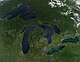
Lake Superior
|
Upper Lake Superior, Lac Supérieur |
||
|---|---|---|

|
||
| Geographical location |
Ontario (Canada), Minnesota , Wisconsin , Michigan (USA) |
|
| Tributaries | Nipigon River , Saint Louis River , Pigeon River , Pic River , White River , Michipicoten River , Kaministiquia River | |
| Drain | Saint Marys River to Lake Huron | |
| Islands | Isle Royale , Michipicoten Island , Slate Islands , Manitou Island , Apostle Islands , St. Ignace Island , Simpson Island , Pie Island , Edward Island | |
| Places on the shore | Duluth , Superior , Thunder Bay | |
| Data | ||
| Coordinates | 48 ° N , 87 ° W | |
|
|
||
| Altitude above sea level | 184 m | |
| surface | 82,100 km² | |
| length | 560 km | |
| width | 260 km | |
| volume | 12,100 km³ | |
| scope | approx. 2940 km | |
| Maximum depth | 406 m | |
| Middle deep | 147 m | |
|
particularities |
The second largest lake in the world (after the Caspian Sea ), the largest freshwater lake in the world |
|
|
||
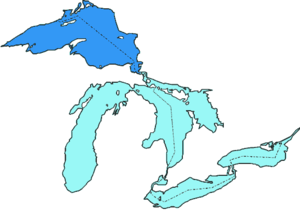
| Location of the Upper Lake to the great lakes | ||
The Upper Lake ( English Lake Superior ; French Lac Supérieur ) is the largest of the five Great Lakes of North America and the after the Caspian Sea in area 's second-largest inland sea in the world and the largest surface freshwater lake (the deepest and largest by volume freshwater lake is Lake Baikal in Siberia ).
The border between Canada and the United States runs through Lake Superior . Its water level is 184 m with a total area of 82,103 km² (roughly the size of Austria ). Its greatest depth is 406 m, from the northernmost point to the southernmost the distance is 290.2 km, the greatest east-west extension is 599.6 km. The Upper Lake borders in the north on the province of Ontario in Canada (Canadian lake portion 29,847 km², American lake portion 52,256 km²) and the US state Minnesota , in the south on the US states Wisconsin and Michigan . The largest island in the lake is the Isle Royale , from the south the Keweenaw Peninsula protrudes far into the lake.
The Obere See is the great lake with the best water quality, since, in contrast to the other lakes, there are only a few industrial plants on its banks and it is not fed by the other lakes.
The lake has over 200 tributaries. The largest are the Nipigon River , the Saint Louis River , the Pigeon River , the Pic River , the White River , the Michipicoten River, and the Kaministiquia River .
The Upper Lake flows over the Saint Marys River into the Huron Sea and is thus part of the Saint Lawrence Seaway . The rapids on this river require locks, the Soo Locks at Sault Ste. Marie , so that ships can overcome the eight meter difference in altitude to Lake Huron.
Surname
In the language of the Anishinabe (also Ojibwa or Chippewa Indians) the lake is called "Gichigami" ("big water"). He is also known as the "Gitche Gumee", such as B. also in Henry Wadsworth Longfellows 1855 epic, The Song of Hiawatha and Gordon Lightfoot's ballad "The Wreck of the Edmund Fitzgerald", which is about the sinking of the Edmund Fitzgerald on the Upper Lake in November 1975. The lake was called "le lac supérieur" (Upper Lake) by French researchers in the 17th century because it is located above Lake Huron.
history
The Upper Lake was already an important traffic route for the indigenous Indians , on the north-west bank two rivers flow with the Pigeon River and the Kaministiquia River, which served as routes into the interior of today's Canada. The first whites were French fur traders who were shown these connections by the Indians. The so-called Grand Portage on the Pigeon River was expanded into a trading base, and the North West Company , founded by traders of French origin in 1783 , set up a fortified camp there, to which they relocated their headquarters in the summer months. The reconstructed base is now designated as the Grand Portage National Monument .
In the 19th century mining settlements arose around the lake, in particular iron ore was mined and transported across the lake by ship. Today, Duluth is the top-selling inland port in the United States, with coal and iron ore the most important goods.
Tourism and nature protection
Today tourism plays an important role, the mild climate makes the area a popular destination in summer and winter. Fishing , boating, hiking, cross-country skiing in winter, and snowmobiling are the most common activities. The water quality makes the lake an attractive diving area despite the low temperatures .
A significant part of the Canadian coast of the lake has been under protection since 2007. The Lake Superior National Marine Conservation Area is located there .
shipping
The Upper Lake is an important transport route for iron ore and other mining products. Large cargo ships, so-called Laker, and smaller seaworthy ships of the Seawaymax class transport such goods on the St. Lawrence Seaway .
The south shore of the lake between Grand Marais and Whitefish Point is considered a ship graveyard, as more ships have sunk in this area than in any other part of the lake. These shipwrecks are protected by the Whitefish Point Underwater Preserve . The last major ship to sink in a storm on the great lake was the SS Edmund Fitzgerald . This ship sank on November 10, 1975 about 17 miles from Whitefish Point with 29 crew members on board. In the history of shipping on the Upper Lake, storms have repeatedly brought down several ships, such as the Mataafa storm of November 28, 1905 or the Great Lakes Storm of 1913 .
In August 2007, for example, the wreck of the Cyprus was found. This 128 m long iron ore freighter sank in a storm on October 11, 1907 on its second voyage from Superior , Wisconsin to Buffalo , New York. The ship, built in Lorain , Ohio , had not entered service until August 17, 1907.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e University of Minnesota: Facts about Lake Superior
- ↑ Frederick Stonehouse: Lake Superior's Shipwreck Coast ( English ). Avery Color Studios, Gwinn, Michigan 1985, 1998, ISBN 0-932232-43-3 , p. 267.
- ^ Associated Press : Century-old shipwreck discovered. In: NBC News. September 10, 2007, accessed September 12, 2018 .