Malaysia
| Malaysia (مليسيا) | |||||
|
|||||
|
Motto : "Bersekutu Bertambah Mutu" ( "unity is strength") |
|||||
| Official language |
Malay English (second language) |
||||
| capital city | Kuala Lumpur | ||||
| Seat of government | Putrajaya | ||||
| State and form of government | Federal parliamentary monarchy ( elective monarchy ) | ||||
| Head of state | King Abdullah Shah | ||||
| Head of government |
Prime Minister Muhyiddin Yassin (PN- Bersatu ) |
||||
| surface | 330,290 km² | ||||
| population | 31.9 million ( 44th ) (2019; estimate) | ||||
| Population density | 96 inhabitants per km² | ||||
| Population development | + 1.3% (estimate for 2019) | ||||
gross domestic product
|
2019 | ||||
| Human Development Index | 0.81 ( 62nd ) (2019) | ||||
| currency | Ringgit (MYR) | ||||
| independence | August 31, 1957 (from the United Kingdom ) September 16, 1963 ( Sabah , Sarawak and Singapore 1 ) |
||||
| National anthem |
Negaraku |
||||
| Time zone | UTC + 8 | ||||
| License Plate | JUST | ||||
| ISO 3166 | MY , MYS, 458 | ||||
| Internet TLD | .my | ||||
| Phone code | +60 | ||||
|
1 Singapore became an independent nation on August 9, 1965
|
|||||
Malaysia [ maˈla͜izi̯a ], more rarely Malaysia , is a constitutional electoral monarchy with 32 million inhabitants, consisting of 13 states in Southeast Asia on the Malay Peninsula or West Malaysia with the capital Kuala Lumpur and East Malaysia on part of the island of Borneo . The South China Sea lies between the two roughly equal parts of the country .
The Malay Peninsula borders Thailand on water and land and has maritime borders with Vietnam , Singapore and Indonesia . In the south it is separated from the Indonesian island of Sumatra by the Strait of Malacca and connected to the city-state of Singapore on the island of the same name by a dam. Eastern Malaysia has land and sea borders with the Sultanate of Brunei in the north and Indonesia in the south and has sea borders with Vietnam and the Philippines .
Malaysia emerged in 1963 from four former parts of the British Empire : the Malaya Federation , the North Borneo Crown Colony , the Singapore Crown Colony (until 1965) and the Sarawak Colony .
The head of state is the king. He bears the title Yang di-Pertuan Agong and is elected every five years from a number of nine noble bearers. The parliament has an upper and a lower house based on the English model. From its founding until 2018, the Barisan Nasional majority coalition led in both chambers under the leadership of the United Malays National Organization party . In 2018, the Pakatan Harapan opposition alliance replaced the previous government and thus appointed the prime minister for the first time.
Malaysia is a founding member of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and is an emerging market economically .
geography
geology
From the swamp and coastal forests of the alluvial plains by the sea (partly overgrown with mangroves ), the land rises significantly everywhere: On the Malay Peninsula to mountain ranges that extend northwards and consist of parallel mountain and hill zones. The main ridge extends to 2190 m above sea level. In Sarawak on a plateau with individual mountain ranges and in Sabah on a highly structured high mountain range in which the 4,095 m high Kinabalu rises, the highest mountain between the Himalayas and New Guinea. Also on Borneo is the Sarawak Chamber, the largest known cave space in the world. The largest island in Malaysia is Pulau Banggi , which is located off the northern tip of Borneo and belongs to the Kudat district in the state of Sabah. Northeast in front, off the coast of Borneo that are Turtle Islands , to the National Park Turtle Islands Park of Sabah was established 1976th
climate
Malaysia lies completely in the humid , hot, humid tropics : Accordingly, the daily and annual temperature differences are very small at 2 ° C, there is a high relative humidity of 98% in the morning and over 65% in the afternoon and the mean annual rainfall is 2000 ( Lowlands in the west) over 4000 mm (northeast under monsoon influence) to 6000 mm (mountains) rain high to very high. The temperatures are all year round in the range of 25 to 28 ° C. From April to October the southwest monsoon and from October to February the northeast monsoon determine the weather.
The four climate diagrams show a west-east profile: Kuala Terengganu and Kuala Lumpur are on the peninsula (West Malaysia), Sandakan and Kuching are on Borneo (East Malaysia).
Kuala Lumpur
(Malacca West)Kuala Terengganu
(Malacca East)Kuching
(Borneo West)Sandakan
(Borneo East)
ecology
Both the Malay Peninsula and the Malaysian Borneo were originally almost entirely covered by evergreen tropical wet forests: up to an altitude of 2000 m from lowland and mountain rainforest and above that from cloud forests and cloud forests . At the beginning of the 21st century, the tropical forests still take up more than half of the country's area. Almost half of this forest is in Sarawak. The valuable tropical woods in the lowlands and the lowest mountain range and the slash and burn farming of the growing population of the indigenous ethnic groups (especially in the interior of Sarawak) increasingly lead to overexploitation and degradation of the forests.
The forests in Sabah and Sarawak on Borneo are among the oldest primeval forest areas in the world. The forests on Mount Kinabalu in particular are therefore characterized by an outstanding biodiversity (North Borneo is one of the five centers of the greatest biodiversity on earth ). With a generally high level of biodiversity , an extremely large number of endemic species, genera and families of plants and animals as well as large ecosystems , the whole of Malaysia is one of the world's megadiversity countries . Gibbons, macaques, sun bears and numerous reptiles such as z. B. Cobras and Pythons. Rarer animal species are elephants, tigers, clouded leopards, golden and marble cats and leopards. The orangutan, classified as a critically endangered species, lives in Borneo. The Sumatran rhinoceros is also endangered. The species-rich bird life includes hornbills, beos, parrots, pheasants and owls. Due to the high risk situation, Malaysia is also listed as a biodiversity hotspot .
The commercial and financial center is the capital Kuala Lumpur, where the federal parliament has its seat. Most government institutions, however, are located in Putrajaya , which was established in 1995 as the new administrative capital. Other important cities are George Town , Ipoh and Johor Bahru .
Tanjung Piai , which is located in the southern state of Johor , is the southernmost point of mainland Asia. As a sea route, the Strait of Malacca is one of the busiest shipping routes.
population
| year | population | year | population |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 6,110,000 | 1990 | 18,038,000 |
| 1955 | 7,040,000 | 1995 | 20,496,000 |
| 1960 | 8,157,000 | 2000 | 23,186,000 |
| 1965 | 9,527,000 | 2005 | 25,659,000 |
| 1970 | 10,804,000 | 2010 | 28,112,000 |
| 1975 | 12,162,000 | 2019 | 31,950,000 |
| 1980 | 13,798,000 | 2030 | 36,815,000 |
| 1985 | 15,599,000 | 2050 | 41,729,000 |
Ethnic groups

The population of Malaysia is made up as follows: 50.4% are Malay , 23.7% Chinese , 11% indigenous peoples ( Orang Asli and Dayak ), 7.1% Indians and 7.8% others.
