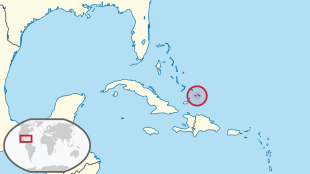
Turks and Caicos Islands
| Turks and Caicos Islands | |||||
| Turks and Caicos Islands | |||||
|
|||||
| Official language | English | ||||
| Capital | Cockburn Town | ||||
| Form of government | British overseas territory | ||||
| Head of state |
Queen Elizabeth II represented by Governor Nigel Dakin |
||||
| Head of government | Prime Minister Sharlene Cartwright-Robinson | ||||
| surface | 616 km² | ||||
| population | 31,458 (2012) | ||||
| Population density | 51 inhabitants per km² | ||||
gross domestic product
|
2018
|
||||
| currency | US dollar (USD) | ||||
| National anthem | God Save the Queen | ||||
| Time zone |
UTC − 5 UTC − 4 (March to November) |
||||
| ISO 3166 | TC , TCA, 796 | ||||
| Internet TLD | .tc | ||||
| Telephone code | +1 (649) see NANP | ||||
The Turks and Caicos Islands , sometimes just called Turks & Caicos , are a British overseas territory in the Caribbean . It is made up of two archipelagos , the Turks and Caicos Islands .
etymology
The name component "Turks" is derived from the autochthonous cactus Melocactus intortus ( English Turk’s cap cactus ), a cactus with a characteristic red fruiting body, which the namesake associated with the typical headgear of the Turks, the Fez . "Caicos" is derived from the term "caya hico" for "chain of islands", which the Lucayans gave to the group of islands.
geography
The Turks and Caicos Islands, although geographically located in the Atlantic, are still part of the Caribbean ; the two small groups of islands form the southeastern foothills of the Bahamas. About 150 km south is the island of Hispaniola with Haiti and the Dominican Republic , 50 km southwest the Inagua archipelago belonging to the Bahamas , 65 km northwest the island Mayaguana of the Bahamas.
The total area of all islands is about 616 km². The capital is Cockburn Town on Grand Turk .
population
The population in January 2012 was around 31,500, consisting of the descendants of African slaves and a mixed European minority.
history
The original indigenous population were the Taino , who were probably displaced or assimilated by the Lucayans. The indigenous population was wiped out by the mid-16th century due to disease and slavery.
There are various theories about the discovery of the islands by the Europeans : Some historians are of the opinion that Christopher Columbus did not land in San Salvador or Samana Cay in the Bahamas in 1492 , but on Grand Turk at what is now the anchorage of Hawks Nest . Today, however, Juan Ponce de León , who first reported on the islands in 1513, is officially considered the European discoverer of the islands.
The islands were settled from Bermuda in the 17th century and were later under Spanish, French and British control. From 1776 to 1848 they were part of the British colony of the Bahamas, and from 1848 to 1959 they were part of Jamaica , which was also British at the time ; In 1959 they were declared a colony of their own. The territory has been on the UN list of sovereign territories without self-government since 1946 . Since about 1976 there have been repeated efforts to become independent, but since about 1982 these have been suspended.
In 1974 there were first efforts in the Canadian parliament to include the islands as the eleventh province in the Canadian state association. However, the bill did not find a majority and was therefore rejected. Since 2003 there have been renewed efforts in this direction. To do this, however, Great Britain would first have to give the islands independence and, second, agree to every single Canadian province; The latter in particular is not very promising because of the very complicated Canadian constitutional procedures.
In September 2008, the islands were hit hard by the hurricanes Hanna and Ike in quick succession . The Turks Islands and South Caicos in particular suffered severe damage.
The British Foreign Office declared the government of the Turks and Caicos Islands to be dismissed in August 2009 due to allegations of corruption. Parliament was dissolved and the constitution governing the autonomy of Great Britain was repealed. The official business was taken over by Governor Gordon Wetherell . Ex-Prime Minister Galmo Williams accused the government in London of recolonization and breach of EU law.
In 2011, an amended constitution was passed that came into force on October 15, 2012. General elections were held on November 9, 2012, Rufus Ewing was sworn in as the new Prime Minister on November 13, 2012 , and the new parliament met for the first time on November 28, 2012. There, Governor Ric Todd announced the establishment of a commission under his leadership to prepare for independence from the United Kingdom, which both parties represented in parliament are striving to achieve.
