England
| England | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Location of England within the United Kingdom | |||
| Symbols | |||
|
|||
| Basic data | |||
| Country | United Kingdom | ||
| Part of the country | England | ||
| Capital | London | ||
| surface | 130,395 km² | ||
| Residents | 55,977,178 ( 2018 ) | ||
| density | 429 inhabitants per km² | ||
| ISO 3166-2 | GB-ENG | ||
| economy | |||
| GDP | € 1,200 billion ( 4th ) (2002 estimate) € 24,503 ( 13th ) per capita |
||
Coordinates: 52 ° 29 ′ N , 1 ° 34 ′ W
England is the largest and most densely populated part of the United Kingdom in northwestern Europe .
England encompasses most of the southern part of the island of Great Britain , bordered by Scotland to the north and Wales and the Irish Sea to the west . In the east the country borders on the North Sea , in the south on the English Channel and in the southwest on the Atlantic .
London is the capital of England and the whole of the United Kingdom. Measured by the number of its inhabitants, it is also the third largest city in Europe (after Moscow and Istanbul ). England's population of over 55 million is nearly 85% of the UK's population.
The country's geography is characterized by low hills and plains, especially in central and southern England. However, there are also highlands in the north and southwest.
In many European languages (e.g. in German, Dutch, French etc.) the name England is used synecdochically for the entire United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
etymology
The name England is derived from the old English word Engaland , which means something like the land of fishing . The Angles were a Germanic tribe who colonized the country in the early Middle Ages . According to the Oxford English Dictionary , the first written record of the name as Engla lande was in the year 1014. The modern spelling England (also Engelland in medieval texts ) was first recorded for the year 1658.
An alternative name for England is Albion . It originally referred to the entire island of Great Britain. The term is also used poetically for England in modern times. The nominally earliest record of this name was probably in the 4th century BC. To be found in the Corpus Aristotelicum . It says roughly: “Beyond the pillars of Heracles there are two very large islands called Britannia; these are Albion and Ierne ”. The word Albion (Ἀλβίων) may derive from the Latin word albus (white), a reference to the white cliffs of Dover (between England and France).
geography
With about 130,000 km² England is the largest part of Great Britain in terms of area and covers about two thirds of Great Britain. The coasts can be mentioned as a typical feature of England. In addition to the coasts, there are other diverse natural spaces in England. England consists for the most part of lowlands, which are criss-crossed by mountain ranges. The highest mountain in England is Scafell Pike in the Cumbrian Mountains at 978 meters. The longest and most famous river in the country is the Thames . The Severn , the Humber , the Trent and the Great Ouse flow through England alongside it .
climate

England is located in the temperate climate zone and, due to the Gulf Stream , has a rather humid but also warm climate. Overall, England has a warmer climate than the countries that are at the same latitude . The weather in England is varied. The reason for this is that England is influenced alternately by warm subtropical air and cold polar air. The coldest months are January and February, while August, and in some parts of the continental east also July, is usually the warmest month. Months with mild to warm weather are also June, September and October. The rainfall is pretty evenly distributed over the year. Since the weather records began, the highest temperature has been 38.5 ° C, and the lowest -26 ° C. Due to climate change , it will be increasingly difficult to secure the supply of England with drinking water in the future.
- Climate diagrams of English cities
Climate diagram of Birmingham
Cambridge climate diagram
Climate diagram of Plymouth
The famous fine “English drizzle” on the south-west coast is a gradient rain on the steep cliffs, in which the moisture from water vapor-saturated warm air masses turns out to be barely visible drizzle without condensation germs (largely absent in the onshore wind ).
Flora and fauna
England accounts for about half of the UK's wooded area. The most common trees in England are oaks and beeches , and pine and birch are also common in the plains . There are also cherry tree and apple tree cultures , gorse and numerous types of wild flowers .
Deer , rabbits , hares , badgers and foxes are common in England . The wolves and wild boars that used to live in England are completely extinct. While there are many species of birds in England such as crows , pigeons , starlings , reptiles are extremely rare. Insectivores and other small mammals are common in England. The hedgehog, for example, is a regular visitor to the municipal gardens. England's seas are a haven for many marine mammals. The gray seal , a relatively rare animal in the world, is found in large numbers along the English coast.
history
Before Roman times
The country's history basically starts with the creation of the island . Around 8500 BC During the last ice melt, the sea level rose and made Britain approx. 7000 BC. To the island. In the Neolithic Age, which only appeared on the island around 4000 BC. Began agriculture and animal husbandry.