The population is not evenly distributed over the national territory of Malaysia, because in the eastern part of Malaysia, i.e. the two states of Sarawak and Sabah located on the island of Borneo , only about 5 million people (around 20% of the population of Malaysia) live, although the two states are together make up about 60% of the land area of Malaysia, whereas the remaining 80% of the population (about 22 million people) live in the smaller western part of the country.
The Malays, who largely belong to Sunni Islam , have been claiming political leadership since Malaysia's independence, they are systematically promoted by the government and preferred to be hired in the public service, this has been the case since the introduction of the Malaysian new economic policy in the 1960s secured by the so-called Bumiputra status. Furthermore, the overseas Chinese make up about a quarter of the population. They currently still dominate in the cities. The Chinese play an important role in trade and economy. Another seven percent of the population are of Indian descent. These are Hindus , Muslims, Sikhs , Christians or Buddhists . About 85% of the Indian population of Malaysia are Tamils , minority groups are the Malayalis , Punjabis and Telugus .
In the sparsely populated eastern Malaysian states of Sarawak and Sabah, non-ethnic Malay indigenous peoples make up half and two thirds of the population, respectively. Like the Malays, they are counted among the original population of Malaysia and are therefore also considered Bumiputras. These indigenous peoples are grouped under the collective term Dayak in Sarawak and include the Iban and the Bidayuh . Indigenous ethnic groups like the Murut or the Kadazan live in Sabah .
There are also indigenous people on the Malay Peninsula, but in smaller numbers, they are referred to by the collective term Orang Asli . These belong to a large number of ethnic groups but have cultural similarities. They were followers of animistic local religions until the 20th century . Since then, many have converted to Christianity or Islam. Although the Orang Asli differ in culture from the Malays, many have assimilated Malay culture, for example by moving to the cities or by marriage. Some groups of the Temiar Senoi , who live there as isolated peoples , have withdrawn into the inaccessible mountain rainforests of north-central Malaysia .
Notable minorities are the Europeans, people from the Middle East , Cambodia and Vietnam . The Europeans are mostly British and some Portuguese , whose ancestors have lived there since colonial times. Most Cambodians and Vietnamese came to Malaysia as refugees from the Vietnam War .
Overall, there are around four to six million immigrants living in Malaysia (as of 2021). Most of the migrant workers come from Nepal , Bangladesh , Indonesia or Myanmar .
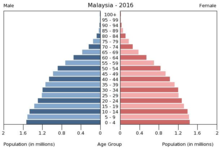
Population growth is relatively high at around 1.6% annually, and around a third of the population is under the age of 15. The urbanization rate is around 75%. The average life expectancy in the period from 2010 to 2015 was 74.7 years (men: 72.6 years, women: 77.1 years) and the infant mortality rate was around 13 per thousand. The average age in 2016 was 28.2 years. A woman had an average of 1.9 children, which is why the population will age significantly in the future.
languages
The official language of Malaysia is Bahasa Malaysia (Malaysian) . The English language due to the long British rule in Malaysia enjoys a special role and for many Malaysians second language. Due to a large Chinese minority also plays Chinese an important role (mainly Cantonese , Mandarin , Hokkien , Hakka , Chaozhou (Teochew), Hainan , the Fuzhou dialect ). Due to the Indian minority also living in Malaysia, numerous Indian languages, in particular Tamil , Telugu and Malayalam, are spoken. A large number of indigenous languages are also spoken in East Malaysia, the most important of which are Iban and Kadazan . A total of 140 different languages and idioms are spoken in Malaysia.
British English is used in official documents . However, through television, American English has already had some influence. The English used in colloquial language in Malaysia is very different from British English and is therefore also known as Manglish . Except for a few slang expressions, it is very similar to the Singlish spoken in Singapore .
Religions
- overview
All world religions are represented in Malaysia in significant numbers.
Population censuses show the following proportions of the population by religion:
| year | Islam | Buddhism | Christianity | Hinduism | Chinese folk religions such as Daoism, Confucianism | Non-denominational | Other confessions or no information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 60.4% | 19.2% | 9.1% | 6.3% | 2.6% | 2.4% | |
| 2010 | 61.5% | 19.6% | 9.2% | 6.3% | 1.3% | 0.7% | 0.5% |
The Chinese are mostly Buddhists (20%) or belong to other Chinese religions such as Daoism or Confucianism (2.6%). Christians (9%) are found in all ethnic groups. The Indians are made up of Hindus and Sikhs (6.5%).
- Islam
The Islam to which 60% of the population profess, is the state religion .
The Shafiʿite school of Sunni Islam is practiced in theology and jurisprudence. Other Islamic schools, especially Shiite ones, are prohibited.
Malaysia first came into contact with Islam through Arab traders and merchants at the end of the 7th century. However, various Buddhist and Indian-Hindu kingdoms were dominant in Malaysia at this time, so that Muslims never made up more than 10% of the population until the 14th century. Since the 13th century, more Arabs settled in Malaysia, who eventually mixed with the local population and thus promoted the Islamization of the Malays. Like Indonesia , Malaysia was Islamized in the 14th and 15th centuries.
Until well into the 1970s, many Muslim Malays were considered liberal (similar to the Abangan in today's Indonesia). With the Dakwah , an Islamic revival movement, however, a wave of Islamization began (triggered by various ethnic and social conflicts, see, among others, Parti Islam Se-Malaysia and Al-Arqam ), so that Malaysia is now Orthodox Islamic. The Malays, who make up 50.4% of the total population, are virtually all Muslim. About 70% of Malaysian women of Malay origin wear a headscarf. Traditional Malay clothing of Islamic origin is also worn by many Malays.
According to the country's constitution, all ethnic Malays are automatically Muslim from birth . You cannot marry people of different faiths. A falling away from Islam is seen very reluctantly and is difficult in practice. To do this, a “Borang Keluar Islam” (form for leaving Islam) must first be filled out. Afterwards it has to be proven for about two years that one cannot be converted to Islam after all, for example in “re-education centers”, where those who want to leave are detained. Ultimately, a Sharia court has to decide on resignation - the freedom of religion enshrined in the constitution only exists in theory. This is also shown by cases from 2007.
