Minnesota
| Minnesota | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
| List of states | |||||
| Capital: | Saint Paul | ||||
| State motto: | L'Étoile du Nord ( French : "Star of the North") | ||||
| Surface: | 225,171 km² | ||||
| Residents: | 5,519,952 (estimated in 2016) (23 inhabitants / km²) | ||||
| Member since: | May 11, 1858 | ||||
| Time zone: | UTC − 6 (CST) or UTC − 5 (CDT) | ||||
| The highest point: | 701 m ( Eagle Mountain ) | ||||
| Average Height: | 365 m | ||||
| Deepest point: | 183 m ( Upper Lake ) | ||||
| Governor : | Tim Walz ( DFL ) | ||||
| Post / Office / ISO : | MN / MN / US-MN | ||||
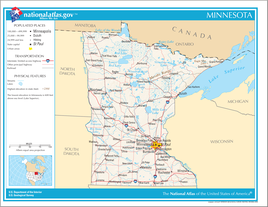
| Map of Minnesota | |||||
| General Geographic Map of Minnesota | |||||
Minnesota (pronunciation [ ˌmɪnɪˈsoʊ̯ɾə ] ; from Mnísota "cloudy water" from the Sioux language Dakota; abbreviation: MN or Minn.) Is the 32nd state of the United States of America . The twelfth largest US state in terms of area is located in the north of the country on the border with Canada . It was created in 1858 from the eastern part of the Minnesota Territory and a small part of the Wisconsin Territory .
More than half of Minnesota's population lives in the metropolitan area of Minneapolis-Saint Paul ( Twin Cities ) , with Minneapolis being the most populous city in the state with just under 383,000 inhabitants. St. Paul - as the second largest city with approx. 285,000 inhabitants - is the capital. Some large, internationally active companies have their headquarters in the twin cities. The largest shopping center in the USA, the Mall of America , is also located in that metropolitan area, namely in the city of Bloomington .
Minnesota bears - derived from its state motto ("L'Étoile du Nord", French for "Star of the North") - the nickname North Star State ( English " North Star State "). Another nickname for the state is The Gopher State . Gopher is the name given to the thirteen-striped croissant that is widespread there, in particular in Minnesota , which was initially only the namesake and mascot of most of the sports teams at the University of Minnesota (" Golden Gophers ") and only later became the name for the entire state. Despite two legislative initiatives, the chipmunk did not become Minnesota's official heraldic animal. Because of its many lakes , Minnesota is also known as the “Land of Ten Thousand Lakes”.
geography
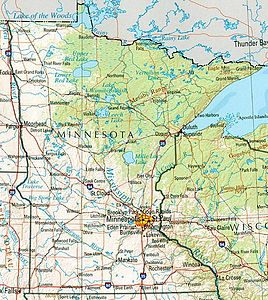
Minnesota is the northernmost state in the USA after Alaska , the so-called Northwest Angle is the only part of the 48 contiguous states that extends north beyond the 49th parallel. The northeast of the state lies on the shores of Lake Superior and shares maritime borders with the Canadian province of Ontario and the states of Michigan and Wisconsin . Wisconsin borders the east and south-east of Minnesota, the south Iowa , the west North and South Dakota and the north the Canadian provinces Ontario and Manitoba . At 225,171 square kilometers (about 2.25 percent of the total area), Minnesota is the twelfth largest state in the United States and the second largest in the Midwest . The extension in north-south direction is around 660 kilometers, in east-west direction around 560 kilometers.
Geology and landscape
Minnesota has some of the oldest rocks on earth; some gneisses are up to 3.6 billion years old. About two billion years ago, lava was able to escape through cracks in the primordial ocean. The remaining parts of the volcanic rock formed the Canadian Shield in northeast Minnesota. After the volcanic activity that lasted until 1.1 billion years ago, the geological activity was relatively low. Since then , volcanism , orogeny, and earthquake activity have occurred to an extremely minor extent.
The foothills of the volcanic mountains formed lakes in northern Minnesota during the Precambrian . These lakes caused a flattening of Minnesota which intensified with the glaciation that began 600,000 years ago. Glaciers at least a kilometer thick moved over the areas, shaping Minnesota's current landscape. The last of four major glaciers, the Wisconsin Glacier , retreated from Minnesota 12,000 years ago. The extent of these glaciers extended over all of Minnesota with the exception of the outer southwest and southeast.
The glaciers left a bed of bedload, typically at least 15 meters, across the state. When the last glaciers had retreated, the huge Lake Agassiz formed in the northwest ; the outflow of this lake formed the course of the Minnesota River and the bottom of the lake became the fertile land of the Red River Valley . There is little geological activity in Minnesota these days. Earthquakes occur irregularly, but they are mostly weak. The strongest earthquake of the last century occurred near Morris in 1975 and was measured with 4.6 to 4.8 magnitudes on the Richter scale.