Roman times and Christianization
The Romans first settled under Caesar's leadership in 55 and 54 BC. In England, but initially not as a conqueror. It was not until almost a century later that England was occupied by the Romans. Scottish peoples repeatedly penetrated the power vacuum that developed after the retreat of the Romans around 410 AD. In the following years groups of Angles , Jutes and Saxons immigrated . The early Middle Ages began in Britain . The Anglo-Saxon peoples brought their Germanic religion with them, and by the early 9th century the Christianization of England was complete, although pagan beliefs were still widespread.
Viking age
The Danish Vikings finally sailed to England in the late 8th century. At first they only carried out raids, but later they settled down, demanded tribute payments and built their own villages. In 878 Alfred defeated a large Danish army at Edington . Thereupon the Danish king Guthrum , who had already come into contact with Christianity, was baptized with 30 of his men. They then withdrew to their core area in East Anglia ( Danelag ). This success led to the recognition of Alfred as ruler in Mercien .
High Middle Ages
The victory of Wilhelm led to the introduction of the effective feudal system of the Normans . A small Norman upper class almost completely replaced the established nobility . Wilhelm ordered the creation of the Domesday Book , which recorded taxes on the entire population, their lands and possessions. This created a completely new system of government . The system was the forerunner of English parliamentarianism , which still exists today.
Society in the High Middle Ages:
In the period from the middle of the 10th to the middle of the 14th century, the English population is estimated to have tripled, probably up to six million people. This development had a number of economic and social consequences: arable farming was intensified with the introduction of three- field farming and the reclamation of more areas. However, self-sufficiency with food was only possible in climatically favorable and politically stable times.
Late Middle Ages
The Hundred Years War is characteristic of the late Middle Ages . The deposition of Richard II by the later Henry IV and the failures in the Hundred Years War were the reasons for the outbreak of the subsequent Wars of the Roses .
Society in the late Middle Ages:
After the growth phase of the Early and High Middle Ages, the plague shaped development in England in the late Middle Ages . After two severe plague attacks in 1348 and 1361/62 there were several small outbreaks of the epidemic, which roughly halved the population. After the great plagues were over, the development of cities accelerated, especially London.
The Elizabethan Age
According to Henry VIII's succession to the throne and the assurances made by Maria I to the magnate when she married, Elizabeth I ascended the throne in 1558. The new, Protestant queen was enthusiastically received by the people. From the beginning of her reign , a possible marriage of the queen was the dominant theme. Several parliaments have asked them to do so with the aim of obtaining a male heir to the throne. She was responsible for the implementation of the Reformation, but also for the poorer relations with Spain .
Society in the 16th century: By 1550, the English population had grown again to around three million after the plague. The rural population was by far the majority. However, by 1500 London already had a population of 60,000 and grew to around 215,000 by the end of the century. The next largest cities around 1500 were significantly smaller: Norwich with 12,000 and Bristol with 10,000 inhabitants.
population
With over 55 million people, England is by far the most populous country in the United Kingdom. England accounts for almost 85% of the UK population . The density of 417 people per square kilometer is also very high. However, it must be taken into account here that 8.3 million of the 55.3 million inhabitants in Greater London live on just 1.3 percent of the total area. In the rest of the country, the population density is just 357 people per square kilometer.
language
English is predominantly spoken in England . While there is no law stating that English is the official language, English is the only language that is used for official purposes. It is also of international importance, around 1.5 billion people in the world speak English, 375 million of them as their first language. English is mostly seen as the "world lingua franca".
English became popular in England from the 15th century. In the English Renaissance , many words were adopted from French and Latin.
It is estimated that 133,000 people in England speak Welsh .
