Europe
| surface | 10,523,000 km² |
|---|---|
| population | 746 million (mid-2019) |
| Population density | 75 inhabitants / km² |
| countries | approx. 50 |
| Time zones | UTC ± 0 ( Iceland ) to UTC + 5 ( Russia ) |
Europe ( ancient Greek Εὐρώπη Eurṓpē ) is a continent that extends over the western fifth of the Eurasian land mass. Although it is geographically only one subcontinent that forms the continent of Eurasia together with Asia , it is historically and culturally justified and often viewed as an independent continent . This indicates that the term “Europe” is not limited to the geographical definition, but also refers to historical, cultural, political, economic, legal and ideal aspects.
The inhabitants of Europe are called Europeans . With over 700 million inhabitants, who live in an area of around 10.5 million square kilometers, Europe is one of the more densely populated parts of the world . Europe is heavily urbanized , especially in the area of the capital cities and the megalopolis " Blue Banana ". Important political alliances in Europe are above all the Council of Europe and the European Union .
Surname
The name "Europe" goes back to the ancient Greek Εὐρώπη ( Eurṓpē ) . Within the Greek of the name could as a compound of εὐρύς , Eurys , "far, broad" and ὄψ , ops , "view face" be interpreted to give the meaning "the Breitgesichtige" would result "the broad with the view" or.

According to Greek mythology , Eurṓpē was the name of a Phoenician king's daughter, who kidnapped Zeus in the form of a bull to Crete and seduced her there. According to etymologists, this name comes from a Semitic language and was then Graecised . Discussed an origin from the Akkadian erebu "perish" (relative to the sun) or from the Phoenician erob "Evening, West" (see. The term " West ").
In the 5th century BC, the Greek writer and geographer Herodotus referred the term Eurṓpē , which at that time had only referred to the Peloponnese as a geographical term , to the land masses north of the Mediterranean and the Black Sea , which he derived from the land masses of Asia ( Asía ) and Africa ( Libýe ) .
Europe itself is the namesake for the chemical element europium, discovered in 1890 .
geography
In the east, Europe has no clear geographical or geological boundary with Asia . That is why the 'borders of Europe' are a question of social agreement. A geographical definition of Europe is always arbitrary. According to Bernard-Henri Lévy , Europe is “not a place, but an idea”. Today, when drawing the boundaries between Europe and Asia, one usually largely follows the definition of Philip Johan von Strahlberg . After that, the Ural mountains and the river form the eastern border of Europe. Between the Caspian Sea and the Black Sea , the borderline runs through the Manytn lowlands north of the Caucasus Mountains , as a strait once connected the Caspian Sea with the Black Sea in its place. The globe shown above draws - slightly different - the border along the main Caucasus ridge; this demarcation is preferred in the English- and French-speaking countries (→ Inner Eurasian border ).
Overall, Europe has an area of around 10.5 million square kilometers, making it the second smallest continent after Australia . The northernmost point of mainland Europe is Kinnarodden on the northern chin peninsula in Norway , the southernmost is the Punta de Tarifa in Spain, the westernmost the Cabo da Roca in Portugal . The north-south extension is about 3800 km. In the east-west direction, the European mainland measures about 6000 km, from the Ural Mountains in Russia to the Atlantic coast of Portugal.
climate
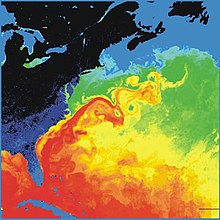
The continent lies mainly in the temperate latitudes . The climate in Europe is milder compared to areas of the same geographical latitude in other parts of the world due to the influence of the relatively warm Gulf Stream . The average annual temperature of Bordeaux , for example, is 12.8 ° C, while Halifax (Nova Scotia) in Canada, which is at almost the same latitude, only reaches 6.3 ° C.
In large parts of Western Europe, mild winters contrast with cool summers . In areas that are far from the sea, i.e. also from its climatically compensating influence, the temperature differences are greater in different seasons. In most of Eastern Europe , the lack of a sea in the immediate vicinity means that the climate is predominantly continental . Cold winters and hot summers are prevalent in these regions.
Due to the rotation of the earth and the associated distracting force, winds come mainly from the west. Since the winds mainly blow from the Atlantic Ocean in the coastal areas of Western Europe , it rains almost all year round. In Eastern and Central Europe , on the other hand, the amount of precipitation is comparatively low, as the influence of the sea on these regions is again too small. Mountains also have a strong influence on the amount of precipitation. Parts of the north-western Alps are among the regions with the highest rainfall in Europe, while central Alpine valleys are comparatively dry. In this case, the Alps act as a barrier for rain fronts.
Areas near the Mediterranean Sea have a predominantly Mediterranean climate , i.e. dry and hot summers, while winters are mild and humid. In summer there are predominantly winds from the north, in winter westerly winds from the direction of the Atlantic Ocean bring with them frequent precipitation. In northern Europe there is an arctic climate , in the southeast on the Volga, on the other hand, a continental climate with hot summers and little precipitation. So it can be B. also be that in Lapland there is still snow, while in Sicily complained of heat it on the Shetland islands constantly raining and Andalusia is plagued by years of drought.
flora
The vegetation in Europe can be roughly divided into four zones based on the climate: arctic, boreal, temperate and Mediterranean. Through millennia of use, the original vegetation of Europe in the temperate and Mediterranean zone has been destroyed except for tiny remains. In northern Europe, only shrubs , mosses and lichens can be found in the arctic tundra . Further south, in Scandinavia and northern Russia, boreal coniferous forests (mainly made of spruce and pine ), in which extensive moors are embedded. In the temperate zone between the Atlantic Ocean and the Carpathians, under natural conditions , deciduous forests would presumably grow mainly characterized by red beech , in the warmest low-lying areas also those with deciduous oaks and hornbeams . To the east of the distribution area of the common beech, for example from the Vistula and the Dniester to the southern Urals, mixed forests would probably have formed in which common oak , winter lime , Scots pine and - in the transition to the coniferous forest zone to the north - the spruce play the most important role. To the south, this mixed forest zone north of the Black Sea is followed by a region in which steppe vegetation would have developed under natural conditions .