The highest point in the state is Eagle Mountain at 701 meters, which is only about 21 kilometers from the lowest point at 183 meters on the shores of Lake Superior. Precipitation can drain into the Gulf of Mexico via the Mississippi River , into the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence Seaway, or into the Arctic Ocean via Hudson Bay .
The nickname of the state Land of 10,000 Lakes (German: "The Land of 10,000 Lakes") is no exaggeration. Minnesota has 11,842 lakes spanning over four acres. With almost 3900 km², the Upper Lake has the largest water surface and about 393 meters the greatest water depth in the state. Minnesota has 6,564 rivers with a total length of approximately 110,000 kilometers. The Mississippi River begins at Lake Itasca and crosses the border with Iowa after just 1090 kilometers downstream. In his lead at Fort Snelling the Minnesota River in Hastings the St. Croix River in Wabasha of the Chippewa River and many other small streams in the southeast. Over the Red River , on the former bottom of the Agassizsee , the water of the northwest of the state flows north into the Canadian Hudson Bay .
Protected areas
Minnesota has 66 state parks, 57 state forests with an area of approximately 16,000 km² and numerous nature reserves. The first state park, Itasca State Park , was established in 1891. The two national forests, Chippewa National Forest and Superior National Forest, extend over an area of 22,200 km² . In the Superior National Forest , on the northeastern border of the state, lies the Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness , which covers over 4000 km² and a thousand lakes. The Voyageurs National Park is the only national park in the state. There are also two National Monuments : Pipestone National Monument preserves the quarries where Plains Indians mined the stone for their pipes and still win today, and Grand Portage National Monument is a memorial for the history of the fur trade at a trading post on Lake Superior .
Flora and fauna
The vegetation of Minnesota largely corresponds to that of North America: prairie grasslands in the west and southwest of the state, deciduous forest in the southeast and the northern boreal forests . The northern coniferous forests are vast areas overgrown with pines and spruces with occasional birch and poplar trees. Much of the northern Minnesota forest has been cut down. Only a few areas such as the Chippewa National Forrest and the Superior National Forest , which is home to 1,620 km² of unearthed forest, are originally overgrown. As a result of the regrowth, the state's forest cover is back at around a third.
Although numerous native animals such as spruce marten , elk , buffalo , puma , reindeer and bobcat have lost large parts of their habitat due to the destruction of nature , numerous other native animal species are thriving. Minnesota has the second largest wolf population in the United States after Alaska and has healthy black bear , moose , and white-tailed deer populations . On the Mississippi Flyway, the state is home to migrating waterfowl such as geese and ducks, as well as wild birds such as grouse , pheasant and turkey . Minnesota is also home to birds of prey such as the bald eagle , the red-tailed buzzard and the snowy owl . In the lakes there are numerous eyeglasses , striped bass , muskellungen and European pike . The rivers in the southeast are populated by brook trout , brown trout and rainbow trout .
climate
Minnesota has a continental climate . The winters, with temperatures well below zero degrees Celsius, are more polar, Minnesota is the coldest state after Alaska. The summers, on the other hand, are hot and humid, especially in the south of the state. Cold air inrushes and blizzards can occur throughout winter . The annual mean temperature is two to eight degrees Celsius. According to the Köppen / Geiger climate classification , the southern part of the state falls into the humid continental climate with hot summers (Dfa), the northern two thirds are assigned to the humid continental climate with warm summers (Dfb).
The regions in the northeast are also influenced by the balancing effect of the Upper Lake. This means that the winter temperatures are comparatively moderate for the region, while the lake has a cooling effect in summer.
Depending on the location, annual precipitation ranges from around 480 mm in the north-west to 860 mm in the south-east, with droughts occurring roughly every ten to 50 years. The growing season varies from 90 days in the Iron Range to 160 days in southeast Minnesota near the Mississippi. Southern Minnesota is part of the Tornado Alley area .
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duluth | −13 | −9 | −4 | 4th | 11 | 16 | 19th | 18th | 13 | 7th | −2 | −10 |
| International Falls | −16 | −12 | −4 | 4th | 12 | 17th | 19th | 18th | 12 | 6th | −4 | −13 |
| Rochester | −11 | −8 | −1 | 7th | 14th | 19th | 21st | 20th | 15th | 8th | −1 | −8 |
| Twin cities | −11 | −7 | 0 | 8th | 15th | 20th | 23 | 22nd | 16 | 9 | 0 | −7 |
structure
Minnesota is divided into 87 counties.
history
Aboriginal and Discovery
Before the European colonization, Minnesota was populated by the Anishinabe , Sioux and other indigenous people. In the south-west of the state are the quarries where catlinite , the pipe stone, was and is extracted. It was traded throughout the Great Plains and all the Plains Indians preferred it to carve the heads of their peace pipes (calumets).