- Christianity

The Council of Churches of Malaysia is an ecumenical organization that represents the Christian churches and affiliated groups in Malaysia. The Christian press is difficult to publish in Malay, but it is readily available in English, Chinese and Tamil . The distribution of publications to members of associations or churches is unrestricted. Attempts at censorship (specifically: prohibition of the word “ Allah ”) were also made here by the government, which was initially lifted by a court, but reintroduced in 2013. The Islamic Religious Office JAIS made headlines in January 2014 when it illegally entered the premises of the Bible Society of Malaysia with police support and confiscated 300 copies of Al-Kitab , the Bible written in Malay.
The construction of churches in metropolitan areas often leads to difficulties with the planning authorities.
training
The education system in Malaysia is subordinate to the Ministry of Education ( Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia ). It is divided into two main departments, of which the Education Sector deals with all matters relating to pre-schools, primary and secondary schools, while the Higher Education Sector is responsible for the universities . Although the federal government is responsible for education policy, every Malaysian state has its own ministry of education . The legal basis for government education policy is the Education Act 1996 .
Malaysia has a publicly owned school system that guarantees free multilingual education to all citizens. There is also the option of attending a private school or taking part in homeschooling . Compulsory schooling is limited to primary level. As in many Asia-Pacific countries, such as South Korea , Singapore and Japan , the curricula and final exams follow a uniform, cross-school system.
In 2015, the literacy rate in Malaysia was 94.6% of the adult population. For women it was 93.2% and for men 96.2%. In the 2015 PISA ranking, the country's students ranked 45th out of 72 countries in mathematics, 51st in science and 46th in reading comprehension.
story
The Malay Peninsula became a major trading center in Southeast Asia when trade between China and India began to flourish. At that time there was a hustle and bustle in the Strait of Malacca . The first Malay kingdoms emerged from ports established in the 10th century. The main early kingdoms were Langkasuka and Lembah Bujang in Kedah , Beruas and Gangga Negara in Perak, and Pan Pan in Kelantan . The Islam came in the 14th century Terengganu on. In the early 15th century, the Sultanate of Malacca was established. It attracted the interest of Portugal because of its prosperity . The port then became a center of colonization by the Dutch and the British.
The British crown colony, Straits Settlements , was established in 1826 and Britain gradually gained control of the rest of the peninsula. The Straits Settlements included Penang , Singapore, and Malacca. Penang was founded in 1786 by Captain Francis Light and served as a military and trade base. It was soon overtaken in importance by Singapore, which was founded in 1819 by Sir Stamford Raffles . Malacca was finally in British possession after the Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824. The colony was ruled by the British East India Company , based in Calcutta , until its headquarters were moved to London in 1867 .
At around the same time, British policy towards the Malay states became increasingly aggressive. Within a few years, several Malay states on the west coast of the peninsula came under British control. At the instigation of the traders in the crown colonies, the government interfered in the affairs of the tin-producing states. At the same time, the British colonial power had to pacify civil wars and interference from Chinese secret societies. The British brought about a peaceful solution with their military might, which the traders preferred. With the Treaty of Pangkor in 1874 the way was cleared for British rule. In 1896 the four sultanates Pahang, Selangor, Perak and Negeri Sembilan were combined to form the Federated Malay States , which were subordinate to the Commissioner of Singapore. He was also the governor of the Straits Settlements. This governor, in turn, was subordinate to the Colonial Office in London.
The other states on the peninsula were not directly subordinate to London, but the sultans had British advisors at their court. The four northern states of Perlis , Kedah , Kelantan and Terengganu were under the control of Thailand until 1909 . The area of today's state of Sabah was a British protectorate that originally belonged to the Sultanate of Brunei and Sultanate of Sulu and was administered by the British North Borneo Company under the name of North Borneo . The vast wooded area of Sarawak was the personal property of the British Brooke family, who received the land as a fief from the Sultan of Brunei and ruled it as White Rajas for almost a century. During the Second World War, what is now Malaysia was occupied by Japan. During this time support for the country's independence from the European colonial power grew. The British plans to form a Malay Union were rejected by many Malays. They demanded a system that took greater account of the wishes of the Malays, excluded Singapore out of concerns about the sinization of the country and denied immigrants double citizenship . On August 31, 1957, the Malaya Federation , consisting of the nine Malay sultanates and the two Straits Settlements Penang and Malacca , gained its independence.
On September 16, 1963, a new federation was founded under the name Malaysia , which included the Malaya Federation , the British Crown Colony Singapore and the Protectorates of North Borneo (now Sabah) and Sarawak. The early years were determined by territorial claims of the neighbors, in particular by the Konfrontasi initiated by Indonesia , by Singapore's departure from the federation in 1965 and by the North Borneo dispute in which the Philippines want to assert claims to Sabah .
politics
Form of government

Malaysia is a federal , constitutional , parliamentary-democratic electoral monarchy (parliamentary monarchy). The representative head of state is the king , who is chosen every five years from among the rulers of the nine sultanates on a rotating basis . His official title is Yang di-Pertuan Agong . Sultan Abdullah Shah of Pahang has held this office since January 31, 2019 . This system of election from the ranks of the federal rulers (or federal princes) is almost unique in the world. Only the United Arab Emirates are also an elective federal monarchy.
The parliamentary head of government is the Malaysian prime minister . Muhyiddin Yassin has held this post since March 1, 2020 .
The House of Representatives ( Dewan Rakyat ) currently consists of 222 members elected for five years. The country assembly (Dewan Negara) has 70 members. The last elections to the People's Assembly took place in May 2018.
The national holiday is August 31st (Independence Day 1957).
Electoral system
At the federal level there is a majority voting system in which only one candidate per constituency is elected to parliament. Until the 2018 election, this was often an advantage for the closed Barisan Nasional over the divided opposition. The size of the constituencies is sometimes very different, so that a vote has very different weight depending on the constituency.
Active women's suffrage was introduced in 1955 under the colonial administration . When the country gained independence from Great Britain in 1957, active and passive voting rights for women were incorporated into the constitution on August 31, 1957.
Parties
From 1957 to 2018 the party alliance Barisan Nasional, led by the United Malays National Organization ( UMNO for short , in Malaysian Pertubuhan Kebangsaan Melayu Bersatu ) ruled . Initially this alliance was called Alliance and consisted of the Malay party UMNO, the Chinese MCA and the Indian MIC , which represented the three largest ethnic groups. After the race riots that followed the parliamentary elections in 1969, the alliance was expanded and renamed. In 1974 the Barisan Nasional ("National Front") was founded. In addition to the ten named parties, the BN also includes other parties that are primarily of regional importance. The parties of the BN often agreed to only allow one candidate to stand for election, so that there was no competition between them and the votes were distributed among several BN politicians. As a result, she mostly managed to achieve a two-thirds majority in the Malaysian parliament, which allows constitutional changes. Only in the 1969 and 2008 elections did it fail to achieve this two-thirds majority, but was still able to maintain an absolute majority and thus form the government. Some BN members also act as competitors at the state level .
