 'Buffalo Bill' Cody (1846-1917). Buffalo Bill co-founded the town of Cody in the late 19th century.
history
By the end of the 19th century, Wyoming was largely inhabited by Indians of the following tribes : Absarokee , Arapaho , Bannock , Cheyenne , Lakota , Pawnee , northern and eastern Shoshone and Ute . As the whites advanced further and further west from the east, the Wyoming Indian tribes came under increasing pressure.
With the exception of the southwest, Wyoming was part of the French colony of Louisiana since the late 17th century . In 1762 the territory went to Spain, and in 1800 again to France. Three years later, with the Louisiana Purchase , the United States acquired the Louisiana Colony for $ 15 million. The southwest part belonged to Utah first .
At the end of the 18th century, French trappers may have been the first whites to penetrate the Wyoming area in the north, but John Colter's voyages to the Yellowstone area in 1807 are only certain . Hardly anyone believed his reports of geysers and other hot springs . Twenty years later, Jim Bridger was exploring the South Pass over the Rockies. This route became part of the Oregon Trail from 1841 , which was used by many pioneers to venture west. Along the trail, many forts sprang up in a short time , in Wyoming for example Fort Laramie (1834) and Fort Bridger (1843). In 1850, Bridger also discovered the Bridger Pass , which the Union Pacific Railroad used for its railway line from 1868 . After Wyoming was opened up by rail, the railroad company designated the first cities such as Cheyenne, Laramie , Rawlins , Rock Springs and Evanston . In the 20th century, a highway was built over the Bridger Pass, Interstate 80 .
After the Union Pacific Railroad reached what is now Cheyenne in 1867, the number of whites in Wyoming rose steadily. On July 25, 1868, they founded the Wyoming Territory . In contrast to the neighboring states of Montana, South Dakota and Colorado, Wyoming never experienced a sudden increase in population due to larger precious metal discoveries such as gold and silver. Only copper was found in various parts of Wyoming.
The Wyoming Territory (which later became the state) became the first US territory to have women's suffrage in 1869 . Wyoming had the first female justice of the peace and in 1925 with Nellie Tayloe Ross the first female governor (Prime Minister) of a US state.
In 1872 the US government established the world's first national park , Yellowstone National Park, 96 percent of which is in Wyoming.
In the 19th century, many Wyoming Indian tribes waged a desperate defensive war against the incoming whites. The allies Lakota, Arapaho and Cheyenne won some skirmishes and battles over troops of the US Army - the most famous victory they won from the Battle of Little Bighorn (1876) - but towards the end of the 19th century they had to face the overwhelming forces of the White capitulate. A major factor was that the whites systematically shot the bison and thus deprived the Indians of their livelihood. One of those who excelled in bison hunting was William Frederick Cody , better known as Buffalo Bill . By the late 19th century, all Wyoming Indians lived on Indian reservations , mostly outside Wyoming. In Wyoming only the Wind River Reservation was established, which is inhabited by the eastern Shoshone and the northern Arapaho.
On July 10, 1890, the state became the 44th annexed to the United States. Wyoming insisted that the unrestricted right to vote for women, which had existed there since 1869, should continue. The US Congress wanted to abolish this in the course of Wyoming's admission as the 44th state of the USA. In 1892, after land disputes between whites, the Johnson County War broke out .
politics
Wyoming's first constitution, dating from 1890, is still in force. At the head of the executive is the governor , who is directly elected for four years. The legislative Wyoming ( Wyoming Legislature ) consists of a Senate with 30 and a House of Representatives with 60 members. Depending on its population, the state sends one representative to the House of Representatives and, like all states, two senators to the Senate . He provides three electors in presidential elections .
Wyoming is considered to be one of the most conservative and nationally one of the most reliable Republican voting states in the United States. Wyoming has not voted for a Democratic presidential candidate since 1964 . In the 2004 presidential election, George W. Bush was the third largest electoral success with 69% of the vote. Bush's Vice President Dick Cheney grew up in Casper, Wyoming, and represented the state in Congress from 1979 to 1989 .
However, since 1975 the governorship has been predominantly occupied by Democrats. Long-time governor Dave Freudenthal was elected in 2002 and 2006 and had one of the highest approval ratings in the country. When he was not allowed to run again after two terms, he was replaced in January 2011 by Republican Matt Mead , who was re-elected in 2014. Mead was replaced in 2019 by Mark Gordon , who is also a Republican.
Wyoming is represented in Congress by Senators Mike Enzi and John Barrasso and MP Liz Cheney ; all of them are Republicans.
congress
Governors
Culture and sights
National parks
| National park | location | view | |
|---|---|---|---|
Grand Teton National Park
Commons : Grand Teton National Park - Pictures
|
|