The first European settlers were French fur traders who arrived at the beginning of the 17th century. When the Ojibwe Indians later moved further west to Minnesota, tension arose with the Sioux. Explorers such as Daniel Greysolon, Sieur du Lhut , Louis Hennepin , Jonathan Carver , Henry Schoolcraft and Joseph Nicollet carried out research trips in the area of what is now the state of Minnesota and mapped it. In 1679, after an expedition, Greysolon built a fort on the shores of Lake Superior and from then on claimed the territory of northern Minnesota for France.
As a result of the French and Indian War, France had to cede these areas to Great Britain in 1763. With the Peace of Paris and the Declaration of Independence, the area between the Great Lakes and the Mississippi became part of the Northwest Territory and was part of the United States for the first time. Nevertheless, the region remained strongly influenced by Great Britain until around 1816. With the Louisiana Purchase , the USA also acquired the southern and western areas of what is now Minnesota from France. The first big wave of German immigrants came between 1860 and 1870 and still shape the cultural image of Minnesota today.
Beginning of statehood
In 1805, the explorer and officer Zebulon Pike acquired land at the confluence of the Minnesota and Mississippi rivers . However, it was a few years before the first settlers came to the area. As a result, Fort Snelling was the first permanent settlement to be built between 1819 and 1825 . In addition, soldiers built a water mill and a sawmill at Saint Anthony Falls . As the industry later grew, the city of Minneapolis was formed there . In the meantime, many people had settled near the fort. In 1839 the army forced them to move downstream and they settled in the area that would later become Saint Paul . The Minnesota Territory was founded on March 3, 1849. By 1858, thousands more settlers came to Minnesota. In just under ten years the population had multiplied from 6,000 to more than 170,000. On May 11, 1858, Minnesota was founded from the eastern part of the Minnesota Territory and the western part of the Wisconsin Territory as the 32nd state of the United States of America.
Contracts in which the European settlers bought parts of their territories from the indigenous people, slowly pushed the Sioux and Ojibwe from their land to smaller reserves and increased the settlement and agricultural areas of the European settlers. When living conditions for the Sioux deteriorated, tensions grew and led to the Sioux uprising in 1862 . The result of the six week long war was the execution of 38 Indians, the largest mass execution in US history, in Mankato, and the banishment of most of the remaining Sioux to the Crow Creek Reservation in Nebraska .
Minnesota experienced an economic boom after the end of the Civil War around 1870. The demand for the abundant wood made agriculture and forestry the mainstays of the early population of Minnesota. The sawmills at Saint Anthony Falls and logging camps in St. Croix, Stillwater and Winona produced large quantities of timber. These cities were ideally located on rivers for transportation. Later, the Saint Anthony Falls were used to provide energy for flour mills. Innovations by the millers of Minneapolis led to the production of patent flour , which was considered one of the finest bread flours of its time. In 1900, led by Pillsbury and the Washburn-Crosby Company (a forerunner of General Mills ), 14.1 percent of US grain was milled in Minnesota.
The iron ore mining began with the discovery of large deposits in the north of the state in the 1880s. The ore was transported by rail to Two Harbors and Duluth , then loaded onto ships and transported east across the Great Lakes .
The state in the 20th century
The industrial development and the increasing division of labor caused the population to slowly migrate from rural areas to cities at the beginning of the 20th century. Yet agriculture remained the most important economic factor. The economy was hit hard by the Great Depression, resulting in lower prices for farmers, layoffs of miners, and labor unrest. In addition, western Minnesota and Dakota were hit by droughts from 1931 to 1935 and suffered major crop failures. Only new economic development and trade programs led to a turnaround in the economy. The Civilian Conservation Corps and other programs created work for Indians on their reservations. The Indian Reorganization Act of 1934 allowed Indian tribes to form their own tribal governments, giving them greater weight in the state and greater respect among the population.
After the Second World War, industrial development accelerated. New technologies improved the productivity of the farms by automating the feedlots for pigs and cattle, machine milking on dairy farms and the large-scale rearing of chickens in large halls. Hybrids of maize and grain were used in plant breeding . Agricultural machines such as tractors and combine harvesters were also used from then on. Norman Borlaug associated the concept of the Green Revolution with this development . At the same time, the development of the suburbs accelerated due to the increased need for accommodation and the availability of private means of transport after the war. The higher mobility also made more specialized professions possible. In the period that followed, Minnesota continued to develop into a center of the chemical industry, mechanical engineering, and the aerospace and food industries.
In the 1980s, the issues of the environment and education came to the fore in political action. Educational and transport facilities have been expanded, and progressive measures to protect the environment and control land consumption have been adopted.
Cities

The capital of Minnesota is Saint Paul . It is located in the east of the state on the Mississippi . Together with Minnesota's largest city, Minneapolis , St. Paul forms the Twin Cities, which together with the surrounding areas form the sixteenth largest metropolitan area in the United States of America. Around 60 percent of Minnesota's residents live in this area. The remaining, more rural areas are also known as "Greater Minnesota" or "Outstate Minnesota".
