LGM-30 Minuteman
The LGM-30 Minuteman is a three-stage US ICBM manufactured by Boeing . It forms the core of the US nuclear force . The Minuteman is equipped with nuclear warheads , has an integrated, automatic inertial navigation system and is propelled in all three stages with solid fuel . It is named after the Minutemen militia . The Minuteman Associations are part of the US Air Force and have been under the Air Force Global Strike Command since 2009/10 .
General
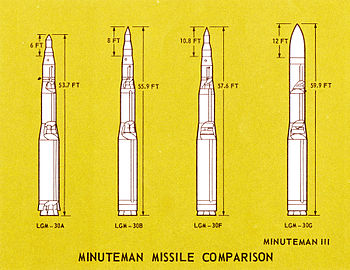
The first launch of a Minuteman-I took place on September 15, 1959, a Minuteman-II on September 24, 1964 and a Minuteman-III on August 16, 1968. Minuteman-I and -II have since been deactivated, the Minuteman-III missiles should remain in use until around 2030. Several thousand of this type of rocket had been produced by the end of production in 1977.
The Minuteman-I, armed with a nuclear warhead, were originally intended to be mounted on railroad cars because mobile launch ramps are less vulnerable to initial strikes. After this plan was abandoned at the end of 1961 for financial reasons, the size and weight restrictions necessary for rail transport could be abandoned. As a result, the type Minuteman-II was developed. 500 of these missiles were deployed, with the end of the Cold War they were all decommissioned. Some of these rockets will be converted into Minotaur launch vehicles for satellite launches by Orbital Sciences Corporation .
The further development to the Minuteman-III enabled the use of three independently controllable warheads ( MIRVs ). First it was the W-62 / Mk.12 with 170 kt explosive power. At the end of the 1970s, part of the Minuteman III was retrofitted with the W-78 / Mk.12A with 335 kt. The W-62 is now being replaced by the modernized W-87 / SERV of the retired MX Peacekeeper .
The Minuteman missiles are stationed in underground missile silos ready for launch . The silos are connected in groups of ten to underground command posts (LCC). These are manned around the clock by two officers who have to execute an incoming fire order by turning two ignition switches at the same time. In addition, an order to fire must also be given from a neighboring command post. The Minuteman-III are permanently held in a status at T-30sec, which means that they can leave the silo 30 seconds after a valid start command. The individual silos are at least 10 km apart. There is also the option of firing the missiles from an airborne launch crew (see Boeing E-4 ). This system is intended to ensure that the rockets can also be fired if the silo has lost contact with the control bunker. This was last rehearsed in 2012 at the Vandenberg Air Force Base .
A test on June 16, 2010 was the 200th flight of a Minuteman III since it was first launched in 1968. A test flight of a Minuteman III on July 27, 2011 with an inert warhead from the Vandenberg Air Force Base was a failure, the missile was hit by Blown up flight control after an anomaly occurred. The cause of the error has not yet been announced. The last known test flight of a Minuteman III took place on the evening of April 26, 2017. The target of the missile, which had no warhead, was the Kwajalein Atoll in the South Pacific, almost 8,000 kilometers away .
In 2007, the deactivation of 50 of a total of 500 missiles stationed at Malmstrom AFB began. As of September 1, 2012, the USA reported the following stationing figures for their Minuteman III fleet under the New START contract:
- 449 active launch silos with 449 missiles (150 Malmstrom AFB, 150 Minot AFB , 149 Warren AFB )
- 57 inactive launch systems and 263 non-deployed missiles
The USA are planning the further development of the LGM-30H Minuteman-IV. However, it should not be introduced until 2030 at the earliest.
Discontinued Minuteman I and II missiles will continue to be used in partly modified form as targets for missile defense development in the USA and satellite carriers.
Warheads of the type W78 as multiple warheads ( MIRV ) Mk12A for an LGM-30G Minuteman-III
Technical specifications
Minuteman-II (LGM-30F)
- Summit height: 1,300 km
- Starting thrust: 780 kN
- Takeoff weight: 33,014 kg
- Diameter: 1.70 m
- Length: 17.6 m
- Fin span: 1.80 m
- Mass of the warhead: 680 kg
- Range: 11,300 km
- Number of warheads: 1
- Warhead: W56 (explosive force 1,200 kt TNT)
- Maximum speed: 29,030 km / h
Minuteman-III (LGM-30G)
- Summit height: 1,300 km
- Starting thrust: 780 kN
- Takeoff weight: 35,300 kg
- Diameter: 1.70 m
- Length: 18.23 m
- Fin span: 1.80 m
- Mass warhead + RV: ~ 400 kg
- Range: 13,000 km
- Number of warheads: 1 to 3
- Warhead: W-62 / Mk.12 (170 kt); W-78 / Mk.12A (335 kt); W-87 / Mk.21 (300 kt, upgrade to 475 kt possible)
- Maximum speed: 29,030 km / h
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ wired.com: In Nuclear Silos, Death Wears a Snuggie. Retrieved March 11, 2012 .
- ↑ 200th Test Launch Of A Minuteman III Missile. Retrieved May 15, 2019 .
- ↑ Minuteman III destroyed during test launch ( Memento from March 15, 2013 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Minuteman missile from Vandenberg: Did you see the launch? In: Mercury News. April 26, 2017. Retrieved April 27, 2017 .
- ↑ New START Treaty - Aggregate Numbers of Strategic Offensive Arms (PDF; 1.7 MB)
Web links
- Minuteman in the Encyclopedia Astronautica (English)
- 60 Minutes shocked to find 8-inch floppy drive nuclear deterrent (English)