In 2007, around 800,000 students spoke a foreign language at home due to immigration. A 2011 census shows that England is the second most spoken Polish country after English .
religion
The Christianity already held in the final phase of the Roman Empire in the 1st to 4th century moving into the former Roman province of Britannia . After the retreat of the Romans and the Anglo-Saxon conquest in the 4th to 5th centuries, a phase of paganism followed. Most of England was Christianized in the first half of the 7th century by Gregorian missionaries under Augustine of Canterbury . In the Middle Ages the English Church kept a certain distance from the Popes. John Wyclif (approx. 1325–1384) was a forerunner of the later reformers. After the beginning of the Lutheran Reformation, the then King Henry VIII initially behaved negatively, but in 1531 initiated the separation of the English Church from the Roman Catholic Church less for religious and more for personal reasons. The newly founded Anglican Church (Church of England) initially largely corresponded to the Roman Catholic Church in liturgy and theology, but in the following decades it incorporated more and more Protestant elements. The Anglican Church became the State Church of England. Membership in the Church of England was a prerequisite for higher office. In addition to the state church, Protestant free churches ("nonconformists") also developed. In addition, there was still a small Catholic minority, which, however, was massively disadvantaged by the state. The Catholics had a reputation for being enemies of the state who sympathized with the traditional Catholic opponents of England, Spain and France. Today the Church of England continues to have state church status . Its head of church is the ruling monarch of the United Kingdom. There are approximately 26 million followers of the Church of England.
With the emancipation of Catholics in 1829, Catholics received civil equality. During the time Ireland belonged to the United Kingdom from 1801 to 1923, the Catholic population increased sharply due to immigration from Ireland.
Up until the 19th century there was practically no Jewish population worth mentioning in England, as the Jews were expelled from England in 1290 under King Edward I. It was not until the Lord Protector Oliver Cromwell that the Jews were allowed to resettle in 1656. Nevertheless, the Jewish population remained very small for a long time. The Jews in England did not receive full legal equality until 1858. There was a major wave of immigration of Jews from Eastern Europe (especially from the Russian Empire ) at the end of the 19th and beginning of the 20th century. During the period of National Socialism , many people from Central Europe persecuted as Jews found asylum in England, where they made significant contributions to the war effort of the United Kingdom.
After the Second World War , the British colonies gradually became independent. There was significant numerical immigration from Commonwealth countries , bringing many Muslims into the country. The largest groups were immigrants from Pakistan and immigrants from Bangladesh .
Many churches and cathedrals in England are historic buildings and of great architectural value. Well-known historical buildings are z. B. Westminster Abbey , York Minster , Durham Cathedral and Salisbury Cathedral .
| Distribution of religions in England (according to 2011 Census) |
||
|---|---|---|
| religion | Proportion of the population |
in % |
| Christianity | 31,479,876 | 59.4% |
| Islam | 2,660,116 | 5.0% |
| Hinduism | 806.199 | 1.5% |
| Sikhism | 420.196 | 0.8% |
| Judaism | 261.282 | 0.5% |
| Buddhism | 238,626 | 0.5% |
| other religions | 227.825 | 0.4% |
| without confession | 13.114.232 | 24.7% |
| No Answer | 3,804,104 | 7.2% |
| total | 53,012,456 | 100% |
politics
The government of the kingdom, like the royal family , is based in the British capital, London . In contrast to Scotland, Wales or Northern Ireland , England has neither a state parliament nor a state government. Their functions are carried out by the Parliament and the Government of the United Kingdom. However, there are discussions, especially after the failed independence vote in Scotland, as to how England can also be better considered in the context of devolution . For example, regional parliaments in England, an English state parliament or the retention of the previous competence of the British House of Commons with the future exclusion of non-English parliamentarians in questions that only affect England are discussed.
National symbols
The English flag , known as the St. George Cross , is a red cross on a white background and has been in use since the 13th century.
Another national symbol since the Wars of the Roses has been the Tudor rose , which is said to be a symbol of peace. The rose is z. B. used as an emblem by the England rugby union team .
The Three Lions ("Three Lions") go back to Richard the Lionheart and form the coat of arms of England.
England itself does not have an official national anthem . At sporting events in which England appears as an independent team, the British national anthem God Save the Queen is mostly used, and less often the anthem Jerusalem , e.g. B. at Test Cricket .