The opposition was not unified. In the 1999 parliamentary elections, four opposition parties formed the Barisan Alternatif alliance. This fell apart again after it was unable to achieve any notable successes either in 1999 or in the next election in 2004. The most important opposition parties and members of the former opposition alliance are the PAS , the DAP and the PKR . The PAS represents a Malay-Islamist policy. The DAP has a social democratic program and is mainly elected by Malaysians of Chinese origin. These three parties reunited in 2008 to form an alliance, the Pakatan Rakyat coalition, led by the disempowered, very popular former UMNO politician Anwar Ibrahim, and achieved a surprising success in the 2008 parliamentary elections when they gained a majority in five of the 13 states And prevented the Barisan Nasional from gaining a two-thirds majority in the national parliament, which was the case for the first time since 1969.
The coalition government of Prime Minister Najib Tun Razak emerged victorious from the parliamentary elections in May 2013 , despite a significant loss of votes. It reached 133 of 222 parliamentary seats and had an absolute majority with 59.91% of the seats, although the Pakatan opposition alliance was able to unite more votes. In the following election in 2018 , however, the opposition alliance Pakatan Harapan , led by the former long-time Prime Minister Mahathir bin Mohamad , managed to win a majority in the lower house. It replaced the Barisan Nasional (BN) for the first time and provided the new Prime Minister.
Federal structure
Malaysia is divided into 13 states (Malaysian: negeri ) and the three federal territories (Malaysian: wilayah persekutuan ) Kuala Lumpur, Putrajaya (new seat of government) and the island of Labuan . The head of state in nine federal states is a sultan or a Raja in Perlis , who is mainly responsible for representative tasks; in the remaining four, a governor, the Yang di-Pertua Negeri , appointed by the Malaysian king on the proposal of the federal government, assumes the function of head of state.
The state legislature is exercised everywhere by a unicameral parliament . The state executive is in each case carried out by a chief minister and the other ministers; the appointment of the head of government is done by the sultan or governor according to the majority in parliament ( Westminster system ).
The division of competencies between the federal government and the individual state is regulated in an annex to the federal constitution, which contains a list of the federal, the member states and the competing legislative competences.
- The federal government is particularly responsible for external relations, defense, internal security, civil and criminal law, federal state and administrative law, finance, trade, trade and industry, transport, education, labor law, health law, media law and tourism.
- The member states are responsible for areas such as Sharia law and courts, land rights, agriculture and forestry, municipal law, accommodation, markets, the licensing of theaters, cinemas and other places of entertainment, regional public works, regional state and administrative law, inland fishing as well as libraries, museums and archaeological sites. The states of Sabah and Sarawak are also responsible for ports and domestic shipping, land surveying and water supply, and Sabah for the Sabah State Railway .
- Competing legislation applies to social welfare, scholarships, nature and animal protection, urban and local planning, the hiking industry, public health care, land improvement and erosion control, fire protection, culture and sport, housing construction, water supply and monument preservation. In Sabah and Sarawak, family law, shipping and fishing at sea, agronomic research and plant protection, hydroelectric power stations, theaters, movie theaters and other places of entertainment are also subject to competing legislation.
Political indices
| Name of the index | Index value | Worldwide rank | Interpretation aid | year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fragile States Index | 57.6 out of 120 | 120 of 178 | Stability of the country: Stable 0 = very sustainable / 120 = very alarming |
2020 |
| Democracy index | 7.19 out of 10 | 39 of 167 | Incomplete democracy 0 = authoritarian regime / 10 = complete democracy |
2020 |
| Freedom in the World Index | 52 of 100 | - | Freedom status: partially free 0 = not free / 100 = free |
2020 |
| Freedom of the press ranking | 39.47 out of 100 | 119 of 180 | Difficult situation for freedom of the press 0 = good situation / 100 = very serious situation |
2021 |
| Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) | 51 of 100 | 57 of 180 | 0 = very corrupt / 100 = very clean | 2020 |
Foreign policy
Malaysia's foreign policy is determined by its geographic location, its integration into global trade and its own demographic composition. Foreign policy guidelines are non-interference in internal affairs and the promotion of exchanges with other emerging countries.
Malaysia is a member of the Non-Aligned Movement , Group of Eight Developing Countries , the Commonwealth of Nations and the Group of 77 . Malaysia has a particular interest in the countries of the Middle East, although the country has no diplomatic relations with Israel. Since Prime Minister Najib took office, Malaysia has been more cautious in the Middle East. Malaysia has joined coalitions against IS terrorism, but excludes its own military support without a UN mandate. Malaysia also provides troops for the UN.
As a founding member of ASEAN, Malaysia sees itself committed to the central role of ASEAN and to closer cooperation between the member states. Under the Malaysian presidency, the ASEAN Economic Community was launched in 2015 and strengthened Malaysia's regional integration. Malaysia plays an important role in the organization. In addition to ASEAN-centered regional activities, Malaysia is a member of a large number of other international and regional organizations of religious ( Organization for Islamic Cooperation ) and economic character, including those of South-South cooperation. In relation to the two most important partners outside of ASEAN - China and the USA - Malaysia is geared towards balancing interests. The relationship with China is qualified as a "comprehensive strategic partnership". It is characterized by intensive economic contacts and foreign direct investments by China in Malaysia as well as its diverse cultural and scientific connections. China is Malaysia's most important trading partner. A special aspect of the relationship is the fact that a good fifth of the Malaysian population is of Chinese descent. However, competing territorial claims in the South China Sea have not yet been clarified. Relations with western countries including the US, Australia and the EU remain of great importance. This is particularly true with regard to security policy, trade and investment as well as technology transfer and student exchanges.
There are good relationships with all member states of the European Union. The European External Action Service is represented in Kuala Lumpur. Great Britain as a former colonial power occupies a special position.
Human rights
In May 2018, Mahathir Mohamad surprisingly became prime minister. His election promises included strengthening human rights in Malaysia.
- death penalty
The death penalty in Malaysia is among other things murder, kidnapping, terrorism, firearms possession and drug trafficking, sometimes mandatory. It is carried out by hanging, based on the implementation in British colonial times. (As of 2018). At the end of 2018, the government said there were almost 1,200 convicts waiting on death row in Malaysian prisons.
Parliament has been deliberating on a cabinet decision since October 2018, which provides for the abolition of the death penalty. As a result, the government suspended all executions. The last executions were carried out in Malaysia in 2017.
In 2013, more than 100 death sentences were passed annually in Malaysia, 70% for drug smuggling. However, they were seldom carried out.
