Rocky mountains
| Rocky mountains | |
|---|---|
|
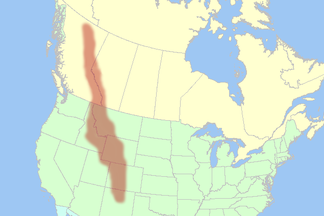
actual Rocky Mountains in Canada and the USA |
|
|
View of the Rocky Mountains in Montana from an airplane |
|
| Highest peak | Mount Elbert (highest peak of the actual Rocky Mountains) ( 4401 m ) |
| location | USA , Canada |
| Coordinates | 44 ° N , 111 ° W |
| Type | Fold Mountains |
The Rocky Mountains [ ˌɹɒkiˈmaʊntənz ] (German, but also outdated rocky mountains , colloquially also known as the Rockies ) are extensive folded mountains in western North America . The mountains extend, depending on the definition, over 4,500-5,000 km from New Mexico through the continental United States to Canada and form one of the major geographic provinces of the United States .
The Coast Mountains , the Cascade Range and the Sierra Nevada do not belong to the Rocky Mountains . At 4401 m, Mount Elbert in Colorado is the highest mountain in the Rocky Mountains.
The Rocky Mountains are part of the Cordilleras that stretch from Tierra del Fuego to Alaska . They are home to major national parks such as Yellowstone National Park and various winter sports centers . They are also rich in natural resources. The region of the US states located in the Rocky Mountains is called the Mountain States .
Geology and geography

Huge mountains formed in North America as early as 600–750 million years ago, but they were almost completely eroded again in the following 400 million years. Only a few rock masses in the south still come from that past time.
Today's rocky mountain range originated for the most part during what geologists call the laramic orogeny , which began around 70 million years ago and ended around 30–40 million years ago. After the mountains were about as high as the Himalayas today, parts of Northwest America began to stretch and large parts of the crust in the southwest of the mountain plateau were subject to a strong stretching process, which caused them to break up into mountain ranges, plateaus and valleys. This area is now known as the Basin and Range Province and includes the Great Basin Desert and neighboring regions.
Between the end of the Pleistocene and the Holocene (70,000–11,000 years ago) the Rocky Mountains were largely glaciated.
The Rocky Mountains consist for the most part of metamorphic and igneous rock . Younger sedimentary rocks can also be found at the edges of the southern Rocky Mountains, and volcanogenic rocks from the Tertiary can be found in the San Juan Mountains and other areas .
The width (east-west extension) of the mountain ranges varies greatly. The widest are the Rocky Mountains in the US state of Colorado with 500–600 km. From the Yellowstone area to the north they split into several mountain ranges, some with narrow widths of 50 to 120 km.
On average, the Rocky Mountains are 2000-3000 meters high. The highest mountains of the Rocky Mountains can be found in the area of the US state Colorado and its direct neighbors, where there are many peaks over 4000 m. From Glacier National Park to the north, the peaks are increasingly glaciated. Also in the northern half are partly extensive plateaus - the largest is the Great Divide Basin - which are bordered by parallel mountain ranges. In the southern part, the mountain forms mostly have rounded erosion forms.
In the area of the Yellowstone National Park , the earth's crust is sometimes very thinned out and permeated with magmatic layers. Thousands of volcanic objects such as geysers and hot springs can be found there .
Rivers
The North American watershed (Continental Divide) runs along the Rocky Mountains . The rivers that arise in the Rocky Mountains eventually flow into three different oceans : the Atlantic Ocean , the Pacific Ocean and the Arctic Ocean . The 2,444-meter-high Triple Divide Peak in Glacier National Park is the watershed point from which rainfall drains into all three seas.
The following major rivers have their source in the Rocky Mountains:
climate
In the Rocky Mountains there is often a westerly wind that drives the clouds up from the Pacific, causing them to accumulate and rain down. This results in above-average rainfall for the Pacific coast and drought for the Great Plains behind . The weather in the Rocky Mountains themselves is therefore mostly cloudy. An exception is the Yellowstone area, where there can be weeks of fine weather.
