Big lakes
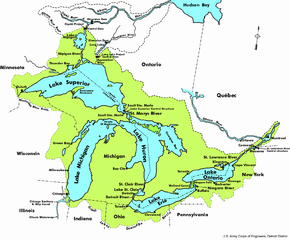
The Great Lakes ( english Great Lakes ) are a group of five contiguous freshwater lakes in North America .
geography
The Great Lakes include:
- Lake Erie (Lake Erie)
- Lake Huron (Lake Huron)
- Michigan (Lake Michigan)
- Lake Superior (Lake Superior)
- Ontario (Lake Ontario)
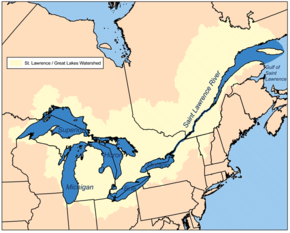
From a hydrological point of view, Lake Huron and Lake Michigan together form only one lake with a narrow point, the Mackinac Strait . The maximum difference in altitude between the individual lakes is around 150 meters, the largest part of which is formed by the Niagara Falls between Lake Erie and Lake Ontario. Due to their size, the tides are noticeable on the Great Lakes , but the effects are minor and are masked by meteorological effects. Lake Michigan is the only one of the Great Lakes to be located entirely in the USA ; the other four are along the Canadian-US border . They are drained into the Atlantic by the St. Lawrence River.
There are over 35,000 inland islands or groups of islands in the Great Lakes area. In the Canadian part of Lake Huron , for example, there is Manitoulin Island, the largest inland island in the world at 2,766 square kilometers .
In winter, the surface of the Great Lakes creates the Lake Effect , and the resulting Snow Belt stretches across five states.
geology
The area around the Great Lakes and the lowlands of the St. Lawrence River, as well as its funnel mouth, which continues deep into the shelf under the sea, geologically represent a unit.
Glacial clearing, deposition of moraine debris and crust movements determine the shape of the lake area, the hollow forms of which, however, were already created by large-scale tectonic depressions in the Tertiary and at the beginning of the Pleistocene .
A mighty Paleozoic series of layers, the Onondaga Formation , consisting of various resistant sandstones and limestone , frames the lakes in the south. The Niagara strata , which consists of hard dolomite rock and soft slate , extends between Lake Ontario and Lake Erie and north of Lake Michigan . On the northern edge of the Great Lakes, the Canadian Shield comes to the surface.
Comparison of the lakes
| lake | Lake Superior | Lake Huron | Lake Michigan | Lake Erie | Lake Ontario | total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height above sea level |
183 m | 176 m | 176 m | 174 m | 75 m | - |
| Surface share USA share Canada |
82,103 km² 52,256 km² 29,847 km² |
59,586 km² 23,235 km² 36,351 km² |
58,016 km² 58,016 km² - km² |
25,667 km² 12,945 km² 12,722 km² |
19,011 km² 9,042 km² 9,969 km² |
244,383 km² 155,494 km² 88,889 km² |
| Water volume | 12,100 km³ | 3,540 km³ | 4,918 km³ | 484 km³ | 1,639 km³ | 22,681 km³ |
| Average depth |
149 m | 59 m | 85 m | 19 m | 86 m | - |
| Maximum depth |
406 m | 229 m | 282 m | 64 m | 244 m | - |
| Big settlements |
Duluth Sault Ste. Marie Thunder Bay |
Sarnia |
Chicago Gary Green Bay Milwaukee |
Buffalo Cleveland Erie Toledo |
Hamilton Kingston Oshawa Rochester Toronto |
- |
Economy and Infrastructure
The Great Lakes are an important reservoir for supplying water to the United States and Canada. With about 244,000 square kilometers, they form the largest freshwater surface on earth , with Lake Baikal exceeding the Great Lakes in freshwater volume due to its great depth.
Due to the heavy settlement and industrialization of the area, however, there was an ever higher level of pollution and the proliferation of introduced animal and plant species, such as the sea lamprey , the black-mouthed goby and the triangular mussel . A water protection agreement was signed between the USA and Canada in 1978.
There is a shipping connection to the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway , to the Saint Lawrence River and thus the Atlantic via the Saint Lawrence Seaway . Due to the special conditions on the lakes, a separate type of bulk carrier has emerged, the Great Lakes ship .
The Interlake Steamship Company has existed since 1987.
See also
- Nipigo Lake , which geologically belongs to the Great Lakes and is also called the sixth of the Great Lakes.
- Lake St. Clair
- Great Lakes Storm of 1913
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ William Ashworth: The Late, Great Lakes: An Environmental History . Wayne State University Press, 1987, ISBN 9780814318874 , p. 27
Coordinates: 45 ° 48 ′ 38 " N , 84 ° 40 ′ 57" W.