The Mediterranean area was also originally largely forested. There the vegetation would be characterized by a Mediterranean hardwood forest without human influence , which is dominated by evergreen oak species (especially holm oak ), in the southernmost and warmest locations also with a strong participation of olive trees , pistachios and pines . Due to the anthropogenic influence, however, mainly maquis or garigue plants grow today . In the cooler locations of the Mediterranean region, various deciduous oak species, such as the downy oak , also play a major role. In the middle and higher elevations of the mountains, the original vegetation is better preserved than in the lower elevations. Here, several superimposed height levels are formed in a relatively small space , the individual components of such height level zoning can be very different depending on the climate. In the mountain forests of the middle upper elevations, in addition to the common beech, mainly fir and pine species are important, in the northern mountains also spruce and larch . Above the tree line, dwarf shrub heaths , alpine lawns, and thorn cushion vegetation in the Mediterranean area can be found in the mountains . Towards the top, the closed vegetation is replaced by individually growing rock and debris plants.
According to the controversial megaherbivore hypothesis, however, Europe would have been less forested before the influence of humans, rather varied pasture landscapes of meadows, bushes and smaller hat forests dominated over a large area, formed by herbivores such as aurochs , bison , tarpan and red deer. This hypothesis is u. a. supported by the abundance of oak and hazel pollen and the occurrence of other open land species in Central Europe during the early Holocene .
Today, most of Europe is characterized by agricultural use, the remaining forests are intensively used for forestry . Areas less impaired by humans are mainly in the higher elevations of the mountains.
fauna
Large predators such as the brown bear , Eurasian wolf or lynx can only be found in larger populations in the north or east. In the far north and east of Europe, reindeer and elk are still relatively common. After its extinction, the bison was released back into the wild in Eastern Europe from zoo populations. Red deer , roe deer and wild boar can be found in most regions of Europe. A typical European large animal species is the chamois , which is only found in Asia Minor and the Asian parts of the Caucasus outside of the European mountains. Different species of ibex live in the Alps, the Pyrenees and the Caucasus . The saiga antelope was widespread as far as the Ukraine in the Middle Ages, today it is limited in Europe to areas on the lower reaches of the Volga. Many species have been exterminated centuries ago ( Ur , Tarpan ). The population of birds of prey, such as golden eagles , white-tailed eagles and griffon vultures , has also been severely decimated in recent centuries. Only in southern Europe are there a larger number of lizards , snakes and turtles due to the warm climate . Seals and other seal species live on the coast . In the northern seas the most famous whales are killer whale and porpoise , in the Mediterranean there are various species of dolphins . The most famous saltwater fish are herrings and various types of tuna .
Cities and metropolises
The cities and municipalities form the smallest administrative units in the administrative structure of the states. Lisbon was one of the first cosmopolitan metropolises of modern times, as it was the center of a great colonial empire in the age of imperialism . In 1950 four cities in what is now the European Union were among the 20 largest in the world, since then European cities have barely grown, and in some cases have lost their population. These four largest EU cities today were London in second place behind New York , Paris in fourth place behind Tokyo, and Milan and Naples in 13th and 19th place.
But in the second half of the 20th century, the cities of the rest of the world, especially those in developing countries, e. B. Mexico City , Manila or São Paulo , in the population and now lead the table in the world. Despite stagnation in older cities, there are numerous other processes in spatial development in the 21st century, such as B. the gentrification of inner cities.
The problem when comparing the metropolises is that there are often polycentric metropolitan areas in which the core cities are very small compared to the metropolitan area (e.g. Rhine-Ruhr , the Upper Silesian industrial area or Central England ). Therefore, even if they are sometimes very large, they do not appear in the table below.
Cities with more than 1.5 million inhabitants in Europe are:
| # | city | Country | Population in millions | Established (after document or reference) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| with metropolitan area | |||||
| 1 | Moscow |
|
10.4 | 13.8 | 1147 |
| 2 | London |
|
7.4 | 12.0 | 47 AD |
| 3 | Istanbul (West) * |
|
6.9 ** | 16.0 | 660 BC Chr. *** |
| 4th | St. Petersburg |
|
4.8 | 5.3 | 1703 |
| 5 | Berlin |
|
3.5 | 4.5 | 1237 |
| 6th | Madrid |
|
3.3 | 5.3 | 1083 |
| 7th | Kiev |
|
2.8 | 3.3 | 840 |
| 8th | Rome |
|
2.7 | 3.8 | 753 BC Chr. |
| 9 | Paris |
|
2.1 | 11.5 | 53 BC Chr. |
| 10 | Minsk |
|
1.7 | 2.7 | 1067 |
| 11 | Bucharest |
|
1.9 | 2.6 | 1459 |
| 12 | Vienna |
|
1.9 | 2.8 | 881; 1st century AD |
| 13 | Hamburg |
|
1.7 | 2.6 | early 9th century |
| 14th | Budapest |
|
1.7 | 2.4 | 89 AD |
| 15th | Warsaw |
|
1.7 | 2.4 | 1281 |
| 16 | Barcelona |
|
1.6 | 3.9 | 230 BC Chr. |
| 17th | Munich |
|
1.5 | 2.4 | 1158 |
- * Istanbul lies on the border between Europe and Asia, the old city center and around 2/3 of the city area belong to the European part
- ** Number of inhabitants of the European part of Istanbul
- *** as Byzantion on the European side
Time zones
The United Kingdom, Ireland, Portugal and Iceland have assigned themselves to Western European Time (GMT / WET), which is identical to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). It corresponds to the mean solar time at the prime meridian , which runs through London and eastern England.