There are disagreements with London on a number of political issues, for example the introduction of a VAT, which is rejected on the islands. However, London is aiming for a long-term stabilization of the islands' finances, which will no longer be secured by British guarantees from 2016.
politics
The Turks and Caicos Islands are an overseas territory of the United Kingdom . The 2011 constitution has been in force since October 15, 2012.
The head of state is Queen Elizabeth II , who is represented by a governor appointed by her .
The Parliament (House of Assembly) has 21 members, namely 15 members elected for four years, four appointed members, the Attorney General (without voting rights) and the speaker. For the parliamentary elections, the Turks and Caicos Islands form both a single common constituency and ten constituencies. Of the 15 elected members of parliament, five are elected in the common constituency and one member for each of the ten constituencies.
The majority leader in parliament is appointed prime minister by the governor . The government (cabinet) consists of the governor, the prime minister, up to six other ministers from among the elected or appointed members of parliament, the deputy governor and the attorney general.
On January 28, 2016, the EU Commission presented a package of measures to combat tax evasion , including the Turks and Caicos Islands on the black list of tax havens .
administration
The Turks and Caicos Islands are divided into six administrative districts, two of them in the Turks Islands and four in the Caicos Islands. The administrative districts are headed by district commissioners.
economy
For a long time, salt production dominated the economy of the Turks and Caicos Islands. Even before the arrival of the Europeans, the Taíno exchanged salt for honey and fruits from Hispaniola . English colonists from Bermuda began building salt marshes at the end of the 17th century . Salt was mined extensively on South Caicos , Grand Turk and Salt Cay for the next 250 years . Salt production reached its peak at the beginning of the 20th century; Around 60,000 tons of salt were produced annually on around 320 hectares of salt pans. A lack of competitiveness due to the relatively small size of the farms led to the discontinuation of salt production after the middle of the 20th century.
Today the country is economically very dependent on tourism . Hotels and restaurants generate more than a third of the gross domestic product . Financial services contribute around 10% of GDP, the relative importance of this sector has decreased somewhat in recent years.
The nominal gross domestic product of the Turks and Caicos Islands in 2018 was around 1113 million US dollars, which corresponds to 26,909 US dollars per capita. The trade balance is very negative; in 2018 imports of 483.7 million US dollars were compared with exports of only 5.8 million US dollars. The main export goods are fishery products such as the large fencer and the Caribbean lobster , but fishing today only accounts for a small share of GDP. The current account was also negative in 2018, with the deficit exceeding $ 90 million according to preliminary calculations. In contrast to this, considerable surpluses were generated in the previous years.
By far the most important trading partner is the United States , from which more than 85% of all imports come, followed by the Bahamas with 9.4% of imports.
The US dollar is used as the currency .
Infrastructure
The Turks and Caicos Islands Port Authority operates several seaports on the Turks and Caicos Islands. South Dock on Providenciales is the main port through which the majority of international trade is carried out. Other international ports are South Dock on Grand Turk and Conch Ground on South Caicos. There are also other landing stages for local traffic.
Passenger ferries run several times a day between Providenciales and North Caicos. There are ferry connections between Providenciales and South Caicos and between Grand Turk and Salt Cay three times a week.
The main airport is Providenciales Airport , which currently (as of 2020) handles all international scheduled flights to and from the Turks and Caicos Islands. The country's second international airport, JAGS McCartney International Airport on Grand Turk, is only served by domestic flights. Further domestic airfields are on South Caicos and Salt Cay ; the North Caicos Airport is served exclusively by charter flights. There are also two privately operated airfields on Pine Cay and Ambergris Cay. The airport on Middle Caicos is currently closed (2019). Air traffic between the islands is operated by InterCaribbean Airways and Caicos Express Airways .
literature
- Carlton Mills: A History of the Turks & Caicos Islands . Macmillan Caribbean, London 2009, ISBN 978-1-4050-9894-6 (English).
- Herbert E. Sadler, Marjorie Sadler, Karen Collins: Turks Islands Landfall. A History of the Turks & Caicos Islands . Marjorie E. Sadler, Grand Turk 1997, ISBN 976-8138-62-9 (English).
- Theodoor de Booy : The Turks and Caicos Islands, British West Indies . In: Geographical Review . tape 6 , no. 1 , July 1918, ISSN 0016-7428 , p. 37-51 , JSTOR : 207448 (English).
Web links
- About the Turks and Caicos Islands. In: visittci.com. Visit Turks and Caicos Islands Limited.
- Martin Mühlbauer: The Turks and Caicos Islands. 2006, archived from the original on September 29, 2007 .