Minnesota has 16 cities with more than 50,000 inhabitants (as of 2010), of which only three ( Rochester , Duluth and St. Cloud ) are outside the metropolitan area of the Twin Cities. Population growth is mainly limited to urban areas. While Sherburne and Scott counties doubled their populations between 1980 and 2000, 40 of Minnesota's 87 counties fell in the same period.

Demographics
population
| Population development | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Residents | ± in% | |
| 1850 | 6077 | - | |
| 1860 | 172.023 | 2,730.7% | |
| 1870 | 439.706 | 155.6% | |
| 1880 | 780.773 | 77.6% | |
| 1890 | 1.310.283 | 67.8% | |
| 1900 | 1,751,394 | 33.7% | |
| 1910 | 2,075,708 | 18.5% | |
| 1920 | 2,387,125 | 15% | |
| 1930 | 2,563,953 | 7.4% | |
| 1940 | 2,792,300 | 8.9% | |
| 1950 | 2,982,483 | 6.8% | |
| 1960 | 3,413,864 | 14.5% | |
| 1970 | 3,804,971 | 11.5% | |
| 1980 | 4,075,970 | 7.1% | |
| 1990 | 4,375,099 | 7.3% | |
| 2000 | 4,919,479 | 12.4% | |
| 2010 | 5,303,925 | 7.8% | |
| Before 1900
1900–1990 2000 + 2010 |
|||
Minnesota's population rose from 6100 in 1850 to 1.75 million in 1900. Within the next six decades, the population grew by 15 percent, so that in 1960 the number had risen to 3.41 million inhabitants. In the years that followed, population growth slowed to around 10 percent per decade. As of April 1, 2010, there were 5,303,925 people in Minnesota, according to the US Census Bureau. Although ethnic minorities make up a significantly smaller proportion of the total population, they have shown above-average growth. 50.4 percent of the population are female, 49.6 percent male.
Minnesota had approximately 71,000 births and approximately 37,500 deaths in 2005. The birth rate was 13.9 / 1000 inhabitants and the death rate 7.3 / 1000 inhabitants. The natural population growth was accordingly 6.6 / 1000 inhabitants. The infant mortality rate was 5.2 deaths per 1,000 births, below the US average of 6.8 per 1,000 births.
ancestry
Over two-thirds of Minnesota's population descended from ancestors in Western Europe. At 34 percent , people of German origin form the largest group, while 15.3 percent are Norwegian , 10.4 percent Irish and 8.0 percent Swedish . (Status 2014) The composition has changed in recent years. Forecasts predict a significantly above-average increase in the black and Hispanic population groups from 9 percent in 2000 to 22 percent in 2030, but also in immigrants from Asia, the Middle East and the areas of the former Soviet Union. In 2010 the population was made up as follows:
- 83.1% white population (Europe)
- 5.2% African American
- 4.7% Hispanic Americans or Latinos
- 4.1% Asian Americans / Pacific Islanders
- 1.1% indigenous people (Indians and Inuit)
- 2.4% multi-ethnic residents
age structure
The age structure of Minnesota is composed as follows (as of 2010):
- 24.2% <18 years
- 62.9% 18-64 years
- 12.9% ≥ 65 years
Religions
According to a survey, the population of Minnesota consists of 25 percent of residents with a Roman Catholic and 24 percent with a Lutheran faith. Smaller Christian groups also follow. Overall, 77 percent of the population have a Christian belief, three percent have a Jewish , Muslim , Buddhist or Hindu belief and 14 percent have none. Six percent gave no answer. The main Lutheran church is the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America with 853,448 members.
Economy and Infrastructure
| gross domestic product | $ 254.97 billion |
| GDP per inhabitant | $ 49,200 |
| Income per capita | $ 41,105 |
| Economic growth | 2.2% |
| Employees | 2,676,350 |
| Unemployed | 260,679 |
| Unemployment rate | 8.9% |
Minnesota's economy has changed dramatically over the past 200 years. At the beginning of the state's history, agriculture, forestry and the trade in goods dominated economic activity. In the course of industrialization , the secondary sector also gained in importance. The region in the northwest around Duluth in particular benefited from the iron ore deposits. As in all industrialized countries, however, the share of the service sector in gross domestic product has continued to rise in Minnesota since the 1950s . Today more than 80 percent of all employees work in it, whereas less than one percent are employed in the primary sector. In the USA, however, the state is still one of the largest producers of agricultural products such as sugar beet , sweet corn and peas .
In 2007 Minnesota's gross domestic product was $ 255 billion. The per capita income was $ 41,105, making it the 12th highest in the United States. The median household income was $ 52,024 (# 11 in the US). The real gross domestic product per capita real GDP - the most important indicator of prosperity - was USD 41,353 in 2007 (national average of the 50 US states: USD 38,020; national ranking: 9th). In the wake of the financial crisis from 2007 onwards , the number of unemployed in Minnesota rose sharply and reached its highest level since 1983.
