Gorse
| Gorse | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Gorse ( Ulex europaeus ) in full bloom |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Ulex europaeus | ||||||||||||
| L. |
The gorse ( Ulex europaeus ) is a plant of the genus gorse ( Ulex ) within the family of the Leguminosae (Fabaceae).
The gorse has a high risk of fire, especially in the hot summer months, because its green branches contain two to four percent highly flammable oils.
The gorse, with its many twigs and large, strong thorns (10 to 20 millimeters), prevents animals from eating its flowers. Twigs and thorns can form an impenetrable thicket in which dead shrubs can also pile up.
description
Vegetative characteristics
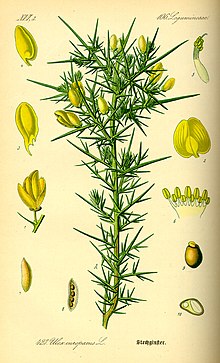
The gorse is a deciduous, thorny, sparsely branched shrub that reaches heights of growth of up to 2 meters. Its leaves are rolled up into fine needles. The leaves and short shoots are transformed into thorns.
Generative characteristics
The flowering period extends from early spring to early summer, from April to July. The flowers are solitary in the leaf axils. The hermaphroditic flowers are zygomorphic with a length of about 2 centimeters and five-fold with a double flower envelope . The five yellow petals stand together in the typical shape of the butterfly blossom.
Usually two seeds are located in a 15 to 20 millimeter long, hairy legume , which remains covered by the corolla that is then withered.
The number of chromosomes is 2n = 96.
ecology
Vegetative propagation occurs through root shoots. The spiny thorns and thorn-like, stinging leaves of the gorse serve as protection against feeding against various ruminants , but are not effective against rabbits , horses and goats, for example . The thorns are of course also ecologically important as points of condensation. The youth leaves, on the other hand, are pinnate and not thorny. The branches are green and photosynthetically active; however, in severe winters they freeze back.
From an ecological point of view, these are "butterfly flowers with a quick mechanism" without nectar . Pollinators are bumblebees and bees .
The seeds have an oil-containing elaiosome for ants to spread . There is also human spreading through overgrowth from plantings. Fruit ripening is from July to August. The seeds are long-lived and fire-resistant.
Occurrence
The gorse is originally in the Atlantic regions of Europe . The gorse is considered one of the world's 100 worst invasive species. As a hedge plant by English settlers brought that very strongly and is vegetatively proliferating gorse one on earth widespread, many people hated invasive neophyte . It also occurs in larger parts of Germany.
In a temperate climate, the gorse grows preferably on dry or swampy sandy soils . He is a character species of the Pruno-Rubion association.
Systematics
The first publication of Ulex europaeus was done by Carl von Linné .
One can distinguish several subspecies in Ulex europaeus :
- Ulex europaeus L. subsp. europaeus
- Ulex europaeus subsp. latebracteatus (Mariz) Rothm. : It occurs in Portugal and Spain.
Some authors also differentiate between:
- Ulex europaeus subsp. borealis Rothm.
Ingredients and toxicology
The fruits and branches are very poisonous to humans. The legumes are very poisonous , especially because they contain up to 1 percent cytisine .
The seeds and young shoots serve as medicinal drugs . Important ingredients are cytisine , anagyrine , methylcytisine , flavonoids and lectins (ullectin).
use
Gorse works well as an ideal natural barrier for pets such as chickens , cattle and horses . At the same time, it promotes soil fertility, as it binds a lot of nitrogen from the air in its root nodules and delivers it to the soil .
A yellow dye can be obtained from the flowers for dyeing textiles (dye plant ).
The lectin from gorse is used in immunohematology to detect the H antigen on erythrocytes. While certain amounts of H antigen can be found in almost all patients depending on the AB0 blood group , the H antigen is completely absent in patients with the rare Bombay blood group and can therefore be determined by an examination with the lectin. Ulexlectin is also used in experimental medicine as a marker for endothelial or tumor cells of vascular origin.
literature
- Ruprecht Düll , Herfried Kutzelnigg : Pocket dictionary of plants in Germany and neighboring countries. The most common Central European species in portrait. 7th, corrected and enlarged edition. Quelle & Meyer, Wiebelsheim 2011, ISBN 978-3-494-01424-1 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Erich Oberdorfer : Plant-sociological excursion flora for Germany and neighboring areas. 8th edition. Verlag Eugen Ulmer, Stuttgart 2001, ISBN 3-8001-3131-5 , p. 582.
- ↑ Global Invasive Species Database (2019)
- ↑ Data from ILDIS World Database of Legumes 2010: Ulex europaeus In: Euro + Med Plantbase - the information resource for Euro-Mediterranean plant diversity.
- ↑ a b c Karl Hiller, Matthias F. Melzig, Lexicon of medicinal plants and drugs. 2 volumes, approved special edition for area Verlag, 2006, ISBN 3-89996-682-1 .
- ↑ gifte.de - gorse
- ↑ Baumkunde.de - Gorse.
- ↑ AjitC Gorakshakar, Kanjaksha Ghosh: Use of lectins in Immunohematology . In: Asian Journal of Transfusion Science . tape 10 , no. 1 , 2016, ISSN 0973-6247 , p. 12 , doi : 10.4103 / 0973-6247.172180 , PMID 27011665 ( ajts.org [accessed April 3, 2019]).
Web links
- Gorse . In: BiolFlor, the database of biological-ecological characteristics of the flora of Germany.
- Ulex europaeus L., common gorse. In: FloraWeb.de.
- Distribution map for Germany. In: Floraweb .
- Ulex europaeus L. In: Info Flora , the national data and information center for Swiss flora . Retrieved November 12, 2015.
- Distribution in the northern hemisphere according to Eric Hultén
- Thomas Meyer: Data sheet with identification key and photos at Flora-de: Flora von Deutschland (old name of the website: Flowers in Swabia )
- Ulex europaeus in the Red List of Threatened Species of the IUCN 2013.1. Posted by: Contu, S., 2010. Retrieved September 21, 2013.
- Ulex europaeus at Plants For A Future
- The poisonous gorse at giftpflanze.com .