- The Turks and Caicos Islands Constitution Order 2011. In: legislation.gov.uk. Government of the United Kingdom, July 13, 2011(2011Constitution).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b 2012 Population and Housing Census - Preliminary Report. (PDF; 1.69 MB) In: caribbeanelections.com. KnowledgeWalk Institute, p. 26 , accessed on October 2, 2019 .
- ↑ a b Statistics Department: Latest Indicators. In: gov.tc/stats/. Government of the Turks and Caicos Islands - Statistics Department, accessed May 7, 2020 .
- ↑ Time zones Turks and Caicos Islands. In: timeanddate.de. Time and Date AS, accessed October 20, 2019 .
- ^ Physical Characteristics. (PDF; 23 kB) Land areas of the Turks and Caicos Islands. Department of Economic Planning and Statistics, Government of Turks and Caicos, archived from the original on March 25, 2009 ; accessed on October 2, 2019 .
- ↑ flaggenlexikon.de , accessed on March 29, 2020.
- ↑ canadiancontent.net , accessed March 29, 2020.
- ↑ Jacqui Goddard: Hurricane Ike: Royal Navy heads for Turks and Caicos Islands with aid. In: timesonline.co.uk. Times Newspapers Ltd. September 8, 2008, archived from the original May 21, 2009 ; accessed on May 7, 2020 (English).
- ↑ Rebecca Bird: South Caicos demolished by Hurricane Ike. In: tcweeklynews.com. Turks and Caicos Weekly News, accessed May 7, 2020 .
- ↑ Turks & Caicos Caribbean Islands. British coups in their own paradise . Spiegel Online , August 15, 2009
- ↑ Martin Hirsch: EU wants new black list of tax havens. Press release from the Austria Press Agency (APA). In: trend.at . January 28, 2016; accessed on October 21, 2019
- ^ History of the Salt Industry in the Turks and Caicos Islands. In: visittci.com. Visit Turks and Caicos Islands Limited, accessed May 7, 2020 .
- ^ National Accounts (GDP): Turks and Caicos Islands Percentage Contribution of Gross Domestic Product by Economic Activity in Current Prices 2009-2019p. In: gov.tc/stats/. Government of the Turks and Caicos Islands - Statistics Department, accessed May 7, 2020 .
- ↑ International Trade: Value of Imports and Exports 2002–2019p. In: gov.tc/stats/. Government of the Turks and Caicos Islands - Statistics Department, accessed May 7, 2020 .
- ^ Aylin Ulman et al .: Reconstruction of total marine fisheries catches for the Turks and Caicos Islands (1950–2012) . Discussion paper. Fisheries Center, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC 2015 (English, seaaroundus.org [PDF; 459 kB ; accessed on May 7, 2020]).
- ↑ Olivia Rose: Fishery products continue to dominate TCI's exports. In: tcweeklynews.com. Turks and Caicos Weekly News, March 26, 2018, accessed May 7, 2020 .
- ↑ Merchandise Trade Statistics 2018 . Turks & Caicos Islands Government - Department of Statistics, 2019, Table 47. Annual Balance of Payments (BPM 6): 2014–2019f, pp. 72 (English, online at gov.tc/stats/ [PDF; 2,3 MB ; accessed on May 7, 2020]).
- ↑ International Trade: Imports by Country 2018–2019p. In: gov.tc/stats/. Government of the Turks and Caicos Islands - Statistics Department, accessed May 7, 2020 .
- ↑ Year Book of Statistics 2001–2017 . Turks & Caicos Islands Government - Department of Statistics, 2018, Table 4.21: Tonnage Imported by Country and Port 2017, p. 71–73 (English, online at gov.tc/stats/ [PDF; 17.9 MB ; accessed on May 7, 2020]).
- ↑ Services. In: portstci.com. Turks and Caicos Islands Port Authority, accessed May 7, 2020 .
- ↑ Domestic Flights and Ferries. In: visittci.com. Visit Turks and Caicos Islands Limited, accessed May 7, 2020 .
- ^ Providenciales Airport (PLS). In: visittci.com. Visit Turks and Caicos Islands Limited, accessed May 7, 2020 .
- ^ Grand Turk JAGS McCartney International Airport (GDT). In: visittci.com. Visit Turks and Caicos Islands Limited, accessed May 7, 2020 .
- ↑ Airports. In: visittci.com. Visit Turks and Caicos Islands Limited, accessed May 7, 2020 .
- ↑ AIP-SUPP-1-19. (PDF; 88 kB) In: AIP Supplement. Turks & Caicos Islands Airports Authority, January 30, 2019, accessed May 7, 2020 .
Coordinates: 21 ° 45 ′ N , 71 ° 35 ′ W