All Central and some Western and Eastern European countries use Central European Time (UTC + one hour), these are Spain, France, Andorra, Monaco, the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, Denmark, Sweden, Norway, Germany, Poland, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, Italy, San Marino, the Vatican, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Serbia, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Kosovo, Malta and Albania.
The Eastern European Time (UTC + 2 hours) use Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Ukraine, Romania, Moldavia, Bulgaria and Greece.
The Moscow time (UST + 3 hrs.) Use Belarus and much of European Russia and Turkey.
Most states use a daylight saving time from late March to late October , with clocks advancing one hour over that period. This applies to all EU states, including most of the European non-EU states, but not Iceland, Russia, Belarus and Turkey.
history
The oldest records of representatives of the genus Homo currently come from the Sierra de Atapuerca in Spain and are up to 1.2 million years old. Even older fossil finds from Georgia (outside the current borders of Europe) are 1.8 million years old and are called " Homo erectus ergaster georgicus ". In northern Alpine Europe, the oldest settlement horizon with Homo heidelbergensis began around 600,000 years ago.
Only about 40,000 years ago did Homo sapiens come to Europe (cf. human expansion ) and gradually replaced the Neanderthals . With the Neolithic and Bronze Ages , a long history of great cultural and economic achievements began in Europe, first in the Mediterranean, then also in the north and east.
The Greek culture, the Roman Empire and Christianity in particular have left their mark to this day. In ancient times , at the time of Augustus , the Roman Empire united all of southern Europe for the first time together with the other coastal countries of the Mediterranean in one great empire. In the Roman Empire, the new religion of Christianity could spread quickly. Despite all persecutions, Christianity was promoted in late antiquity by Constantine the Great ( Constantine turn ) and made the state religion under Emperor Theodosius I - a development that continues to this day. With the end of antiquity , the Roman Empire collapsed in the west, but continued to exist in the east as a (more and more Greek-influenced) Byzantine Empire until 1453. During this time, with the migration of peoples, a large number of mostly Germanic tribes ( Anglo-Saxons , Franks , Goths, etc.) pushed into Western Europe and formed the foundation for future nations (England, France, Spain).
In the early Middle Ages , the Paderborn epic declared the ruler of the Franconian Empire , Charlemagne , to be the "father of Europe" (pater Europæ) . The Middle Ages were characterized , among other things, by the competition between the new Roman emperor in the west (→ Roman-German emperor ) and the Byzantine emperor in Constantinople (→ two- emperor problem ), on whose two spheres of influence the later deepening division into western and eastern Europe can be traced back (→ Oriental schism ). Missionaries spread Christianity across Northern and Eastern Europe since the early Middle Ages, so that all of Europe became Christian in the late Middle Ages . In western Europe, however, there have been disputes between the emperor and the pope about supremacy since the investiture dispute in the 11th century . In the age of the Renaissance , the “knowledge of antiquity” was rediscovered in the Latin West, which in part resulted in a cultural boom. The Reformation in the 16th century split the Western Church ( it had already broken with the Orthodox Church in 1054) into a Catholic and Protestant part. Wars of religion were the result. From 1618 to 1648 the Thirty Years' War devastated large parts of Central Europe.
From the 15th century onwards, European nations (especially Spain , Portugal , Russia , the Netherlands , France and the United Kingdom ) built colonial empires with large possessions on every other continent. Europe is the continent that has influenced the other continents the most (for example through Christian proselytizing , colonies , slave trade , exchange of goods and culture ).
In the 18th century, the Enlightenment movement set new accents and demanded tolerance , respect for human dignity , equality and freedom . In France , the French Revolution brought the bourgeoisie to power in 1789 . In the early 19th century, half of Europe had to follow the will of the French Emperor Napoleon , who came to power after the revolution , until he experienced a fiasco in Russia in 1812 . The conservative victorious powers then attempted to restore pre-revolutionary conditions at the Congress of Vienna , which only succeeded temporarily. The industrialization began in parts of Europe in the 18th century and changed rapidly everyday life in the general population. As a result of the impoverishment of the workers, the communist movement emerged in the 19th century . In addition, the 19th century was strongly determined by the spread of democratic ideas and systems, the conservative reaction to them and the imperialism of the great powers, which went hand in hand with unbridled nationalism . Both the First World War (1914 to 1918) and the Second World War (1939 to 1945) broke out in Europe and caused enormous damage. Around 60 million people lost their lives in the latter; an estimated six million of them were Jews who the National Socialists tried to exterminate in their racial madness, as well as homosexuals and " gypsies ".
After World War II and during the Cold War , Europe was divided into two major political-economic blocs: socialist nations in Eastern Europe and capitalist nations in Western Europe. There was also talk of the Iron Curtain that separated the states of Europe from one another. In between there were a few neutral states. It was not until the mid-1980s that perestroika and glasnost led to a political change in the Soviet Union . In 1989 the Eastern Bloc broke up, the Berlin Wall fell, the Soviet Union and the Warsaw Pact dissolved.