The climate of the Rocky Mountains is typical of the mountain country. The average temperature is around 6 ° C. At 28 ° C, July is the hottest month, and January is the coldest at −14 ° C. The annual precipitation is estimated at 36 cm.
Summers in the Rocky Mountains are warm and dry with 15 ° C and 15 cm of precipitation. In July there was an average of 18 hours of thunderstorm. The thunderstorms often lead to forest fires, especially in August.
The winter, on the other hand, is very cold and wet, with −2 ° C and 29 cm of precipitation. Snow layers of five to six meters are not uncommon; in the north they can be as much as 15-18 meters. However, warm air masses sometimes penetrate inland from the Pacific in winter. This wind is called a chinook and can cause sudden temperature rises of 20-25 ° C.
Effects of climate change
For several years now, forest decline has been taking on alarming proportions across the Rocky Mountains. The reason for this is a massive increase in pests that benefit from the milder climate. Conifers, which are attacked by the mountain pine beetle, are particularly affected . Although this does not kill the trees, it does bring in a fungus that prevents the water from moving upwards so that the trees dry up. When trees are felled, the dark tissue areas destroyed by the fungus can be clearly seen between the light heartwood and the bark. In the Rocky Mountain National Park (Colorado) the dead trees have already been removed from the campsites for safety reasons, so that pioneer plants ( willowherb , thistles, but also real wild roses) can spread there. This attracts z. As moose and elk in the immediate vicinity of the tourists.
Because of the huge areas and the known dangers of pesticides on the ecosystem, no countermeasures are currently being taken.
vegetation

The vegetation of the Rocky Mountains can be divided into several height-specific levels. The first two stages are characterized by sandy soils and precipitation of around 500 mm. There are hardly any dense forests, instead there are isolated trees with strong undergrowth. The lowest level at 1500–2200 m is dominated by various juniper ( Utah and lonely juniper ) and pine species ( Colorado fir , coastal pine ), the following level up to 2700 m by yellow pines and Gambel oaks . Subalpine larches are also common between 1800 and 2400 m .
From the third level (2700–3200 m) the trees become denser and the undergrowth decreases. Therefore, the northern, higher Rocky Mountains are significantly more densely forested than the southern, which are often overgrown with grass up to the top. The precipitation on this level is about half greater than on the two lower levels. Here are frequently Douglas , American aspen and Colorado fir to find.
The fourth stage extends to the tree line at around 3800 m. The trees there grow less in height and the forests are separating. The most common tree species at this level are Engelmann , blue and white spruce , rock fir, and Nevada and awning pines .
On the last stage, the alpine tundra, small plants such as shrubs, bushes, flowers and grasses grow. Willow species (for example arctic willows ) are particularly common here . The shrubs are dominated by buttercups ( Ranunculus adoneus ), common herbs ( Erigeron simplex ), predatory leaves ( Eritrichum aretioides ) and thick-leaf plants ( Rhodiola integrifolia ); in the case of the grasses alpine panicle grass and turf smear .
History of human settlement
Towards the end of the last great ice age, an ice-free corridor opened between the glaciers of the Rocky Mountains and the Laurentide Ice Sheet . In climate history and paleontology , it is discussed whether and from when the corridor was passable for game and people following it. It is considered to be a possible migration route for people to the interior of the continent when settling America .
With the further retreat of the glaciers, Indian peoples inhabited the Rocky Mountains. At the time of the conquest of North America by European colonists, the Absarokee , Apaches , Arapaho , Bannock , Blackfoot , Cheyenne , Flathead , Lakota , Shoshone and Ute lived temporarily or permanently in the Rocky Mountains or the plateaus in between. Many of these peoples moved to the plains in autumn and winter to live on bison and other large game, and in spring and summer to the mountains where they caught fish, hunted game, and picked berries and roots.
