Barcelona
| Barcelona | ||
|---|---|---|
 collage
|
||
| coat of arms | Map of Spain | |

|
|
|
| Basic data | ||
| Autonomous Community : | Catalonia | |
| Province : | Barcelona | |
| Comarca : | Barcelonés | |
| Coordinates | 41 ° 24 ' N , 2 ° 10' E | |
| Height : | 12 msnm | |
| Area : | 101.4 km² | |
| Residents : | 1,636,762 (Jan 1, 2019) | |
| Population density : | 16,141.64 inhabitants / km² | |
| Postal code : | 08001-08042 | |
| Municipality number ( INE ): | 08019 | |
| Nearest airport : | Barcelona-El Prat Airport | |
| administration | ||
| Mayor : | Ada Colau ( Barcelona en Comú ) | |
| Website : | www.barcelona.cat | |
Barcelona ( Catalan [ bəɾsəˈɫonə ]; Spanish [ baɾθeˈlona ]; German [ baɐ̯səˈloːna ] or [ baɐ̯t͡səˈloːna ]) is the capital of Catalonia and the second largest city in Spain after Madrid . It is located on the Mediterranean Sea , around 120 kilometers south of the Pyrenees and the border with France. Barcelona is the administrative seat of the province of the same name and the comarca of Barcelonès .
About 1.62 million people live within the urban area. This makes Barcelona the eleventh largest municipality in the European Union , after Hamburg the second largest that is not the capital of a member state, and after Paris the second most densely populated metropolis in Europe. Together with the municipalities of the agglomeration united in the Àrea Metropolitana de Barcelona , the population is 3.16 million. A total of 4.86 million people live in the wider catchment area of the metropolitan region ( Àmbit Metropolità de Barcelona ). With more than seven million tourists from abroad every year, Barcelona is also one of the three most visited cities in Europe.
In a ranking of cities according to their quality of life , Barcelona ranked 43rd out of 231 cities worldwide in 2018. According to the Global Wealth and Lifestyle Report 2020 , Barcelona has a European top position in terms of price-performance ratio for luxury living.
geography
location
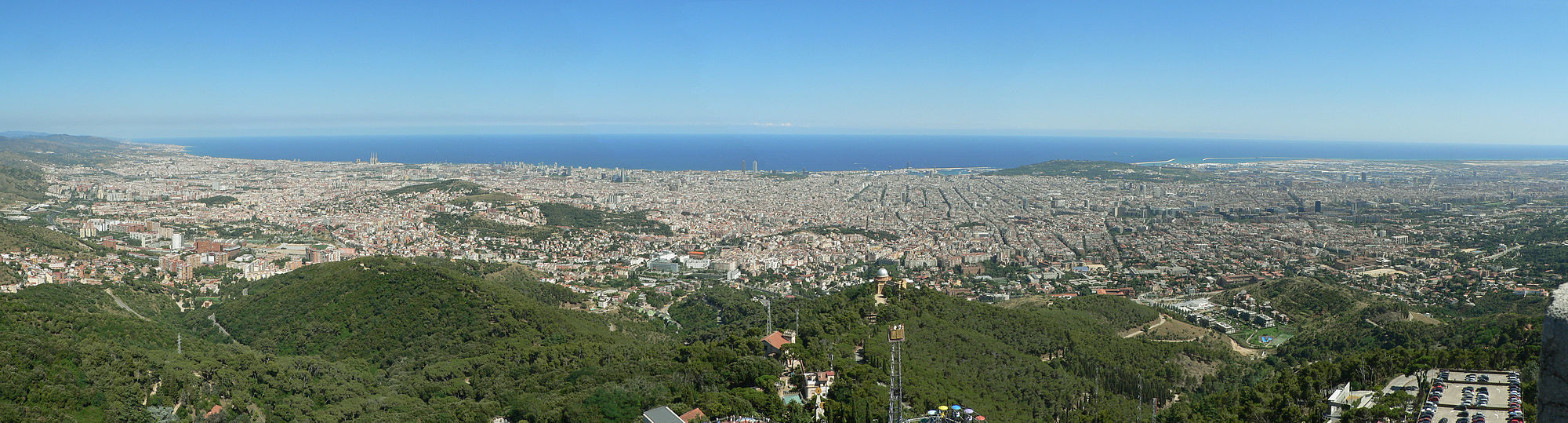
Barcelona is located in the northeast of the Iberian Peninsula on the coast of the Mediterranean Sea on a five-kilometer-wide plateau bounded by the Serra de Collserola mountain range and the Llobregat rivers in the south and Besòs in the north. The Pyrenees are about 120 kilometers north of the city.