Since the last decades of the 20th century, the cultures of Europe have been growing closer together, which is demonstrated on the one hand by institutions such as the EU , but also by the population and economic focus .
politics
Countries of Europe
Depending on the drawing of the border between Europe and Asia as defined by Strahlberg (see: Geography section ), there are currently 47 to 49 sovereign states (excluding Kosovo) that are wholly or partially located in Europe.
- (Capitals in brackets)

-
 Albania ( Tirana )
Albania ( Tirana ) -
 Andorra ( Andorra la Vella )
Andorra ( Andorra la Vella ) -
 Azerbaijan ( Baku )
Azerbaijan ( Baku ) -
 Belgium ( Brussels )
Belgium ( Brussels ) -
 Bosnia and Herzegovina ( Sarajevo )
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( Sarajevo ) -
 Bulgaria ( Sofia )
Bulgaria ( Sofia ) -
 Denmark ( Copenhagen )
Denmark ( Copenhagen ) -
 Germany ( Berlin )
Germany ( Berlin ) -
 Estonia ( Tallinn )
Estonia ( Tallinn ) -
 Finland ( Helsinki )
Finland ( Helsinki ) -
 France ( Paris )
France ( Paris ) -
 Georgia ( Tbilisi )
Georgia ( Tbilisi ) -
 Greece ( Athens )
Greece ( Athens ) -
 Ireland ( Dublin )
Ireland ( Dublin ) -
 Iceland ( Reykjavík )
Iceland ( Reykjavík ) -
 Italy ( Rome )
Italy ( Rome ) -
 Kazakhstan ( Nur-Sultan )
Kazakhstan ( Nur-Sultan ) -
 Kosovo ( Pristina )
Kosovo ( Pristina ) -
 Croatia ( Zagreb )
Croatia ( Zagreb ) -
 Latvia ( Riga )
Latvia ( Riga ) -
 Liechtenstein ( Vaduz )
Liechtenstein ( Vaduz ) -
 Lithuania ( Vilnius )
Lithuania ( Vilnius ) -
 Luxembourg ( Luxembourg )
Luxembourg ( Luxembourg ) -
 Malta ( Valletta )
Malta ( Valletta ) -
 Moldova ( Chișinău )
Moldova ( Chișinău ) -
 Monaco
Monaco
-
 Montenegro ( Podgorica )
Montenegro ( Podgorica ) -
 Netherlands ( Amsterdam )
Netherlands ( Amsterdam ) -
 North Macedonia ( Skopje )
North Macedonia ( Skopje ) -
 Norway ( Oslo )
Norway ( Oslo ) -
 Austria ( Vienna )
Austria ( Vienna ) -
 Poland ( Warsaw )
Poland ( Warsaw ) -
 Portugal ( Lisbon )
Portugal ( Lisbon ) -
 Romania ( Bucharest )
Romania ( Bucharest ) -
 Russia ( Moscow )
Russia ( Moscow ) -
 San Marino ( San Marino )
San Marino ( San Marino ) -
 Sweden ( Stockholm )
Sweden ( Stockholm ) -
 Switzerland ( Bern )
Switzerland ( Bern ) -
 Serbia ( Belgrade )
Serbia ( Belgrade ) -
 Slovakia ( Bratislava )
Slovakia ( Bratislava ) -
 Slovenia ( Ljubljana )
Slovenia ( Ljubljana ) -
 Spain ( Madrid )
Spain ( Madrid ) -
 Czech Republic ( Prague )
Czech Republic ( Prague ) -
 Turkey ( Ankara in Asia )
Turkey ( Ankara in Asia ) -
 Ukraine ( Kiev )
Ukraine ( Kiev ) -
 Hungary ( Budapest )
Hungary ( Budapest ) -
 Vatican city
Vatican city
-
 United Kingdom ( London )
United Kingdom ( London ) -
 Belarus ( Minsk )
Belarus ( Minsk )
- Footnotes
- ↑ a b Depending on the interpretation (partly) in Europe, see #Countries partly in Europe
- ↑ a b c d e f Has non-European possessions, see # Non-European possessions of European countries
- ↑ a b c Is partly in Europe, see #Countries partly in Europe
- ↑ Controversial. Kosovo is recognized by the majority of European states as independent. (See Disputed Areas )
Disputed areas
-
 Kosovo (capital Pristina ): The parliament in the UN- administered Kosovo province unilaterally declared its independence from Serbia on February 17, 2008. Serbia, whose constitution explicitly mentions the Serbian province as an indivisible part of the republic, continues to regard the region as part of Serbia. Kosovo is recognized by the majority of European countries (including Germany, Austria and Switzerland) as independent; others, including Greece, Russia or Spain, do not recognize Kosovo as a separate state.
Kosovo (capital Pristina ): The parliament in the UN- administered Kosovo province unilaterally declared its independence from Serbia on February 17, 2008. Serbia, whose constitution explicitly mentions the Serbian province as an indivisible part of the republic, continues to regard the region as part of Serbia. Kosovo is recognized by the majority of European countries (including Germany, Austria and Switzerland) as independent; others, including Greece, Russia or Spain, do not recognize Kosovo as a separate state.
-
 Transnistria (own name: Pridnestrovie , capital: Tiraspol ): In 1992, a state that was de facto independent from the Republic of Moldova was established in Transnistria , but which is not recognized by any other sovereign state.