- Legal status of homosexuals
In Malaysia - in contrast to most other neighboring Southeast Asian countries - homosexuality is generally punishable. For this reason, there are no anti-discrimination regulations to protect sexual orientation or official recognition of same-sex couples. Rather, it can be observed that cautious attempts to achieve an objective discussion in public and in the media are increasingly being opposed by state repression.
In February 2015, Malaysian opposition leader Anwar Ibrahim was sentenced to five years in prison for allegedly having had a homosexual relationship with an employee. Anwar himself and human rights organizations such as Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch criticized the process as politically motivated.
military
The armed forces of Malaysia (Angkatan Tentera Malaysia) are divided into army , air force and navy with a total strength of just over 100,000 active soldiers . The Malaysian Armed Forces can trace their history back to earlier military units that arose under British colonial rule. The British concentrated their soldiers, whose men usually came from India, in Singapore . In the sultanates only armed police units from Indians were set up, such as the 1st Perak Sikhs (1874), Selangor Military Force (1875, 530 men) and Sungei Ujung Police (1874). In the 1895 treaty, the princes undertook to collectively finance the Malay States Guides , which were formed from the police forces . Then there was the 1st Battalion Perak Sikhs. All of these mercenaries were recruited in Punjab and commanded by the British. A European militia, the Malay States Volunteer Rifles , was set up in 1902 (1911: 561 men, 22 officers, 6 months of training). The First Malay Experimental Company was established on March 1, 1933 and consisted of Malay recruits and British instructors. In 1935 it was upgraded to the Malay Regiment , and a short time later, Malays were also used as officers for the first time, instead of just as simple men as before. When Japan conquered large parts of Southeast Asia during World War II , the Malay Regiment, which had now grown to 1,400 soldiers, joined forces with British units in the ultimately unsuccessful defense of the Malay Peninsula and Singapore. It was disbanded during the Japanese occupation. The Malay Regiment, which had already been re-established in September 1945 with the surviving veterans of the pre-war unit, was constantly strengthened and by 1953 had reached a strength of seven battalions or about 5,000 soldiers. In 1952, the Federation Regiment and the Federation Armored Car Squadron were also founded. The Malaya Federation (at that time still a British colony) now had its own de jure army for the first time. On August 31, 1957, the Malaya Federation, consisting of the nine Malay sultanates and the two Straits Settlements Penang and Malacca , gained their independence. The Malayan Emergency , the fight with the Malayan Races Liberation Army (MRLA) lasted until 1960. On September 16, 1963 a new federation was founded under the name Malaysia , which also included the British Crown Colony of Singapore and the protectorates of North Borneo (now Sabah ) and Sarawak included. Today's armed forces were formally re-established from the units of the Malaya Federation and the Sarawak Rangers . The early years were determined by territorial claims of the neighbors, in particular the Konfrontasi (1963-1966) initiated by Indonesia, the departure of Singapore from the federation in 1965 and the North Borneo dispute in which the Philippines claimed Sabah ( the former North Borneo ) want to assert. The armed forces of Malaysia were supported by Australia and Great Britain until 1971 under the ANZAM and the Anglo-Malayan Defense Agreement . From the 1990s, the Malaysian armed forces have been extensively modernized. Malaysia also participated in global peace missions .
Malaysia spent just under 1.1 percent of its economic output or $ 3.5 billion on its armed forces in 2017.
police
The Polis Diraja Malaysia (Royal Malaysian Police) is the police department of Malaysia. It also includes the Pasukan Gerakan Khas special unit .
business

Generally
Malaysia is a country rich in natural resources and raw materials ( tin , rubber , palm oil , petroleum ). Malaysia is also home to the automobile manufacturers Inokom , Perodua and Proton as well as the oil multinational Petronas . Since the beginning of the 1990s there has been rapid industrial development, which has pushed the country up into the ranks of the up-and-coming emerging countries .
Malaysia is economically and politically one of the most stable countries in Southeast Asia, where the convergence of tradition and modernity, Islam and capitalism is propagated. It is a member of ASEAN , the D-8 and the G15 . As a result of this orientation, the country experienced a fundamental change from a previously majority agricultural state to a technical and capital-intensive industrial location with high development potential. The country has opened up significantly to foreign investors since the 1990s. Another advantage is the global networking of the Chinese ("bamboo network") and Indian minorities in the country.
Despite some liberalization measures, the economy is still regulated by the state. The state fund Khazanah Nasional acts as a strategic arm of the government and invests in numerous industries. Ethnic Malays are often preferred to foreigners and Malaysian Chinese in business life.
The Asian crisis that began in 1997 also hit Malaysia, but the economy has since recovered and is growing again by around 5 to 6%. In 2012, more than 600 mergers and acquisitions valued at more than $ 23 billion with the participation of Malaysian companies were announced. The inflation rate was around 3.8% in 2017. The gross domestic product was US $ 9,360 per inhabitant in 2016 (comparable to Russia). The unemployment rate is given as 3.4% in 2016 and is therefore relatively low. This does not include underemployment. In 2012, 11% of the workforce worked in agriculture, 36% in industry and 53% in the service sector. The total number of employees is estimated at 14.9 million for 2017, of which 38.1% are women. Migrant workers make up 20 to 30 percent of the workforce in Malaysia. Overall, there are around four to six million immigrants living in Malaysia (as of 2021). Most of the migrant workers come from Nepal , Bangladesh , Indonesia or Myanmar . Malaysian wages are an opportunity for people to better provide for their families in their home countries. In 2018, foreign workers transferred more than 8.4 billion euros to their families abroad.
Tourism is of great importance for the country's economy. With over 26.7 million tourists, Malaysia was the 12th most visited country in the world in 2016. Tourism revenues were over $ 18 billion in the same year. The most visited city in Malaysia is Kuala Lumpur. Most of the visitors to the country come from Singapore, Indonesia and the People's Republic of China.
In 2016, Malaysia was ranked 25th worldwide in the Global Competitiveness Report of the World Economic Forum , making it the Asian country with the sixth highest competitiveness. In 2017, the country was ranked 23rd out of 180 countries in the index for economic freedom .
Foreign trade
Malaysia is very export-oriented and, as a full member of the World Trade Organization as well as in ASEAN and APEC, has been committed to the dismantling of trade barriers. The foreign trade volume corresponds to 1.2 times the gross national product. The domestic economy is therefore also dependent on demand in the main sales markets. The most important export goods are electronic goods (36.6%). The share of crude oil, oil products, liquefied natural gas (LNG), palm oil, palm oil products and rubber products in Malaysian exports has continued to fall to around 22 percent. At the beginning of 2017, raw material prices rose slightly again. Due to the relatively successful positioning of the manufacturing industry, Malaysian exports grew by 1.5 percent in 2016.