The Serra de Collserola, part of the coastal mountains, forms the gently rounded background of the city. Its highest point, the Tibidabo , is 512 meters high and is dominated by the 288.4 meter high and widely visible transmission tower Torre de Collserola . The highest point in the city center is the 16.9 meter high Mont Tàber , on which the cathedral is built. The town is criss-crossed by small, mostly built-up hills, which gave their names to the districts built on them: Carmel (267 meters), Monterols (121 meters), Putxet (181 meters), Rovira (261 meters) and Peira (133 meters) . The mountain Montjuïc (173 meters) lies in the southwest and overlooks the port. The fortress from the 17th and 18th centuries, which replaced the Ciutadella, ruled the city. Today the fortress is a military museum, and the mountain is home to some Olympic and cultural institutions, as well as well-known gardens.
In the north the city borders on the municipalities of Santa Coloma de Gramenet and Sant Adrià de Besòs , in the south on L'Hospitalet de Llobregat and Esplugues de Llobregat , in the southeast lies the Mediterranean Sea and in the west lie Montcada i Reixac and Sant Cugat del Vallès and Cerdanyola del Vallès .
climate
| Barcelona (Aeropuerto) (4 m) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate diagram | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Average monthly temperatures and rainfall for Barcelona (Aeropuerto) (4 m)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The climate of Barcelona is typical of the Mediterranean area ; it belongs to the subtropics , which consists of hot, dry summers and mild winters.
history
The history of Barcelona began 2000 years ago with the Iberian settlement of Barkeno . Its easy to defend location on a coastal plain between the Collserola ridge and the Mediterranean Sea on the way from Central Europe to the Iberian Peninsula has ensured the importance of this city through all times.
Origins
Little is known about the origins of Barcelona. From the time before the conquest of the Iberian Peninsula by the Romans , artifacts from the Neolithic and the Copper Age can be found on the plains of Barcelona . Later, in the third and second centuries BC, the landscape was settled by the Laietani , an Iberian people who lived in Barkeno on the Táber Hill (today's Ciutat Vella ) and in Laie (or Laiesken) on Montjuïc. Coins that are still preserved today were minted in both settlements. Around the same time, a small Greek colony called Kallipolis was established in the region, but its exact location is unknown. 218 BC At the beginning of the Second Punic War , the area was conquered by the Carthaginians under the leadership of Hannibal Barkas . Up until this point in time, the northern border of the Carthaginian territories ran along the Ebro , i.e. 150 kilometers south. This military occupation is often referred to as the founding of Barcelona.
Founding legends
There are at least two other versions of the founding of Barcelona originating from fifteenth-century historians. One attributes the founding to the Carthaginian general Hamilkar Barkas , Hannibal's father. He is said to have founded the city around 230 BC as Barkenon, Barcelino or Barci Nova. Because of the similarities in the name of the Carthaginian dynasty Barkas and the present-day city, it is believed that the name Barcelona could be traced back to the establishment or conquest of this settlement by the Barkas dynasty.
The second version (no doubt from the realm of myth) claims that the demigod Heracles founded the city around 1153 BC (around 400 years before the founding of Rome). During the fourth of his labors, Heracles joined Jason and the Argonauts in their search for the Golden Fleece. When one of the nine ships on which they traveled the Mediterranean was lost due to a storm on the Catalan coast, the hero went looking for it and found it on a small hill, destroyed but with a rescued crew. Heracles was so fascinated by the beauty of the area that he founded a city called Barca Nona (Italian Ninth Ship ). This is contradicted by the fact that at that time neither Latin nor the Romance languages (which includes the Italian language ) were spoken on the Iberian Peninsula , which only emerged many centuries later with the spread of Vulgar Latin by the Roman Empire .