Transnistria (own name: Pridnestrovie , capital: Tiraspol ): In 1992, a state that was de facto independent from the Republic of Moldova was established in Transnistria , but which is not recognized by any other sovereign state. -
 Autonomous Republic of Crimea (capital: Simferopol ): Controversial between Russia and Ukraine since the Russian annexation in 2014 .
Autonomous Republic of Crimea (capital: Simferopol ): Controversial between Russia and Ukraine since the Russian annexation in 2014 . -
 Donetsk People's Republic and Luhansk People's Republic : Declared independent in April 2014. Under international law, they are still considered part of Ukraine.
Donetsk People's Republic and Luhansk People's Republic : Declared independent in April 2014. Under international law, they are still considered part of Ukraine.
Other areas
There are also smaller territories that are not an integral part of a state, but are also not fully independent:
-
 Guernsey (capital Saint Peter Port )
Guernsey (capital Saint Peter Port ) -
 Isle of Man (capital Douglas )
Isle of Man (capital Douglas ) -
 Jersey (capital Saint Helier )
Jersey (capital Saint Helier )
- These three areas are crown possessions of the British Crown . They are not part of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
-
 Gibraltar
Gibraltar
- Gibraltar is a British overseas territory . As such, it is under UK sovereignty, but is not part of it.
-
 Faroe Islands (capital Tórshavn )
Faroe Islands (capital Tórshavn ) -
 Greenland (capital Nuuk )
Greenland (capital Nuuk )
- The Faroe Islands and Greenland form the Kingdom of Denmark with the Danish heartland .
-
 Spitzbergen (capital Longyearbyen ), Jan Mayen (capital Olonkinbyen )
Spitzbergen (capital Longyearbyen ), Jan Mayen (capital Olonkinbyen )
- These two areas are part of the Kingdom of Norway and are therefore usually included in Europe. Due to their location between Scandinavia and Greenland (Jan Mayen) or between Scandinavia and the North Pole (Spitzbergen, Norwegian Svalbard ) , the geographical allocation to the continent is not clear.
-
 Azores (capital Ponta Delgada )
Azores (capital Ponta Delgada ) -
 Madeira (capital Funchal )
Madeira (capital Funchal )
- Both archipelagos are autonomous regions of Portugal. Their assignment to Europe follows on the basis of political, cultural and historical similarity.
Madeira is geographically closer to the African than the European coast.
- Both archipelagos are autonomous regions of Portugal. Their assignment to Europe follows on the basis of political, cultural and historical similarity.
Some states located in Europe
- According to the most widespread geographical delimitation, Kazakhstan is located on the Ural River with 5.4 percent of its land area in Europe. Around half of the population are members of European peoples (Russians, Ukrainians, Poles, Germans). It is a member of UEFA and, as the successor state of the Soviet Union, a member of the OSCE . Usually it is politically and culturally part of ( Central ) Asia.
- With up to 25 percent of its area, Russia is in Europe, if you include the North Caucasus . About 65 to 75 percent of the population live in the European part, depending on the North Caucasus. The country is ethnographically, historically and culturally part of Europe. In Asia lie the eastern part of the Ural region , Siberia and the Far East of Russia .
- According to the traditional geographical delimitation, Turkey lies on the Bosporus and Dardanelles with 3 percent of its area in Europe. About 12 percent of the population live in the European part, especially in the old town of Istanbul , the largest city and historical capital. Turkey is a member of the Council of Europe , forms a customs union with the EU and is usually assigned to Europe at international sporting and cultural events. On the political front, the question of Turkey's membership is currently highly controversial , especially in the context of the negotiations on its accession to the EU .
- If you look at the watershed of the Caucasus as the inner Eurasian border , then smaller parts of Georgia and Azerbaijan are also in Europe. Both countries, like Armenia , are members of the Council of Europe.
Non-European possessions of European countries
- Greenland belongs politically to Denmark , but is autonomous and has not been part of the European Union since 1985. Geographically, Greenland is in North America.
- To Spain include lying off Africa Canary Islands and on the coast of Morocco located territories (u. A. The enclaves of Ceuta and Melilla ). Geographically, they are part of Africa.
- The Ilhas Selvagens belong to Portugal and are geographically part of Africa.
- The areas under the sovereignty of the United Kingdom are: Anguilla , Bermuda , British Virgin Islands , British Indian Ocean Territory , Falkland Islands , Cayman Islands , Montserrat , Pitcairn Islands , St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha , South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands , Turks and Caicos Islands
- The following overseas territories belong to France : Clipperton Island , French Guiana , French Polynesia , French Southern and Antarctic Territories , Guadeloupe , Martinique , Mayotte , New Caledonia , Réunion , Saint-Barthélemy , Saint-Martin , Saint-Pierre and Miquelon , Wallis and Futuna
- The Kingdom of the Netherlands includes: the "countries" of Aruba , Curaçao and Sint Maarten ; as well as the “special parishes” Bonaire , Saba and Sint Eustatius .
- In the Southern Ocean, Norway administers the uninhabited outlying area of Bouvet Island, which does not belong to the mother country .
Political Organizations
In the middle of the 20th century, the Council of Europe was founded as the first joint European institution , which after the end of the East-West conflict comprised 47 states. Also of great importance is the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE), which was founded in 1975 as the Conference for Security and Cooperation in Europe ( CSCE ) across the bloc and to which the USA and Canada belong in addition to European countries .