Thirty-six of the United States’s 1,000 top-selling companies are based in Minnesota, including Target , UnitedHealth Group , 3M , Medtronic and General Mills . Cargill , the largest privately held company in the country , is also based in Minnesota.
Insolvency
On Friday, July 1, 2011, Minnesota became the first American state to default and was unable to pay its bills. As a first episode, the zoo and national parks were closed on Independence Day, July 4th. Road construction ceased and 22,000 government employees took unpaid leave. A good three weeks later, the Democrats and Republicans were able to agree on a restructuring plan and end the budget crisis.
energy
With the Pine Bend Refinery near St. Paul, Minnesota has the largest oil refinery in the states that do not have their own production facilities. This covers around 70 percent of the fuel required by around 27.2 million liters of petrol every day. The rest of the demand is obtained from refineries in other states. Minnesota is also connected to the Lakehead Pipeline and the Minnesota Pipeline . The fuel requirement increases by around two percent every year. In 2006, Minnesota was the first US state to introduce a requirement that ten percent ethanol (E10) must be added to gasoline. In 2013 this figure rose to 20 percent.
Natural gas is mainly used for heating . Over two thirds of all private households use this for heating. Wind energy has also gained in importance over the past few years . The wind turbines, which are mainly located in the southwest ( Coteau des Prairies ), have a total output of up to 812 megawatts. Further plants with an additional output of 82 megawatts are being planned. By 2025, the share of renewable energies is to increase to 25 percent of total electricity consumption.
traffic
The Minnesota Department of Transportation is responsible for transportation in Minnesota . The main hub of automobile traffic is the metropolitan area of Minneapolis-St. Paul. Major Interstate Highways I-35 and I-94 run through the metropolitan area, I-90 runs through the south, along the Iowa border, and connects to I-35 near Albert Lea . In 2006 a law was passed that at least 40 percent of the tax revenue from private automobile traffic should benefit public transport.
There are over 20 rail lines running through the state, primarily for freight transportation to and from Minnesota-St. Paul and Duluth, which has the largest port in the state (Twin Harbor Duluth- Superior ). In addition to shipping traffic across the Mississippi, the Upper Sea in particular is used for shipping. With the Empire Builder from Amtrak several cities in Minnesota and the Midwest are connected in rail-bound passenger.
The largest commercial airport is Minneapolis-St. Paul International Airport , where Delta Air Lines and Sun Country Airlines operate a cargo and passenger hub. It is the tenth largest airport in the United States and handles around 540,000 flight movements annually. The larger airports are Duluth and Rochester Airports, which are connected to the aviation hubs as national airports. There are regional airports in Bemidji , Brainerd , Hibbing, International Falls, St. Cloud and Thief River Falls .
Local public transport is limited to bus transport in some larger cities. Only the Twin Cities since 2004 with an earlier Hiawatha Line -called light rail fitted which runs between Bloomington and downtown Minneapolis and St. Paul. A national bus service is offered by the private operators Greyhound , Jefferson Lines and Coach USA .
Culture
The Twin Cities are considered the cultural center of the Upper Midwest . Well-known museums such as the Weisman Art Museum , the Walker Art Center or the Minneapolis Institute of Arts are located there. With the Saint Paul Chamber Orchestra and the Minnesota Orchestra there are also professional and traditional music ensembles . After New York City, the Twin Cities have the highest per capita density of theaters in the USA. Around 2.3 million theater tickets were sold in more than 30 theaters. The Minnesota State Fair has around 1.7 million visitors annually.
music
Some musicians of different genres achieved national and international renown, such as Atmosphere , Bob Dylan , Hüsker Dü , Jimmy Jam and Terry Lewis , Judy Garland , Low , Motion City Soundtrack , Prince , Soul Asylum , The Andrews Sisters and The Replacements .
literature
The literature of the first half of the 20th century was mainly influenced by the general living situation and the rural life. In addition to Ole Rolvaag , the author Laura Ingalls Wilder achieved great fame. Through the depiction in Our Little Farm she made Walnut Grove the epitome of a typical small town in the American Midwest. Life in the Midwest also played a special role in the novels of authors Sinclair Lewis and Garrison Keillor . Born in St. Paul F. Scott Fitzgerald is regarded as one of the main representatives of American modernism and "Generation Lost" is the so-called ( " Lost Generation ") counted, who turned away in the 1920s from America and went to Europe.
education
One of the first acts of the Minnesota government after the founding of the state was the opening of the first normal school in Winona in 1858. Since 1885 there has been compulsory education. The state is among the best educated in the United States. In a survey by Morgan Quitno for Smartest State Award Minnesota came in 13th with 84 percent of the people who have high school completed, which represents the nation's fifth best value.
Education also includes the numerous public and private higher education institutions. 32 public universities and colleges are united in the Minnesota State Colleges and Universities System , four institutions belong to the University of Minnesota . There are also more than 20 private colleges and universities. With a holdings of over four million books, the University of Minnesota library is one of the largest university libraries in the United States.
health
Minnesota residents are among the healthiest in the United States. The state achieves the best national scores, especially in the areas of child mortality and mortality before the age of 75. Around 91 percent of the population have health insurance. Life expectancy is the second highest of any US state.