Under the Romans

Little is known about the time between 218 BC and the New Age. The Roman Republic first took control of the region and then conquered the rest of the Iberian Peninsula in the Cantabrian Wars , which ended under Augustus in 19 BC. The northeast of the peninsula was the first region to fall under Roman control, so it served as a base for further conquest. Although the Romans settled in Barcino, it was much less significant than the capitals of Tarraco and Caesaraugusta . The name Barcino was chosen at the end of the reign of Augustus, Rome's first emperor. It was the short form for the Colonia Faventia Iulia Augusta Pia Barcino, founded in 133 BC. As a colony, it was designed to provide land for retired soldiers. The Roman geographer Pomponius Mela reports of Barcino as a number of smaller settlements under the control of Tarragona (Tarraco). Nevertheless, the city's strategic position on an arm of the Via Augusta allowed its economic development and it enjoyed tax exemption.
In the time of Emperor Augustus, Barcino had the appearance of a castrum ( i.e. a military camp) with its usual right-angled main streets, the Cardo in north-south and the Decumanus in east-west. The forum (today Plaça de Sant Jaume) was on Mont Tàber, which is now the highest point of the Barri Gòtic . The walls extended over a length of 1.5 kilometers and enclosed 12 hectares. In the second century the city had grown into a real oppidum and had a population of 3500 to 5000 people. The economy was based on the cultivation of the surrounding land and viticulture. The archaeological finds of this period (sculptures, mosaics, amphoras) testify to a relatively wealthy population, although the city did not have any of the important public buildings, such as an amphitheater or a circus, that existed in more important Roman cities such as Tarragona. There was only one public building, and that was the temple dedicated to Augustus ( Augustus Temple ), which was probably built at the beginning of the first century. It was quite large - measured by the size of Barcino - 35 meters long and 17.5 meters wide and surrounded by Corinthian columns.
As the decline of the empire approached, the first Germanic incursions also occurred around the year 250, after which the fortifications were strengthened in the later years of the third century under Claudius II . The new double wall was at least two meters high (up to eight meters in some places) and lined with 78 towers that were 18 meters high. These new facilities were the strongest in this Roman province and would later be important for the increasing importance of Barcino compared to Tarragona.
The first Christians
The first Christian communities in the province of Tarragonas were founded during the third century. The Diocese of Tarragona was founded in 259 when its bishop, Saint Fructuosus and the deacons Augurius and Eulogius were killed on the orders of Emperor Valerian . The Christian community of Barcino seems to have been built in the later half of the 3rd century. The persecution of Christians under Diocletian at the beginning of the fourth century resulted in a martyr in the Barcinos region, St. Cucufato . Allegedly of African descent, Cucufato worked in some areas of the province (Barcino, Egara - now Terrassa - and Iluro - now Mataró ) before he was crucified in Castrum Octavium (now Sant Cugat del Vallès near Barcelona). The holy virgin Eulalia is also said to be a martyr from Barcelona. The Edict of Milan under Emperor Constantine (313) granted Christians freedom of religion in the Roman Empire. The first known Bishop of Barcinos was Pretextat (died around 360) who attended the Synod of Sofia in 347. Pacian and Lampius (died 400) followed him. Pacian is especially known for his works De baptismo ("On Baptism") and Libellus exhortatorius ad poenitentium ("On Penance"). The first church, the Basílica de la Santa Creu on the site of the modern cathedral, was built at the end of the 4th century.
Among the Visigoths

At the end of the 5th century the fall of the Western Roman Empire began to emerge from Germanic peoples who carried out some severe attacks on the empire. In 410 Rome was conquered under the Visigoth Alaric I. Alaric's stepbrother and successor, Athaulf , led the Visigoth troops to southern Gaul, and after the defeat by the Roman forces at Narbona (414) he fled across the Pyrenees to the province of Tarragona . Athaulf established his seat in Barcino, where he was murdered by his own troops in 415.
The death of Athaulf changed the relationship between Romans and Visigoths. Under Walia (415–419) they became allies to control the other Germanic tribes in Spain. Walia was so successful in this that Emperor Flavius Honorius expanded the territory of the Visigoths to include the provinces of Aquitania and Gallia Narbonensis. Walia was based in Tolosa (now Toulouse ). However, Barcino remained a significant center of the Visigoth kingdom due to its excellent defensive walls.