The People's Republic of China has been the most important trading partner since 2009. With the exception of the USA, the top 10 trading partners are in the region. The total share of the EU member states in Malaysia's foreign trade was constant at 10.1 percent. Germany is the most important trading partner in the EU. Foreign trade with Germany increased in 2016 and is now around EUR 12.3 billion. German exports to Malaysia were almost at the previous year's level at EUR 4.8 billion, while imports to Germany rose by 4.5 percent to EUR 7.6 billion. This means that Germany and Malaysia have a negative trade balance of € 2.8 billion.
Key figures
| year | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
| Change in% yoy | 5.6 | 9.4 | 3.3 | −2.5 | 7.0 | 5.3 | 5.5 | 4.7 | 6.0 | 5.0 | 4.2 | 5.9 |
| absolute (in billion USD) | per inhabitant (in thousands of USD) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| year | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | year | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
| GDP in billions of dollars | 296.4 | 296.5 | 314.5 | GDP per inhabitant (in thousands of dollars) | 9.6 | 9.5 | 9.9 |
| Development of foreign trade (GTAI) in billion US dollars and its year-on-year change in percent | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | ||||
| Billion USD | % yoy | Billion USD | % yoy | Billion USD | % year-on-year | |
| import | 208.8 | +1.5 | 176.2 | −15.6 | 168.4 | −4.4 |
| export | 234.1 | +2.5 | 200.2 | −14.5 | 189.4 | −5.4 |
| balance | +25.3 | +24.0 | +21.0 | |||
| Export (in percent) to | Import (in percent) of | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
14.6 |
|
20.4 |
|
|
12.5 |
|
10.4 |
|
|
10.2 |
|
8.2 |
|
|
8.1 |
|
8.0 |
|
|
5.6 |
|
6.1 |
|
|
4.8 |
|
6.0 |
|
|
4.1 |
|
5.2 |
|
|
40.1 |
|
35.7 |
State budget
The state budget included expenditures in 2016 of the equivalent of 63 billion US dollars , which were income equivalent to 52.4 billion US dollar against. This results in a budget deficit of 3.6% of GDP . The national debt for the third quarter of 2012 was $ 159 billion, or 51.8% of GDP. The country 's government bonds are rated A− by the rating agency Standard & Poor’s and the outlook is considered stable (as of 2018). The country thus has a relatively high credit rating and can take out new loans at moderate interest rates.
From the $ 16.3 billion budget for development spending, Malaysia invested in the areas in 2012
- Health : $ 622 million (3.9%),
- Education : $ 2.8 billion (17.4%) and for
- Security : $ 1.4 billion (8.8%).
The expenditure on security is divided into the defense budget (1.2 billion US dollars) and the budget for homeland security (272 million US dollars).
traffic
Thanks to high investments and a decade-long economic boom, Malaysia now has a relatively efficient infrastructure. In 2018, Malaysia ranked 41st out of 160 countries in the Logistics Performance Index , which is compiled by the World Bank .
railroad

- story
The first railroad in Malaysia ran from Taiping to Port Weld and opened on June 1, 1885. In 1886 a route followed from Kuala Lumpur to the port of Klang . In 1903 the railway reached Butterworth across from Penang in the north and Negri Sembilan in the south . Also in 1903 the route from Singapore to Woodlands was opened. In 1910, continuous rail traffic between Kuala Lumpur and Singapore was possible, but there was still a ferry from the mainland to Singapore . The permanent connection, a road and rail embankment, was not completed until 1923. After Great Britain annexed the northern sultanates of Thailand in 1909 in favor of Malaya , the railroad was advanced in the north. Cross-border traffic with Thailand was put into operation in 1918, the eastern border crossing at Sungai Kolok on November 1, 1921. The Bukit-Bunga-Ban-Buketa Bridge is the newest bridge to Thailand.
- Infrastructure
The railway infrastructure of Malaysia covers 1792 kilometers of route (as of 2011). Of this, 1735 km are in the meter gauge, which is historically customary for Malaysia , and 57 km in standard gauge of 1435 mm. The majority of the network runs on the mainland and is operated by the Keretapi Tanah Melayu (Malay Railway). About 207 km of the route are electrified , most of them are on the west side of the peninsula in the greater Kuala Lumpur area. A double-track new line from Kuala Lumpur to Ipoh designed for a top speed of 160 km / h was completed in early 2008. To the north of Ipoh, the extension to Padang Besar near the border with Thailand is currently under construction as part of the Electrified double track project (EDTP). This should be completed in November 2014 and improve the connection between the states of Perak, Penang, Kedah and Perlis with the capital.
In cross-border traffic there are two routes to Thailand, which connect there to the Thai southern railway . In the south there is a cross-border connection to Singapore. However, since July 2011 the trains have only run to Woodlands Train Checkpoint (WTCP) and no longer go to the historic central station.
There is also the Keretapi Negeri Sabah , the state railway of the state of Sabah , which operates a 134 km long line in the 1000 mm gauge on Borneo .
In Kuala Lumpur associate with Kuala Lumpur Star Light Rail Transit , Kuala Lumpur Putra Light Rail Transit , KLIA Ekspres- and KLIA-CRS and KL Monorail several rail-based transportation services.
- business
In terms of price, the railroad in Malaysia is a very cheap means of transport. The ticket from Kuala Lumpur to Woodlands Train Checkpoint in the 1st class sleeping car with a double bed, private bathroom and breakfast costs around EUR 35 (as of 2014) , and accordingly less in the seated car.
road
Due to the British colonial past, there is left-hand traffic . Malaysia has around 125,800 km of paved road (as of 2011), of which around 1,630 km is motorway. The North-South Expressway connects the northern tip of Malaysia on the border with Thailand with Johor Bahru on the border with Singapore in the south. Most of the motorways are subject to tolls , and the fee is collected on the spot at toll stations.
While the roads in the metropolitan areas are exemplary, apart from the densely populated areas, especially in East Malaysia or on the east coast of the Malay Peninsula, there are numerous roads without asphalt. Because of the poorly developed roads in remote areas of East Malaysia, waterways and shipping connections are particularly important.
At the end of 2011, over 21.4 million motor vehicles were registered in Malaysia , almost ten million of which were motorcycles . The state subsidizes the sale of petrol, diesel and liquefied petroleum gas and sets a binding sales price. The petrol price for RON 95 has been RM 2.30 per liter since October 1, 2014, equivalent to EUR 0.56 (rate: Nov 2, 2014).
In 2013, there were a total of 24 road deaths for every 100,000 inhabitants in Malaysia. For comparison: In Germany there were 4.3 deaths in the same year. In total, more than 7,000 people were killed in traffic.