From 1720, the first white trappers, hunters and mineral seekers invaded the Rocky Mountains. Soon the mountains were known as a rich fur area. Fur trading companies like the Hudson's Bay Company and the North West Company in Canada as well as the American Fur Company and the Missouri Fur Company (later: Rocky Mountains Fur Company) in the USA fought doggedly for supremacy in the Rocky Mountains. The Rocky Mountains' white pioneers included William Henry Ashley , Jim Bridger , Kit Carson , John Colter , Thomas Fitzpatrick , Andrew Henry , Jedediah Smith and David Thompson . In 1793, Alexander MacKenzie of the Hudson's Bay Company became the first white man to cross the Rocky Mountains. His route led from Fort Chipewyan over the Peace and Fraser Rivers to what is now Vancouver . The Lewis and Clark Expedition from 1804 to 1806 was the first scientific expedition over the mountains. Botanists, zoologists, geologists, and other professionals gathered initial data on the Rocky Mountains. The expedition was the prelude to the conquest of the west of North America. In the spring of 1824 Jedediah Smith discovered the South Pass in what is now Wyoming, a passage in the middle Rocky Mountains that can be crossed by cargo caravans and covered wagons. The pass became the central point of all trade and settlement flows in the settlement of the American West between 1830 and 1869.
In 1847 the Mormons began to settle near the Great Salt Lake . Gold was found in Colorado in 1858. As a result, the whites opened up the area, built a transcontinental railroad and opened Yellowstone, the world's first national park . More and more white settlers settled in the valleys and mining towns and displaced the Indian peoples into reservations . Towards the end of the 19th century, other areas in the Rocky Mountains were placed under protection. The US government defined mining, logging, agricultural and recreational zones. Camps and tent sites became forts and farms and ultimately villages and towns.
Tourism and industry
Mining and tourism are the major industries in the Rocky Mountains. There is also cattle, forest and some agriculture.
Mining
Valuable minerals such as lead , gold , copper , molybdenum , silver , tungsten and zinc have been found in the Rocky Mountains . The plateaus in between also contain coal , natural gas , crude oil and oil shale .
The Climax mine near Leadville , Colorado was the world's largest producer of molybdenum for over 100 years (1879–1986). Molybdenum is used as an alloying element for heat-resistant steel, for example in turbines and power plants. The Climax mine once employed over 3,000 workers. The Coeur d'Alene mine in Northern Idaho produces silver, lead and zinc. Canada's largest coal mine is located in Crowsnest Coal Field near Sparwood and Elkford, British Columbia, and there are coal mines near Hinton , Alberta.
The mining of mineral resources led to contaminated and polluted waters and soils in many places in the Rocky Mountains.
tourism
With an average of four people per square kilometer, the population density of the Rocky Mountains is fairly low and there are few cities with more than 50,000 inhabitants. Nevertheless, the mountains are a popular holiday destination for people who either enjoy the landscape or want to do sports. Several million tourists travel to the Rocky Mountains every year. In summer the most popular attractions in the USA are Pikes Peak , Royal Gorge , Rocky Mountain National Park , Yellowstone National Park , Grand Teton National Park and Glacier National Park and in Canada Waterton Lakes National Park , Banff National Park , Jasper National Park National Park , Yoho National Park , Kootenay National Park , Mount Revelstoke National Park and Glacier National Park and Mount Robson Provincial Park . Mount Revelstoke National Park and Glacier National Park are located west of the actual Rocky Mountains in the Columbia Mountains, separated by the broad Rocky Mountain Trench through which the Columbia River flows. In winter, on the other hand, skiing is the main attraction. The main ski areas are Aspen , Vail , Keystone , Breckenridge and Copper Mountain in Colorado ; Alta , Park City, and Snowbird , Utah ; Sun Valley , Idaho ; Whitefish Mountain Resort (formerly Big Mountain) and Big Sky in Montana ; Lake Louise and Sunshine Village in Alberta , and Fernie and Whistler in British Columbia .
See also
Web links
- Rocky Mountains ( English, French ) In: The Canadian Encyclopedia .
- Blue Plant Biomes: Plants, Animals, Climate ( Memento from August 12, 2006 in the Internet Archive )
- Thomas J. Stohlgren: Rocky Mountains (PDF; 3.7 MB), US Geological Survey: Geology, Vegetation Zones (English)
- US Geological Survey: Geology (English)
- Bark beetle spread: US Department of Agriculture 2009: Maps showing the spread of the beetle over the last 15 years
- Photos of forest dieback in the Rocky Mountains National Park / Colorado, USA