Medical care is provided by an extensive network of hospitals and medical practices. The University of Minnesota Medical School , which was particularly successful in research, is of international importance . In addition, Mayo Clinic in Rochester based. It is among the world's most prestigious hospitals and is also working in collaboration with the University of Minnesota in medical research and education also.
politics
The political order of Minnesota is based on the constitution of 1857. The powers are divided into an executive , legislative and judicial branch . At the head of the executive is the governor , who is elected for a four-year term. The legislature is divided into a Senate with 67 senators and a House of Representatives with 134 members. The term of office for the senators is four years, for the members of the House of Representatives two years. The judiciary is divided into three levels: the lowest are the District Courts . These are superordinate to the Courts of Appeals . The highest federal instance is the Minnesota Supreme Court , which consists of seven judges .
Governor of the state has been the Democrat Tim Walz since 2019 , who succeeded the Democrat Mark Dayton, who has been in office since 2011 , after his victory over Jeff Johnson in November 2018 . Deputy Governor (lieutenant governor) is Peggy Flanagan .
| year | Democrats | republican |
|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 46.44% 1,367,825 | 44.93% 1,323,232 |
| 2012 | 52.65% 1,546,167 | 44.96% 1,320,225 |
| 2008 | 54.06% 1,573,354 | 43.82% 1,275,409 |
| 2004 | 51.09% 1,445,014 | 47.61% 1,346,695 |
| 2000 | 47.91% 1,168,266 | 45.50% 1,109,659 |
| 1996 | 51.10% 1,120,438 | 34.96% 766,476 |
| 1992 | 43.48% 1,020,997 | 31.85% 747,841 |
| 1988 | 52.91% 1,109,471 | 45.90% 962,337 |
| 1984 | 49.72% 1,036,364 | 49.54% 1,032,603 |
| 1980 | 46.50% 954,174 | 42.56% 873,241 |
| 1976 | 54.90% 1,070,440 | 42.02% 819,395 |
| 1972 | 46.07% 802,346 | 51.58% 898,269 |
| 1968 | 54.00% 857,738 | 41.46% 658,643 |
| 1964 | 63.76% 991,117 | 36.00% 559,624 |
| 1960 | 50.58% 779,933 | 49.16% 757,915 |
The larger parties include the Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party , which belongs to the Democratic Party at national level, and the Minnesota Republican Party, as well as the Independence Party , which is affiliated to the Reform Party at the national level . With Jesse Ventura, she was able to provide governor from 1998 to 2003, but currently has no representatives in the House of Representatives or Senate. The fourth largest party is the Green Party , which so far has only been able to win mandates at the regional level.
| 2019-2021 | House of Representatives | senate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DFL (Democrats) | 75 | 32 | |
| republican | 55 | 35 | |
| New Republican | 4th | 0 | |
| total | 134 | 67 | |
Minnesota, for many decades a stronghold of populist, agrarian left-wing liberalism similar to that in the Canadian provinces of Manitoba and Saskatchewan , is known for an above-average interest of the population in political events. In the 2004 presidential election , 77.2 percent of the population voted, the highest turnout of any US state. Since the 1976 presidential election, Minnesota’s Democratic presidential candidates have won. Along with the District of Columbia , this was also the only state that incumbent Ronald Reagan could not win in the 1984 election against Walter Mondale . Between 1965 and 1969 with Hubert H. Humphrey and from 1977 to 1981 with Walter Mondale, there were two vice-presidents from Minnesota in the history of the United States .
Today, due to the growth of the conservative suburbs of Minneapolis / St. Paul , Minnesota is considered a Swing State and therefore mostly receives special attention in the presidential election campaign, together with the Swing States Wisconsin and Iowa. When the Electoral College is Minnesota ten electors.
In Congress Minnesota provides two senators and eight members of the House of Representatives . After the Democrats had previously provided the majority of the delegation in the House of Representatives, they had to accept the loss of a district in the 2010 congressional elections , with the two large parties each sending four MPs to the 112th Congress . Since the 2012 elections , the Democrats have again had a 5-3 majority. Senators are currently the Democrats Amy Klobuchar and Tina Smith . A tight election result in the 2008 elections between incumbent Norm Coleman and Al Franken had meant that a confirmed final result was only available almost eight months later and the second seat was initially vacant.
State government
congress
- List of US Senators from Minnesota
- List of members of the US House of Representatives from Minnesota
media
The Twin Cities region is ranked the 15th largest media market in the United States by Nielsen Media Research . In addition, the regions Fargo - Moorhead (in 118th place), Duluth - Superior (137th), Rochester - Mason City - Austin (152nd) and Mankato (200th) are among the largest nationally listed media markets.