1951 joined Belgium , the Netherlands , Luxembourg , Germany , Italy and France for the ECSC and the ECSC ( European Coal and Steel Community together). The attempt to found a European Defense Community (EDC) and a European Political Community (EPG) failed in 1954 at the French National Assembly. Then the European Atomic Energy Community (Euratom) and the European Economic Community (EEC) were founded in 1957 with the Treaty of Rome . As of the EC merger agreement in 1967, the three European communities (ECSC, Euratom and EEC) shared the common institutions of the Commission, Council, Parliament and Court of Justice. With the Maastricht Treaty in 1993, the EEC was renamed the European Community (EC) and the European Union was founded, which comprised the three communities and expanded the common foreign and security policy and cooperation in the field of justice and home affairs to include two intergovernmental policy areas . In 2002 the ECSC was dissolved and its functions were taken over by the EC. After the eastward expansion in 2004, 2007 and 2013 as well as the exit of Great Britain, the EU currently has 27 member states. As a result of the Lisbon Treaty , the EC was fully integrated into the EU on December 1, 2009. Today 26 European countries are members of the European Union . The 27th member state of the EU, the Republic of Cyprus , is geographically part of Asia.
Most of the member states of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA), which was also founded in the 1950s, have now converted to the EU; only Iceland , Norway , Switzerland and Liechtenstein are members. Unlike the EU, the EFTA is a pure free trade area without supranational decision-making powers.
From a military point of view, NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) is of great importance in Europe. It was founded in 1949 due to the emerging differences between the Western Allies and the USSR after the end of World War II . In addition to the 23 European members, the USA , Canada and Turkey are also members of NATO.
The World Health Organization (WHO) of the UN knows a region of Europe that includes the Russian Federation and all of Turkey.
Some states do not belong geographically to Europe, but are members of European organizations
- Cyprus is located in the eastern Mediterranean near the coast of Asia, which is why it is geographically included. Historically and culturally, however, it is closely linked to Europe and politically and culturally it is a member of European organizations. The Republic of Cyprus has also been a member of the European Union since May 2004 .
- Depending on the definition, the Transcaucasian states of Armenia , Azerbaijan and Georgia are partially or completely included in Asia. Historically and culturally, however, the two predominantly Christian states Armenia and Georgia are linked to Europe. All three countries are members of the Council of Europe and are usually assigned to Europe at international sporting and cultural events.
- Israel is geographically in Asia. It is often included in international sporting and cultural events in Europe because it is politically isolated in the Arab world.
population
With over 700 million inhabitants, Europe is one of the more densely populated parts of the world. The average population density is around 65 inhabitants per km². In western , central and southern Europe in particular , the population density is relatively high, while it continues to decline sharply towards northern and eastern Europe . The centrally located population concentration in western, central and southern Europe, which stretches in the form of a ribbon between the Irish Sea and the Mediterranean Sea, is classified under the designation " Blue Banana " as an economically and geographically important megalopolis .
- There are eight ethno-linguistic groups in Europe with more than 30 million people. With 456 million people, these eight groups make up 65% of the European population:
-
 Russia → Russians (over 100 million living in Europe),
Russia → Russians (over 100 million living in Europe), -
 Germany , Austria and Switzerland → Germans (around 93 million),
Germany , Austria and Switzerland → Germans (around 93 million),

-
 France , Belgium and Switzerland → French (around 75 million),
France , Belgium and Switzerland → French (around 75 million),

-
 United Kingdom → British (around 66 million),
United Kingdom → British (around 66 million), -
 Italy and Switzerland → Italians (around 60 million),
Italy and Switzerland → Italians (around 60 million),
-
 Ukraine → Ukrainians (38-55 million),
Ukraine → Ukrainians (38-55 million), -
 Spain → Spaniards (41-50 million),
Spain → Spaniards (41-50 million), -
 Poland → Poland (38–45 million).
Poland → Poland (38–45 million).
-
- Other ethnic groups with 10 million or more people living in Europe:
languages
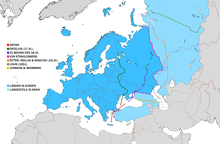
More than 90 percent of the population of Europe speak Indo-European languages . The most widespread are Slavic , Germanic and Romance languages . Also, Greek , Albanian , the Baltic and Celtic languages and the Romani are among the Indo-European languages.
The Uralic languages represent the second largest language family in Europe. They are further subdivided into the Samoyed languages , which are spoken by a few thousand people in the far north-east of Europe, and the Finno-Ugric languages . These include above all Finnish , Hungarian and Estonian as official languages , as well as the Sami languages spoken in Lapland and some minority languages, especially in Russia.
In the European part of Turkey is Turkish , a Turkic language official and Titularsprache, as Kazakh in the European part of Kazakhstan. Other Turkic languages occur as minority languages in Eastern and Southeastern Europe, such as Gagauz and Tatar . With Kalmyk , a representative which is on the eastern edge of the continent Mongolian language family in Europe spoken.
With Maltese , a language of the Semitic branch of the Afro-Asian languages is also represented on the island of Malta . The Basque language spoken in Spain and France is not assigned to any larger language family, its origin could not be reconstructed by modern linguistics and is still unknown. In addition, many other languages are spoken in Europe today from other language families that have recently arrived here as a result of immigrants.
If one considers the main Caucasus ridge as the south-eastern border of Europe, numerous Caucasian languages , including Adygean , Kabardian , Abasin , and the various Nakh-Dagestani languages are among the languages that have closed linguistic areas in Europe. In principle, Georgian and Swan are settled south of the main ridge, but in places they slightly exceed the main ridge to the north. Turkic languages, which are only spoken on the northern flank of the Caucasus in Europe, are Azerbaijani , Karachay-Balkar , Kumyk and Nogai . An Iranian language island in the central North Caucasus is still Ossetian , in the East Caucasus up to the 19th century also Tatisch regionally, the proportion of speakers having declined significantly since then.