|
|
|
Yellowstone National Park
Commons : Yellowstone National Park Pictures
|
|

|
Natural monuments
| Natural monument | location | view | |
|---|---|---|---|
Devils Tower National Monument
Commons : Devils Tower National Monument - Pictures
|
|

|
|
Fossil Butte National Monument
Commons : Fossil Butte National Monument - Pictures
|
|

|
State parks
Sports
Due to its small population, Wyoming lacks large professional sports teams. Some of the most popular sports teams in the state are the University of Wyoming's 17 college sports teams in the National Collegiate Athletic Association . The university teams are the cowboys or cowgirls and are members of the Mountain West Conference (in basketball , cross country , American football , golf , soccer , softball , athletics , tennis and volleyball ), Western Athletic Conference (in swimming ) and the Big 12 Conference ( wrestling ). Their sports facilities are located in Laramie at about 2,200 m above sea level.
Rodeo is also very popular in Wyoming , with the College National Finals Rodeo taking place in Casper since 2001 .
State symbols
The following symbols are considered state landmarks of Wyoming:
| Surname | image | Recorded as a landmark |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| tree |
American black poplar ( Populus sargentii ) |
 |
February 1, 1947 |
| flower |
Indian paintbrush ( Castilleja linariaefolia ) |
 |
January 31, 1917 |
| dinosaur | Triceratops |  |
March 18, 1994 |
| fish |
Cutthroat Trout ( Oncorhynchus clarki ) |
 |
February 18, 1987 |
| fossil | Knightia |  |
February 18, 1987 |
| grass |
Western wheatgrass ( Pascopyrum smithii ) |
 |
2007 |
| insect |
Sheridan's Green Hairstreak ( Callophrys sheridanii ) |
 |
July 1, 2009 |
| Minerals, rocks and precious stones | Nephrite or jade |  |
January 25, 1967 |
| Dollar coin | Sacagawea dollar |  |
March 2, 2004 |
| reptile |
Great short-horned toad lizard ( Phrynosoma hernandesi ) |
 |
February 18, 1993 |
| mammal |
American bison ( bison bison ) |
 |
February 23, 1985 |
| sport | rodeo |  |
2003 |
| bird |
Western larkbird ( Sturnella neglecta ) |
 |
February 5, 1927 |
Economy and Infrastructure
The real gross domestic product per capita real GDP was USD 64,659 in 2016 (national average of the 50 US states: USD 57,118; national ranking: 9). The unemployment rate was 4.5% in November 2017 (national average: 4.1%).
Historically, cattle and sheep raising were the main industries in Wyoming and are still an important part of the culture and way of life. The most important branch of the economy today, however, is mining (above all crude oil, natural gas, coal, salt, uranium, iron ore, Trona and, in the past ten years, increased methane production). Thanks to artificial irrigation, some wheat, beans and sugar beet are grown. Tourism plays an important role , especially in the Rocky Mountains , the two national parks and the National Monuments .
The largest airport in Wyoming is Jackson Hole Airport . Three interstate highways ( 25 , 80 and 90 ) as well as the interstate 180 and thirteen United States highways run through Wyoming .
military
The Francis E. Warren Air Force Base with the headquarters of the Twentieth Air Force is located near Cheyenne . The Francis E. Warren Air Force Base is also based on three seasons Minuteman III of the 90th Missile Wing of the US Air Force . She supervises 150 held in constant readiness nuclear intercontinental ballistic missiles of the type Minuteman III , whose stationing space over the southeastern Wyoming, the western Nebraska and northern Colorado extends.
literature
- John Gottberg: Hidden Wyoming. Ulysses Press, Berkeley 1999, ISBN 1-56975-175-7 .
- TA Larson: History of Wyoming. 2nd, improved edition. University of Nebraska, Lincoln 1990, ISBN 0-8032-7936-1 .
Web links
- Official website (English).
- US Census (Engl.)
- Atlas of Wyoming (Engl.)
Individual evidence
- ↑ List of us states population estimates from April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2012 by the US Census Bureau
- ↑ USA: States and Major Cities - Population Statistics, Maps, Charts, Weather and Web Information. Retrieved February 8, 2018 .
- ↑ CIA World Factbook
- ↑ US Census Estimates ( Memento of December 8, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ US Census Bureau _ Census of Population and Housing . Retrieved February 28, 2011.
- ↑ Extract from Census.gov . Retrieved February 28, 2011.
- ↑ Excerpt from factfinder.census.gov . Retrieved February 28, 2011.
- ^ Pew Forum: Religious Landscape Study Wyoming
- ^ Official website of the Wyoming Cowboys & Cowgirls. Accessed December 25, 2018 .
- ↑ Wyoming Facts and Symbols. In: wyo.gov. State of Wyoming, accessed December 25, 2018 .
Coordinates: 43 ° 5 ′ N , 107 ° 28 ′ W