After the death of Alaric II in the Battle of Vouillé against the Franks (507), his successor Gesaleic (507-511) made Barcino the capital of his empire. Barcino returned to its role as a provincial town with the elevation of Toledo to the capital under Leovigild 573. The Visigoths were only a minority of the urban population, but held positions of power. The first rulers were initially Arians , but tolerated that most of the residents were Catholic. The religious center changed from the Basílica de la Santa Cruz (which became an Arian temple) to the church of Sant Just. Catholic councils were held in 540 under Bishop Nebridi and 599 under Ugers in the re-consecrated basilica. Undoubtedly, the colloquial language spoken at the time was Vulgar Latin, which was also adopted by the Visigoth rulers. The Latin Barcino slowly changed (for example Barcinone, Barcinonem, Barcinonam, Barchinona).
Under the Moors
The Moors' troops reached the Iberian Peninsula in 711. After the destruction of Tarragona in 717, Barcelona surrendered and was thereby saved from major destruction. The Moors' rule in Barcelona lasted less than a century. The cathedral was converted into a mosque and taxes for non-believers were increased.
Barcelona in the Spanish Mark
Louis the Pious , son of Charlemagne, conquered Barcelona in 801 after a siege of several months. The city was said to be the southernmost of his conquests by the Moors, as he was repulsed at Tortosa and by the Llobregat and Cardener rivers . This border region was known as the Spanish Mark . It was administered by several counts who were installed by the king. Barcelona became the seat of a count. The first Carolingian counts of Barcelona were little more than royal officials, but over time their status gained power and independence from central authorities and the weak Carolingian kings. In addition, several areas were assigned to a count.
The last Count of Barcelona to be installed by the Carolingians was Wilfried I , the Hairy. Before that he had already been Count of Cerdanya and Urgell and received the counties of Barcelona, Girona and Besalú in 878 . When he died in 897, Wilfried's possessions were divided between his two sons Wilfried II and Miro the Younger, which meant the introduction of the hereditary nobility in the Spanish Mark.
Wilfried II. Was the last count who had to swear allegiance to the Carolingian court, although the fief was actually only abolished in the Treaty of Corbeil in 1258 . The predominance of the Counts of Barcelona under the rulers of the Spanish Mark was partly the result of their military skills, which enabled them to conquer more territories from the Moorish rulers. They also tried to resettle inland residents whose residents had been decimated by two centuries of war. Barcelona, with its easily defendable and excellent fortifications, flourished as its rulers rose in power, while the other counties had poor prospects.
Under the crown of Aragon


Through the marriage contract between Ramon Berenguer IV. , Count of Barcelona, and the only one year old Petronella , heiress of the Crown of Aragon , a community of states emerged in 1137 from Aragon and the 12th century countries of the Counts of Barcelona, which were largely identical to Catalonia Aragon ”is known. Through further dynastic connections and conquests, it became the leading power of the western Mediterranean in the High and Late Middle Ages. Its economic and cultural center was the Catalan part of the state community, the Principate of Catalonia, whose merchant navy ruled the western Mediterranean and had commercial agencies in numerous ports. At that time, Barcelona was already the largest settlement in Catalonia and an important source of income for the country.
In the Spanish monarchy
The marriage of Ferdinand II of Aragon with Isabella I of Castile in 1469 united the two royal families of Spain. This shifted the political center to Toledo and later, under the Habsburg Philip II, to Madrid, and degraded the former crown of Aragon to a province. In addition, like many Spanish cities on the Mediterranean Sea, Barcelona suffered a huge drop in trade and importance as a result of the discovery of America.
In the conflict between Spain and France in the middle of the 17th century, Catalonia sided with France, but then found itself stuck in the peace agreement of 1659, the Peace of the Pyrenees , and was divided into two parts: The Catalan areas north of the Pyrenees ( Northern Catalonia ) were lost to France.
In the War of the Spanish Succession (1700–1713), which concerned the succession to the throne after the death of Charles II , who remained childless , Catalonia sided with the Habsburg pretender Archduke Charles and against the Bourbon Philip of Anjou - later known as Philip V. After the siege of 1705 , Karl moved into the city. Philip V, who emerged victorious in the Peace of Utrecht, punished Catalonia harshly for this: In 1714, Barcelona was conquered and occupied by French troops , and the Catalan institutions were dissolved, which ended the Catalan self-government.