In relation to the number of residents, the Latin writing system is most common in Europe , followed by the Cyrillic alphabet (in Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, Bulgaria, Serbia, Montenegro, North Macedonia and parts of Bosnia and Herzegovina) and the Greek alphabet . The Latin language has by the Roman Catholic Church can survive to modern times as the written language of the continent.
Religions
Christianity and Islam are the most widespread religions in Europe.
About 75% of Europeans are Christians (mostly Catholic , Protestant , Orthodox ).
Between 42 and 53 million, or 6–8%, are Muslims , with most Muslims living in the European parts of Russia (13–20 million). Approx. 16 million are Muslim immigrants and their descendants in the European Union . 9.5 million live in the European area of Turkey , 2.2 million in Bosnia and Herzegovina and 1.4–2.5 million in Albania .
Almost 2 million (approx. 0.3%) of the European population are Jews , most of them in France (approx. 520,000), the United Kingdom (approx. 270,000), Russia (approx. 260,000) and Germany (approx. 200,000) . Other religions ( Hinduism , Buddhism etc.) are also represented with less than 0.3%.
About 17% of Europeans are non-denominational , especially in Estonia , the Czech Republic , the Netherlands , Russia and East Germany , otherwise v. a. in the cities.
However, mere denomination says little about the actual degree of religiosity in a country. According to the European Values Study , around a third of Europeans described themselves as irreligious and 5% as staunch atheists .
- In Russia, the largest and most populous country in Europe (the European part of Russia has over 100 million inhabitants), over 50% are Christians, at least 30% are atheists or non-denominational and around 14% are Muslims.
- In comparison, Germany has the second largest population with over 82 million inhabitants. Almost 60% are Christians, around 5% Muslims, the rest mostly atheists and non-denominational. In eastern Germany, however, non-denominational people make up up to 70%.
Christianity first reached Europe in the 1st century AD. Islam spread to the Iberian Peninsula in the 8th century , but was ousted again in the course of the " Reconquista " from the 13th to the 15th century. Europeans spread Christianity through immigration and mission in America , Australia and, to a lesser extent, other continents (parts of Southeast Asia , Africa and Oceania ). Today Europe is largely secularized .
The Roman Catholic Church has named six saints as patrons of Europe since 1964 .
economy
In the 19th century, the Industrial Revolution that began in England and spanned the entire continent made Europe the leading economic power. Later, various international institutions and organizations, such as the EFTA (European Free Trade Association) and the European Community - today's EU - brought about a surge in growth that lasted in many parts of Europe into the 1970s and partly into the 1980s. The supply of the population of Europe could also be further expanded by reducing trade restrictions. Eastern Europe is currently experiencing an economic boom and is catching up with the Western European countries. Growth is particularly high at the moment [2006] in the EU countries of Latvia, Estonia, Lithuania and Slovakia, with some double-digit growth rates.
With the Maastricht Treaty , 12 EU states initially formed a monetary union from 1999 . From January 1st, 2002 euro banknotes and coins were introduced. Today the euro is legal tender in 18 EU countries and six other European countries.
Today Europe is a prosperous continent with large industrial metropolises, profitable agriculture and a growing service sector . Nevertheless, unemployment has been a widespread problem in many European countries since the 1970s . Industry and services are mainly concentrated in the metropolitan areas. In most European countries, the problem is no longer food shortages, but overproduction and obesity . Exports are mainly machinery , steel , computer supplies and automobiles . Imported goods include cocoa , tea , rubber , crude oil , natural gas and ores .
Culture
See: Category: Culture (Europe)
Sculpture , painting , literature , architecture and music have a long tradition in Europe. Many cities, such as Paris , Vienna , Rome , Berlin and Moscow, are now regarded as cultural centers. Many cities also have important theaters, museums, orchestras, and other important institutions.
education

In all European countries there is compulsory schooling or at least one compulsory education , which often lasts from 6 or 7 to 15 or 16 years of age. In most countries, primary school takes four to five years - in a few countries it is seven or eight years. This is usually followed by a secondary school , which can also include different types and types of school. The illiteracy rate is very low in almost all countries thanks to various forms of funding from the education system. In many countries there are also well-known colleges and universities , some with specific specialist areas.
Sports
Sport played a special role in the idea of a unified European area, as there have been European championships since the end of the 19th century (first in figure skating in 1891 ). Since the European Union has largely dispensed with its own organization of sport and national monopolies are maintained in the football leagues , which are also strictly demarcated from other European countries, the image of Europe of professional sport is much more present in the public perception than that of the political one Europe.
See also
- NUTS (European Regions)
- Europeanism
- Geographical records in Europe
- National coat of arms of the European countries
literature
- Heinrich Böll Foundation , German Society for Foreign Policy , Le Monde diplomatique (Ed.): Europe Atlas. Data and facts about the continent . Berlin 2014.
- Peter Blickle (Ed.): Handbook of the history of Europe. 9 volumes. Stuttgart 2000 ff.
- Lorraine Bluche, Veronika Lipphardt, Kiran Klaus Patel (eds.): The European - a construct. Stocks of knowledge, discourses, practices. Wallstein Verlag, Göttingen 2009, ISBN 978-3-8353-0444-4 .