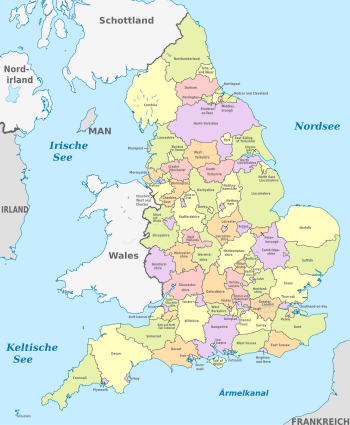
Administrative division
The 39 historic counties
These 39 historic counties (Engl. County, counties ) have existed since the Middle Ages . In their function as administrative districts , they have been restructured several times since the middle of the 20th century , but the historical counties continue to exist in the consciousness of the population. Larger cities were considered part of the counties, but were administered independently as boroughs .
current administrative structure
In the course of the 20th century , the administrative structure was partially adapted to the newly created metropolitan areas. This also changed the boundaries of the 39 historical counties mentioned above . For example, in 1965 the Greater London administrative unit was established. In 1974, six metropolitan counties and the so-called non-metropolitan counties were created , including some smaller new counties such as Avon , Humberside and Cleveland , but some of these were dissolved again in the 1990s.
The counties are subdivided into districts ( metropolitan districts or districts ), which due to their tasks correspond roughly to the city administrations of Germany. These districts usually consist of a large number of cities and smaller settlements, which, however, do not have their own administration. One speaks of a “two-tier administration” (first tier: counties, second tier: districts).
In 1986, the county councils or administrations of the Metropolitan Counties were dissolved. Their tasks have been delegated to the subdivided Metropolitan Districts , so that they take care of all the tasks of the counties and the districts (“one-tier administration”). In their function, the Metropolitan Districts can since then be referred to as Unitary Authorities . The names of the six Metropolitan Counties were retained, but since then they have only been of importance for the description of the geographical location or for statistical purposes.
Numerous non-metropolitan districts were spun off from the counties as Unitary Authorities in the mid-1990s . Since then, they have been taking care of the administrative units of the counties and are therefore comparable to the Metropolitan Districts .
The counties and unitary authorities of England are now grouped into nine regions . For the subdivision of regions and counties, see Administrative Divisions and Administrative Counties of England .
Big cities
In the English language , a distinction is made between city and town . The right to be called "City" is sealed by a royal charter , the so-called Royal Charter . Most of the time, it was based on whether the settlement in question had a cathedral . For example, while little St Davids in Wales is a “City” with fewer than 2,000 inhabitants, Stockport with its 135,600 inhabitants is just “Town”. The distinction is thus similar to the distinction between town and municipality in Germany . All administrative districts with an urban character in England usually also have the status of a borough .
The following list of the “big cities” of England includes Greater London and the Unitary Authorities Bristol and Leicester, the respective Metropolitan Boroughs . Metropolitan Boroughs are single-level administrative units in the metropolitan areas of England, which can be compared with German cities . Formally, they are subdivisions of the Metropolitan Counties , which, however, no longer play a role as administrative units (see also the administrative structure of England ).
| The ten largest urban counties in England (as of 2015) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rank | Surname | Residents | Administrative unit | Metropolitan county | Region in England |
| 1 | London | 8,665,000 | Greater London | ||
| 2 | Birmingham * | 1,111,300 | Metropolitan Borough | West Midlands | West Midlands |
| 3 | Leeds * | 774.100 | Metropolitan Borough | West Yorkshire | Yorkshire and the Humber |
| 4th | Sheffield * | 569,700 | Metropolitan Borough | South Yorkshire | Yorkshire and the Humber |
| 5 | Bradford * | 531.200 | Metropolitan Borough | West Yorkshire | Yorkshire and the Humber |
| 6th | Manchester * | 530,300 | Metropolitan Borough | Greater Manchester | North West England |
| 7th | Liverpool * | 478,600 | Metropolitan Borough | Merseyside | North West England |
| 8th | Bristol * | 449,300 | Unitary Authority | - | South West England |
| 9 | Coventry * | 345,400 | Metropolitan Borough | West Midlands | West Midlands |
| 10 | Leicester * | 342,600 | Unitary Authority | - | East Midlands |
Economy and Infrastructure
economy
England is one of the most deregulated economies in the world, with an average per capita income of € 22,907. England practices the free market , has an advanced infrastructure and is one of the strongest regions in Europe in terms of inflation , interest rates and unemployment . The official currency of England is the pound sterling . It is held by many states as a currency reserve and is one of the most important convertible currencies in the world after the US dollar and the euro . England makes up most of the UK's economy, not least because of London , one of the world's largest financial centers. The country is one of the leading countries in the fields of the chemical and technical industries, especially aerospace, defense and software industries. The Bank of England , founded in 1694, is the central bank of the United Kingdom.