The first television program in Minnesota began broadcasting on April 27, 1948, when KSTP-TV began broadcasting. Today, the Hubbard Broadcasting Corporation , to which KSTP belongs, is the only TV company based in Minnesota. In addition to a TV station, KSTP also operates the radio station KSTP KS95 (official KSTP-FM KS95)
The Twin Cities are also home to the two highest-circulation daily newspapers in Minnesota: the Star Tribune from Minneapolis with a circulation of 361,172 on weekdays and 596,333 on Sundays, and the Saint Paul Pioneer Press (circulation: 190,939 on weekdays, 251,765 on Sundays). A large number of smaller daily and weekly newspapers are also available.
Two of the largest public radio stations are Minnesota Public Radio (MPR) and Public Radio International (PRI). The former airs on 37 different stations and has the largest number of listeners of any public regional radio station in the United States.
Sports
competitive sport
Minnesota is represented by professional teams in all major US sports leagues. Ice hockey is very popular here . The Minnesota Wild from St. Paul, which plays in the National Hockey League (NHL), started playing in 2000 and plays at the Xcel Energy Center . The former NHL team Minnesota North Stars moved to Dallas , Texas in 1993 . The Minnesota Vikings from Minneapolis play in the National Football League . Since 2016 they have played their home games there at the US Bank Stadium . The baseball team of the Minnesota Twins play at Target Field , a pure baseball stadium in Minneapolis. The Twins are the only team from Minnesota that won the World Series in 1987 and 1991 to win big titles. Minnesota Timberwolves basketball players from Minneapolis play in the National Basketball Association . Your home game arena is the Target Center . Before the Timberwolves, the Los Angeles Lakers played in Minneapolis from 1947 to 1960. The name of the team goes back to the time in Minnesota, the "land of 10,000 lakes". The professional football team Minnesota United plays in the Western Conference of Major League Soccer , its home ground is the TCF Bank Stadium on the campus of the University of Minnesota in Minneapolis. The Minnesota Swarm are a professional lacrosse team based out of St. Paul.
In women's sports, the Minnesota Lynx represent the state in the Women's National Basketball Association, the Minnesota Vixen compete in the Women's Professional Football League , and the Minnesota Whitecaps compete in the National Women's Hockey League .
Teams from Minnesota are also represented in college sports. The Golden Gophers of the University of Minnesota are organized in the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) and are the only ones represented in Division I. They compete against other teams in the Big Ten Conference . Other universities join divisions II and III . In ice hockey, five teams from Minnesota are represented in the Western Collegiate Hockey Association .
Minnesota athletes have historically achieved success at the Olympics . At the Miracle on Ice , when the US ice hockey team won the Olympic gold medal in 1980, most of the players on the US national team came from Minnesota in addition to coach Herb Brooks . After winning the silver medal in 1996, swimmer Tom Malchow was able to win the gold medal over the 200 meter butterfly in Sydney four years later . At the 2006 Winter Olympics , the US curling team from the Bemidji Curling Club won bronze with Skip Pete Fenson .
Recreational sports

In addition to professional sports, recreational sports are also popular in Minnesota. In addition to the official state sport of ice hockey, other sports such as basketball, football, baseball or soccer and outdoor leisure activities are popular.
In the warmer seasons, activities on or in the water are preferred. In addition to sports such as water skiing and canoeing , fishing is also very popular. More than 36 percent of the population go fishing, which is the second highest figure in the US after Alaska. In the winter months, the activities usually adapt to the cold climate. Ice fishing, ice skating , curling and snowmobiling are popular here.
The numerous forests and parks are used all year round for hunting , hiking or camping . In addition to many designated hiking trails , the state also has the most miles of bike paths in the entire United States.
Web links
- Official website of the state of Minnesota . Retrieved December 4, 2010.
- Official site for tourism (English)
- Minnesota Historical Society (English)
Individual evidence
- ^ Density Using Land Area For States, Counties, Metropolitan Areas, and Places. As of 2000. US Census Bureau , accessed January 5, 2015.
- ^ Thirteen-Lined Ground Squirrel. Fun facts. The Minnesota Department of Natural Resources Web site, St. Paul, accessed January 5, 2015.
- ^ Minnesota State Symbols — Unofficial, Proposed, or Facetious. Animal / Mammal , Paragraphs 3 + 4. Minnesota Legislative Reference Library (online), accessed January 5, 2015.
- ^ Minnesota State Symbols — Unofficial, Proposed, or Facetious. Nickname / Slogan , Para. 3. Minnesota Legislative Reference Library (online), accessed January 5, 2015.
- ↑ Facts and figures
- ^ A b Greg Breining: Compass American Guides: Minnesota. 3rd Edition, Compass American Guides, 2005, ISBN 1-4000-1484-0
- ^ A b Richard W. Ojakangas, Charles L. Matsch: Minnesota's Geology. University of Minnesota Press, 1982, ISBN 0-8166-0953-5 .