- Hortense Hörburger: European encyclopedia for employees. 100 concise keywords. Schüren Verlag, Marburg 1999, ISBN 3-89472-169-3 .
- Klaus Oschema: Images of Europe in the Middle Ages . (= Medieval research; 43). Thorbecke, Ostfildern 2013 ( digitized version )
- Almut-Barbara Renger, Roland Alexander Ißler (Hrsg.): Europe - bull and wreath of stars. From the union with Zeus to the union of states. (= Founding myths of Europe in literature, music and art. 1). V & R unipress, Goettingen 2009, ISBN 978-3-89971-566-8 , vr.de .
- Wolfgang Schmale : Europe: cultural reference - system of quotations - system of values. In: European History Online . Edited by the Leibniz Institute for European History , 2010. Accessed June 13, 2012.
- Hans Jörg Schrötter: Small European Lexicon. History - Politics - Law. CH Beck Verlag, Munich 2016, ISBN 978-3-423-50782-0 .
Web links
|
Further content in the sister projects of Wikipedia:
|
||
|
|
Commons | - multimedia content |
|
|
Wiktionary | - Dictionary entries |
|
|
Wikisource | - Sources and full texts |
|
|
Wikiquote | - Quotes |
|
|
Wikivoyage | - Travel Guide |
- Federal Agency for Civic Education (bpb): Figures and facts: Europe
- Federal Statistical Office of the Swiss Confederation (Ed.): Stat @ las Europa. An interactive statistical atlas of the European regions
- Center Virtuel de la Connaissance sur l'Europe (ed.): CVCE. The multimedia reference on the history of Europe
Individual evidence
- ↑ Data report 2019 by the German Foundation for World Population (PDF; 0.6 MB)
- ^ European Continent / Map of Europe. December 25, 2018. Retrieved January 20, 2019 (American English).
- ↑ a b Entry "Europe" in the Online Etymology Dictionary (English).
- ↑ Dieter Hägermann : Charlemagne. Ruler of the west . Propylaen Verlag, Berlin and Munich 2000, ISBN 3-549-05826-8 , p. 10.
- ↑ Europe. In: Brockhaus Encyclopedia. 21st edition. F. A. Brockhaus, Leipzig / Mannheim 2006. “The Urals have been the border between Europe and Asia since the 18th century ... Conventional borders with Asia are also formed by the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Manytn lowlands, the Black Sea, the Bosporus, the Sea of Marmara, the Dardanelles and the Aegean Sea ” .
- ↑ Europe. In: The New Encyclopaedia Britannica. 1998. "... West of the Caspian, the European limit follows the Kuma-Manych Depression and the Kerch Strait to the Black Sea" .
-
↑ Europe . In: National Geographic Atlas of the World . 7th edition. National Geographic , Washington, DC 1999, ISBN 0-7922-7528-4 , pp. 68-69 . Asia . In: National Geographic Atlas of the World . 7th edition. National Geographic , Washington, DC 1999, ISBN 0-7922-7528-4 , pp.
90-91 . "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Black Sea with its outlets, the Bosporus and Dardanelles." - ^ CIA - The World Factbook, Major urban areas - population .
- ^ E. Carbonell et al.: The first hominin of Europe. In: Nature . Volume 452, 2008, pp. 465-469.
- ↑ Dieter Hägermann: Charlemagne, ruler of the West. Berlin u. a. 2000, ISBN 3-549-05826-8 , p. 10.
- ↑ Also sanctions: Medical Association for Compulsory Vaccination orf.at, November 23, 2019, accessed November 24, 2019.
- ^ Bureau of National Statistics - United Kingdom: "Population by Country of Birth and Nationality 2013: Table 2.1". Retrieved December 17, 2018 .
- ↑ 15 ° Censimento generale della popolazione e delle abitazioni. (PDF) (No longer available online.) ISTAT , April 27, 2012, formerly in the original ; Retrieved September 22, 2012 (Italian). ( Page no longer available , search in web archives )
- ↑ Bernhard Chiari (ed.): "Guide to the history of the Caucasus." Verlag Ferdinand Schöningh, Paderborn a. a. 2008, PDF download 7 MB mgfa.de ( Memento from June 19, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) (p. 123 ff)
- ^ Christianity in Global Context: Trends and Statistics . Center for the Study of Global Christianity, 2005 ( Memento from April 24, 2010 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ S. Frisch, U. Hengelhaupt, F. Hohm: "Pocket Atlas European Union." Gotha 2007 (sum of the country-specific figures listed on pages 73–203).
- ↑ The proportion of Muslims in the Albanian population is estimated at 40–70%, for details and evidence see Islam in Albania .
- ↑ German Bishops' Conference: Flyer Key Data Church Statistics 2016 .
- ↑ Anja Stichs: How many Muslims live in Germany? (PDF) An extrapolation of the number of Muslims in Germany as of December 31, 2015. BAMF, December 14, 2016 ( ISSN 1865-4967 ).
- ↑ cf. Religious life in Europe: Europe's patron saint. ( Memento of October 20, 2007 in the web archive archive.today ) Union of European Conferences of Major Superiors UCESM
- ↑ cf. James Riordan , Arnd Krüger : European Cultures in Sport: Examining the Nations and Regions. Inellect, Bristol 2003, ISBN 1-84150-014-3 ( Google Book , accessed November 10, 2016).
- ↑ Cf. Vanessa Conze: Review of: L. Bluche u. a. (Ed.): The European - a construct. In: H-Soz-u-Kult. January 22, 2010, accessed January 22, 2010 .
Coordinates: 55 ° N , 25 ° E