science

Prominent English names in science and mathematics include Sir Isaac Newton , Michael Faraday , Robert Hooke , Robert Boyle , Joseph Priestley , Charles Darwin , Alan Turing , Francis Crick , Andrew Wiles , Stephen Hawking, and Richard Dawkins (etc.). As the birthplace of the Industrial Revolution , England was home to many great inventors in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. Famous inventions and discoveries by the English are the first computers , the World Wide Web and also the lawn mower .
Infrastructure
The motorways and trunk roads in England are very extensive. A typical trunk road is the A1 Great North Road , which runs through east England, from London to Newcastle upon Tyne . Bus transport is also widespread across the country, major companies are: National Express , Arriva and Go-Ahead . The red double decker buses in London are a famous symbol of England. The rail transport in England is one of the oldest in the world, passenger railways in England were established in 1825. The largest airport is London Heathrow . It is the largest airport in the world in terms of the number of international passengers. There are around 4,400 miles (7100 kilometers) of waterways in England.
health
The National Health Service (NHS), the publicly funded health system in England, is responsible for the provision of health care. It is financed from taxpayers' money (and not, as in many countries, from social security ). Internationally, also in Germany, the NHS has a negative reputation, which is due to the often very long waiting times. The bad reputation is often justified with a lack of doctors.
The average life expectancy of people in England is 77.5 years for men and 81.7 years for women, the longest life expectancy of any of the four countries in the United Kingdom.
Education System

At the age of three to four you go to kindergarten , at the age of four to eleven you go to elementary school and the secondary school is attended by eleven to sixteen year olds. After completing compulsory school, students do z. B. a GCSE exam and then continue training for about two years.
Public schools are monitored by the Office for Standards in Education and private schools (around 7% of students attend private schools) by Independent Schools Inspectorate .
Arts and Culture
English art is shaped by architecture, painting, handicrafts and sculpture. England is known as the "motherland of football " and the English cuisine has special features that are typical of the country.
architecture
With the renovation of the choir of Canterbury Cathedral by Wilhelm von Sens, which began in 1175, the transition to Gothic took place under the influence of architecture in the Île de France . The English late Gothic, the so-called Perpendicular Style (1350–1530), brought the fan vaulting in addition to the strict, vertical structure of the wall , especially in chapel construction (choir renovation in Gloucester, castle chapel in Windsor, etc.). In the Tudor style (1500–1600, especially palace construction) forms of the late Gothic and the Italian Renaissance mixed . This was followed by a baroque-classicist development, which finally largely closed the continental architectural concept of the baroque and spread classicism in general. Since the end of the 18th century there has been a sense of style in furnishing interiors and engineering architecture made of iron , reinforced concrete and glass .
painting
In the 10th and 11th centuries, English painting began its first heyday. The continental currents that dominated English painting for about 300 years after the beginning of the 15th century were largely the result of the activities of foreign artists in England. Portrait painting reached a new high point after the middle of the 18th century with the further development of the portrait tradition founded by van Dyck . At the beginning of the 19th century, England shaped landscape painting .