- ↑ Table Showing Minnesota Earthquakes ( Memento from April 3, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ Minnesota Map Collection - State, City, Road, County, River, Lake
- ↑ a b Minnesota DNR: Lakes, rivers & wetlands
- ↑ Minnesota North Star: About MN Forests and Parks ( September 23, 2005 memento in the Internet Archive )
- ^ Minnesota Department of Natural Resources: Biomes of Minnesota
- ↑ Tim Bewer: Moon Handbooks Minnesota. Avalon Travel Publishing, 2004, ISBN 1-56691-482-5 .
- ↑ World Map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated . Markus Kottek. Retrieved December 4, 2010.
- ^ National Weather Service Forecast Office: Climate of Minnesota
- ↑ Minnesota Historical Society: TimePieces ( September 17, 2006 memento in the Internet Archive )
- ^ Minnesota State University Anthropology Department. Archived from the original on June 4, 2010 ; accessed on January 23, 2014 .
- ^ A b c Rhoda R. Gilman: The Story of Minnesota's Past. Minnesota Historical Society Press, 2001, ISBN 0-87351-267-7 .
- ↑ Minnesota Historical Society Press: Historic Fort Snelling ( September 19, 2012 memento on WebCite )
- ^ A b William E. Lass: Minnesota: A History. WW Norton & Company, 1998, ISBN 0-393-04628-1 .
- ↑ Population in Metropolitan Statistical Areas Ranked by 2000 Census (PDF; 136 kB)
- ^ Minnesota Demographic Center: Population Estimates ( March 7, 2008 memento in the Internet Archive )
- ^ Environmental Information Report, app. D Socioeconomic Information
- ^ US Census Bureau _ Census of Population and Housing . Retrieved February 28, 2011
- ↑ Extract from Census.gov . Retrieved February 28, 2011
- ↑ Extract from census.gov (2000 + 2010) ( Memento of December 2, 2006 in the Internet Archive ) Retrieved on April 4, 2012
- ^ Environmental Information Report
- ↑ a b c d US Census Bureau
- ↑ Births, Marriages, Divorces, and Deaths: Provisional Data for 2005 (PDF; 203 kB)
- ^ Minnesota - Selected Social Characteristics
- ↑ Minnesota Population Projections by Race and Hispanic Origin ( Memento from August 22, 2006 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF; 398 kB)
- ↑ American Religious Identification Survey, Exhibit 15 ( Memento of December 21, 2008 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ The Association of Religion Data Archives | Maps & Reports
- ↑ Local Unemployment Statistics for March 2009 - Minnesota Unemployment Statistics (Not Seasonally Adjusted)
- ↑ US Census Bureau: Minnesota - DP-3. Profile of Selected Economic Characteristics: 2000
- ^ Minnesota Department of Employment and Economic Development: Wealth of Resources
- ↑ a b U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis: Regional Economic Accounts
- ^ US Bureau of Economic Analysis: Regional Economic Accounts
- ↑ factfinder.census.gov ( Memento from February 10, 2020 in the web archive archive.today )
- ↑ Minnesota gives a foretaste of the US shutdown. Handelsblatt .com, July 4, 2011, accessed on July 4, 2011 .
- ^ Minnesota shutdown: It's over. CNN.com, July 20, 2011, accessed October 17, 2013 .
- ↑ Minnesota Votes: 2005 Senate Bill 4 (Ethanol Mandate Increase)
- ↑ The American Wind Energy Association: Wind Energy Projects Throughout the United States of America ( Memento of November 8, 2010 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Governor Pawlenty signes stronges renewable energy requirement in the nation ( Memento from March 16, 2014 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ Minnesota Department of Transportation: Transportation amendment update ( September 8, 2011 memento in the Internet Archive )
- ^ Smartest State Award
- ^ Education Working Paper 8 - Table 2 ( Memento of February 12, 2007 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ America's Health Rankings (page 55)
- ↑ The Percentage of People Without Health Insurance Coverage by State Using 2- and 3-year Averages: 2003 to 2005 (PDF; 3.8 MB)
- ↑ Explore Minnesota Living (PDF; 945 kB)
- ^ David Leip: Dave Leip's Atlas of US Presidential Elections. Retrieved November 28, 2018 .
- ↑ http://www.electproject.org/2004g
- ↑ 2004 Elections Project
- ↑ 210 Designated Market Areas - 03-04
- ↑ Kstp.com - History
- ↑ Contact Us - KS95 94.5 Today's Variety | Twin cities. In: www.ks95.com. Retrieved November 1, 2016 .
- ↑ Text of Star Tribune press release ( Memento from September 26, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ startribune.com - Pioneer Press circulation rises
- ^ Minnesota Public Radio - About MPR
- ^ Health Statistics - Physical exercise by state
- ↑ It's in the books: Hockey is state's official sport ( Memento from July 4, 2009 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Managing for Results (PDF; 1.8 MB)
- ↑ Explore Minnesota Biking
Coordinates: 46 ° 22 ′ N , 94 ° 27 ′ W