Waterways
Important seaports are located in the cities of Tanjong Kidurong , Kota Kinabalu , Kuching , Pasir Gudang , Penang , Port Klang , Sandakan and Tawau . The country also has around 7,200 km of navigable waterways, 4,000 km of which are in Eastern Malaysia.
aviation
Malaysia has a very dense network of domestic flight connections, not least because of its geography. The country's national airline is called Malaysia Airlines , and Air Asia, the first low-cost airline in Southeast Asia, is based in Kuala Lumpur. Malaysia Airlines serves numerous airports within Malaysia and Southeast Asia, but also offers long-haul flights to Europe and North America. The largest and most important airport in the country is the Kuala Lumpur International Airport , it was opened in 1998.
Culture
- The hibiscus is the national flower of Malaysia.
- The most famous Malaysian draftsman and caricaturist is Lat .
media
The Malaysian media is not independent. A rigid legal framework restricts their freedom to develop, for example the Printing Presses and Publications Act (PPPA) of 1984. This law regulates the printing, importing, reproducing, publishing and distributing of publications. The Minister of the Interior issues annual licenses for printed products that can be revoked at any time. Failure to comply can result in a prison sentence of up to three years.
The state news agency BERNAMA has the exclusive rights to disseminate economic data , news images and other material via the print media. The majority of classic media products (print and television as well as radio) are in government hands or belong to government-related companies. There is hardly any opposition media.
New media are on the rise. In 2008 there were 100 cell phones for every 100 inhabitants. In 2019, 84 percent of Malaysia's residents used the internet . Although the Internet can develop more freely than the classic media, a trend towards control and censorship can also be seen here. In particular, critical political blogs , online newspapers and discussion forums are being monitored more closely by the authorities. These are very popular among the population.
Sports
From 1999 to 2017 Auto Racing (Formula 1) annually at the Sepang International Circuit of the Malaysian Grand Prix held.
Some of the most popular sports in Malaysia include badminton , soccer, and hockey. Badminton in particular has a long tradition in Malaysia. The silat is considered a traditional martial art of the Malays.
literature
- CHEVALLIER-GOVERS, Constance, Malaysia and the European Union: A Partnership for the 21st Century, (co-direction avec Marcinkowski C. & Harun R.), LIT Verlag, 2011, 271 p.
- CHEVALLIER-GOVERS, Constance, Shariah and Legal Pluralism in Malaysia, Islam and Civilisational Renewal, Octobre 2010, pp. 91-108.
- Alois Karl Leinweber: Living and Working in Malaysia. GD Gentlemen's Digest, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-939338-26-0 .
- Jürgen Kremb : Death threats in paradise. Spiegel Online , July 24, 2007, accessed June 23, 2019 .
Web links
- Website of the Government of Malaysia
- Database of indexed literature on the social, political and economic situation in Malaysia
- Climate charts and climate tables for Malaysia
- KL-POST - information magazine for German speakers in Malaysia
- Full text of the Malaysian constitution (PDF; 3.0 MB)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Statistical Handbook Malaysia 2012. (PDF) Department of Statistics Malaysia, May 15, 2013, accessed October 8, 2013 (Malay, English; PDF, 3.03 MB; page 1; PDF page 22).
- ↑ population, total. In: World Economic Outlook Database. World Bank , 2020, accessed February 10, 2021 .
- ↑ Population growth (annual%). In: World Economic Outlook Database. World Bank , 2020, accessed February 10, 2021 .
- ↑ World Economic Outlook Database October 2020. In: World Economic Outlook Database. International Monetary Fund , 2020, accessed February 10, 2021 .
- ↑ Table: Human Development Index and its components . In: United Nations Development Program (ed.): Human Development Report 2020 . United Nations Development Program, New York 2020, ISBN 978-92-1126442-5 , pp. 344 (English, undp.org [PDF]).
- ^ A b The UK Statute Law Database: Federation of Malaya Independence Act 1957 (c. 60)
- ↑ a b c United Nations Treaty Series No. 10760: Agreement relating to Malaysia (July 1963). (PDF; 4.48 MB) In: UN Treaty collection, UNTC . Archived from the original on January 11, 2012 ; accessed on October 8, 2013 .
- ↑ Member States of the United Nations
- ↑ a b Inter-Parliamentary Union: IPU PARLINE database: MALAYSIA (Dewan Rakyat), Last elections. Retrieved September 24, 2018 .
- ↑ a b c Brockhaus online Keyword: Malaysia , Munich 2019, accessed on April 10, 2019.
- ↑ Numbers for 2030 and 2050 are forecasts
- ↑ a b World Population Prospects - Population Division - United Nations. Retrieved July 24, 2017 .
- ↑ population, total. In: World Economic Outlook Database. World Bank , 2020, accessed May 4, 2021 .
- ↑ a b The World Factbook : Malaysia , December 4, 2008
- ↑ a b Meyer's Lexicon online: Malaysia ( Memento from June 25, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) in the Internet Archive
- ↑ a b Peter Bengtsen: Forced Labor in Malaysia: This is how disposable gloves are made for Germany. In: Der Spiegel. Retrieved April 11, 2021 .
- ↑ Urban population (% of total) | Data. Retrieved July 24, 2017 (American English).
- ↑ World Population Prospects - Population Division - United Nations. Retrieved July 19, 2017 .
- ^ Religion . Tourism Malaysia. Archived from the original on April 10, 2011. Retrieved July 15, 2011.
- ↑ Taburan Penduduk dan Ciri-ciri Asa's demographics . Jabatan Perangkaan Malaysia. Archived from the original on November 13, 2013. Retrieved March 25, 2013.
- ↑ malaysianbar.org:PRESS STATEMENT: Malaysia a secular State , July 18, 2007
- ^ Wu & Hickling, p. 35.
- ↑ Vatican Radio : Malaysia: Imprisonment for Hindu marriage ( memento of September 26, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) August 11, 2007
- ↑ a b AsiaNews.it: A Hindu Lina Joy, Subjected to Islamic "re-education" , 15. June 2007
- ↑ Jalil Hamid and Liau Y-Sing: Malaysia braces for ruling on Islam conversion , Reuters, August 13, 2006
- ↑ Jürgen Kremb: Death Threats in Paradise , Der Spiegel , July 24, 2007
- ↑ AsiaNews.it: Death threats against Lina Joy, fighting for her life and religious freedom 29 August, 2006.
- ↑ Shah Yacob, Imran Imtiaz: Doing the Impossible: Quitting Islam in Malaysia , Asia Sentinel, April 27, 2007
- ↑ AsiaNews.it: Kuala Lumpur refuses to recognize Lina Joy's conversion to Christianity , May 30, 2007
- ↑ NZZ : Verdict against religious freedom ( memento of June 2, 2007 in the Internet Archive ), May 31, 2007
- ↑ Daniel Kestenholz: Controversy over God's name - Christians in Malaysia have Allah again. Der Tagesspiegel , January 5, 2001, accessed October 8, 2013 .