Handicrafts
English handicrafts became important to all of Europe in the 18th century. At the end of the 18th century, jasperware was produced in which the shards are colored through and through by metal oxides . In the 19th century England saw a renewal of the arts and crafts in all fields, including printing and book decoration.
plastic
The art of sculpture in England only gained greater importance as cathedral and tomb sculpture in the Gothic period. The lack of own creative powers and the dependence on continental achievements determined the development of the sculpture.
kitchen
Since the early modern era , food in England has been characterized by its triviality and reliance on natural products . Examples of traditional English cuisine include the Sunday roast , fish combined with fries, and the full English breakfast , which is generally made up of bacon, sausages, tomatoes, bread, beans, mushrooms, and eggs. Some popular cheeses are Cheddar , Red Leicester, and Wensleydale . Traditional English desserts include apple pie and other fruit cakes , as well as pudding , and more recently caramel pudding . A classic drink is tea , the popularity of which was increased by Catherine of Braganza , while the most common alcoholic beverages are wine (especially cider ), English beer, and dark beer.
Sports

England has a strong sporting heritage and in the 19th century codified many sports that are played around the world in modern times including football , cricket , rugby , tennis , boxing , badminton , squash , hockey , snooker , English billiards , darts , Table tennis and basketball , with football standing out. FIFA recognizes the English club Sheffield FC as the oldest official club. The English national soccer team won the soccer world championship in 1966 . Today the English Premier League is the most watched and most lucrative league in the world.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Mid 2018 Estimates of the population for the UK, England and Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland
- ^ England Oxford English Dictionary
- ↑ Gerald Massey: A Book of the Beginnings. Volume 1, 2007, p. 440
- ↑ England
- ^ Area of England in the travel guide ( Memento from December 21, 2014 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ How is the climate in England? ( Memento of February 15, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Woodlands Kent
- ↑ Temperature record changes, BBC News
- ↑ MetOffice, English Climate
- ↑ Climate change: Water shortages in England 'within 25 years'. BBC, March 19, 2019, accessed March 20, 2019 (UK English).
- ^ Flora and Fauna , England and Wales Section
- ↑ United Kingdom: Countries and Major Cities - Population Statistics, Maps, Charts, Weather and Web Information. Retrieved April 15, 2018 .
- ↑ The Ten Most Spoken Languages in the World
- ^ Estimation of the number of Welsh speakers in England , Welsh Language Board , January 2007
- ^ Graeme Paton: One-fifth of children from ethnic minorities. The Daily Telegraph , London, 1st October 2007
- ^ The Guardian: Polish becomes England's second language
- ↑ Global Anglicanism at a Crossroads , PewResearch
- ↑ Tara Holmes: Readmission of Jews to Britain in 1656. June 24, 2011, accessed July 6, 2017 .
- ↑ English religion (Census 2011)
- ↑ Emblems of Britain on projectbritain.com
- ↑ Sing Jerusalem for England! BBC 6 September 2005.
- ↑ Office for National Statistics , Regional Accounts ( Memento from August 26, 2009 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Global Finance Index (2003-09) ( Memento of October 7, 2009 in the Internet Archive ), PDF , City of London Corporation
- ↑ British Parliament 2007, p. 17
- ↑ September 27, 1825: Opening of the passenger train ( Memento of October 7, 2013 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ Ardal O'Hanlon: Global Airlines. Elsevier , 2008. p. 205.
- ↑ David Else: Inghilterra. EDT srl, 2007. page 781
- ↑ http://www.bmj.com/campaigns/nhsat60/index.dtl
- ^ Luigi Siciliani, Jeremy Hurst: Explaining Waiting Times Variations for Elective Surgery across OECD Countries. PDF, 426 kB. OECD HEALTH WORKING PAPERS No. 7, October 7, 2003
- ^ Office for National Statistics. Keyword "life expectancy". statistics.gov.uk. Archived from the original on May 25, 2009. Retrieved July 20, 2009.
- ↑ http://www.wissen.de/lexikon/englische-kunst?chunk=intro
- ↑ Is Scotland the real motherland of football? - “There was no revolution in the 19th century”. 11 Friends , October 19, 2011, accessed August 16, 2014 .
- ↑ Else 2007, p. 76.
- ^ "Catherine of Braganza". Tea.co.uk. Retrieved September 5, 2009
- ↑ "Types of Beer". Icons of England. Retrieved September 5, 2009.
- ↑ http://www.fifa.com/world-match-centre/news/newsid/621/801/index.html
- ↑ http://www.thetimes.co.uk/tto/public/ceo-summit/article3804923.ece
- ^ "Premier League towers over world football, says Deloitte". sportbusiness.com. Retrieved January 8, 2010.