- ↑ Decision of a Malaysian Court of Appeal - Only Muslims are allowed to say "Allah". Tagesschau (ARD) , October 14, 2013, archived from the original on October 14, 2013 ; accessed on March 20, 2014 .
- ↑ The Malaysian Insider: Selangor Islamic authorities raid Bible Society of Malaysia, 300 copies of Alkitab seized ( January 5, 2014 memento in the Internet Archive ), January 2, 2014; Accessed January 15, 2014
- ^ PISA study - Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development. Retrieved April 14, 2018 .
- ↑ United Nations Treaty Registered No. 8029, Manila Accord between Philippines, Federation of Malaya and Indonesia (July 31, 1963) ( Memento of January 11, 2012 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ United Nations Treaty Series No. 8809, Agreement relating to the implementation of the Manila Accord (PDF file; 5.56 MB)
- ↑ PROCLAMATION OF SINGAPORE
- ^ Dieter Nohlen, Florian Grotz, Christof Hartmann (eds.): South East Asia, East Asia and the South Pacific. (= Elections in Asia and the Pacific. A Data Handbook. Volume 2). Oxford University Press, New York 2002, ISBN 978-0-19-924959-6 , p. 146
- ↑ June Hannam, Mitzi Auchterlonie, Katherine Holden: International Encyclopedia of Women's Suffrage. ABC-Clio, Santa Barbara, Denver, Oxford 2000, ISBN 1-57607-064-6 , p. 179.
- ^ Mart Martin: The Almanac of Women and Minorities in World Politics. Westview Press Boulder, Colorado, 2000, p. 245.
- ↑ Federal Constitution (as of 2010) , accessed October 19, 2018.
- ^ Ninth Schedule: Legislative Lists, accessed October 19, 2018.
- ^ Fragile States Index: Global Data. Fund for Peace , 2020, accessed February 10, 2021 .
- ^ The Economist Intelligence Unit's Democracy Index. The Economist Intelligence Unit, accessed February 10, 2021 .
- ^ Countries and Territories. Freedom House , 2020, accessed February 10, 2021 .
- ↑ 2021 World Press Freedom Index. Reporters Without Borders , 2021, accessed May 4, 2021 .
- ^ Transparency International (Ed.): Corruption Perceptions Index . Transparency International, Berlin 2021, ISBN 978-3-96076-157-0 (English, transparencycdn.org [PDF]).
- ↑ Foreign Office. Retrieved July 19, 2017 .
- ↑ a b Malaysia plans to abolish the death penalty
- ↑ Amnesty Report Malaysia May 23, 2018 Malaysia 2017/18
- ↑ Drug smuggling - death sentence against Germans - world
- ↑ Malaysia hunts homosexuals , Spiegel-Online from January 1, 2012; Accessed January 1, 2012
- ^ Opposition chief must be arrested for homosexuality , Die Welt Online of February 10, 2015
- ↑ Patrick Morrah: The History of the Malayan Police , Journal of the Malayan Branch, Royal Asiatic Society, Vol. XXXVI (1963), Pt. 2, No. 202, pp. 46-79
- ↑ see also: SMS Emden (1908) (mutiny of the guards 1915 in Singapore)
- ↑ Lim Kai Tong (1999): The Malay Regiment - "Ta'at Dan Setia": 1933-1945 .
- ↑ Kevin Blackburn: The commemoration and memory of the Malay Regiment in modern Malaysia and Singapore . In: Karl Hack / Tobias Rettig (eds.): Colonial armies in Southeast Asia , Routledge: Oxon, New York 2006, ISBN 0-415-33413-6 , pp. 302–326.
- ↑ United Nations Treaty Registered No. 8029, Manila Accord between Philippines, Federation of Malaya and Indonesia (July 31, 1963) ( Memento of January 11, 2012 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ United Nations Treaty Series No. 8809, Agreement relating to the implementation of the Manila Accord (PDF file; 5.56 MB)
- ↑ PROCLAMATION OF SINGAPORE
- ↑ Home | SIPRI. Retrieved July 10, 2017 .
- ^ Institute of Mergers, Acquisitions and Alliances (IMAA) ; Accessed April 4, 2013
- ^ The World Factbook - Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved August 6, 2018 .
- ↑ UNWTO 2017. World Tourism Organization, accessed August 14, 2018 .
- ↑ heritage.org
- ↑ Germany Trade and Invest GmbH: GTAI - Search. Retrieved July 19, 2017 .
- ↑ GDP growth (annual%). Data. Retrieved July 28, 2017 (American English).
- ↑ Malaysia | Data. Retrieved July 28, 2017 (American English).
- ↑ a b Germany Trade and Invest GmbH: GTAI - economic data compact. Retrieved July 28, 2017 .
- ↑ Ministry of Finance Malaysia: Malaysian Economy, Third Quarter 2012 ( Memento of February 5, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF; 660 kB), p. 16; Accessed December 18, 2012.
- ↑ Credit Rating - Countries - List. Retrieved November 28, 2018 .
- ↑ a b c d e Ministry of Finance Malaysia: Ekonomic Report 2012/2013 (PDF; 961 kB), Chapter 4, pp. 131-136; Accessed December 18, 2012.
- ↑ Global Rankings 2018 | Logistics Performance Index. Retrieved September 14, 2018 .
- ^ BR Whyte: The Railway Atlas of Thailand, Laos and Cambodia . White Lotus Co Ltd, Bangkok 2010, ISBN 978-974-480-157-9 , p. 42.
- ^ BR Whyte: The Railway Atlas of Thailand, Laos and Cambodia . White Lotus Co Ltd, Bangkok 2010, ISBN 978-974-480-157-9 , p. 45.
- ↑ a b Statistical Handbook Malaysia 2012. (PDF) Department of Statistics Malaysia, May 15, 2013, accessed on October 8, 2013 (Malay, English; PDF, 3.03 MB; page 45; PDF page 71).
- ↑ Gamuda EDTP page. Gamuda Berhad, 2012, archived from the original on June 23, 2014 ; accessed on March 24, 2014 .
- ↑ Statistical Handbook Malaysia 2012. (PDF) Department of Statistics Malaysia, May 15, 2013, accessed October 8, 2013 (Malay, English; PDF, 3.03 MB; page 46; PDF page 72).
- ↑ Global status report on road safety 2015. Retrieved March 30, 2018 (British English).
- ^ Individuals using the Internet (% of population). World Bank , accessed May 4, 2021 .
- ↑ Knirsch, Thomas S. / Kratzenstein, Patrick: "Freedom of the press, new media and political communication in Malaysia - a society in transition". KAS-Auslandsinformationen 6/2010 , p. 103 ff.
Coordinates: 2 ° N , 112 ° E