The city was the scene of several uprisings in the 19th century. Among other things, there were protests in November 1842 against the charges imposed by the Spanish government. The rebels gained the upper hand in the city and the military withdrew to the fortress on Montjuïc . On December 3, 1842, on the orders of Regent Baldomero Espartero , a bombardment of the city began, which lasted twelve hours. It caused considerable destruction and killed around 100 people. The next day the rebels surrendered and were disarmed.
From the middle of the 19th century, the city experienced a renewed economic boom and became a center of industrial development in Spain, bringing wealth and political influence back to the region. At the same time, in the course of industrialization and the extreme social differences between the big bourgeoisie and the working class , Barcelona developed into a city in which Spanish anarchism found a particularly large number of followers. It was the scene of numerous anarchist attacks in the 1890s. On September 24, 1893, the anarchist Pallas carried out a bomb attack on Arsenio Martínez-Campos in which several people were killed and wounded. Pallas was brought before a firing squad on October 5th . To avenge his execution, another assassination attempt was carried out on November 7th at a performance in the Gran Teatre del Liceu , in which 23 people were killed and around 40 injured.
After the medieval city walls were torn down in 1854–1856, the new Eixample district (literally: "extension") was planned and laid out. The author of the urban design was Ildefons Cerdà , who proposed an isomorphic grid that still characterizes the urban space today. In 1888, Barcelona hosted the World's Fair , which resulted in a large expansion of the city from Parc de la Ciutadella to Barceloneta . In 1897 six surrounding villages, including Gràcia and Sants , were incorporated. The city's prosperity also led to its re-emergence as a cultural center. With the Exposición Internacional de Barcelona , a second major international exhibition was organized in 1929, which was recognized as a world exhibition and led to the urbanization of the area around Plaça d'Espanya and the construction of the subway . The Palacios de Alfonso XIII y Victoria Eugenia or Palau Nacional, which was built from 1918 to 1923, is a widely visible sign of the structural changes of this time. The palace complex now serves as a museum for modern art and architecture.
The second republic and the civil war
After the electoral victory of the Spanish left, which formed the Frente Popular (the “Popular Front”) in 1936 , Barcelona was to become the venue for a People's Olympiad , a counter-event to the Berlin Olympic Games in National Socialist Germany. With the outbreak of the Spanish Civil War in July 1936, however, the competitions had to be abandoned with the opening ceremony. Some of the athletes subsequently joined the socialist, communist and anarchist militias in defense of the Spanish republic, which became the nucleus of the later International Brigades .
In Barcelona, a stronghold of republican forces, the insurgent troops were quickly crushed by militias and civil Guard associations loyal to the government . In 1937, however, there was an armed conflict in the city within the republican camp, between anarchists and left-wing Marxists on the one hand and communists and socialists on the other - the so-called May events of Barcelona, a civil war within a civil war that could only be ended after days and hundreds of deaths .
In 1938, Barcelona was the target of numerous heavy air raids by the insurgents, in which German aircraft from the Condor Legion took part. The Royal Italian Air Force flew the heaviest attack on January 19, 1938. With the approaching military collapse of the Second Republic, the nationalist units reached the limits of the city at the end of 1938, and on January 26, 1939 it fell under the control of Franco's troops .
Under Franco
The massive resistance of Barcelona to the Franco coup had devastating consequences for Catalonia after the defeat of the republican government. The region's autonomous institutions - such as the Generalitat de Catalunya - were abolished and the use of the Catalan language in public, education and publishing was suppressed, rendering Barcelona a political and cultural center. Nonetheless, it remained one of the country's economic and industrial centers, and in the decades that followed, it attracted many immigrants from poorer Spanish regions (particularly from Andalusia and Galicia ). The increase in the number of inhabitants led to accelerated urbanization, the development of the subway and road network, but also the construction of large sleeping cities on the outskirts. In addition, the immigration of Spanish-speaking sections of the population intensified the pushing back of Catalan culture in Barcelona, which was driven by the Franco regime, a development from which the city quickly recovered after the end of the Franco era.
Modern Barcelona
The death of Franco in 1975 led to a democratization movement in Spain, the Transición , which found widespread support, especially in Catalonia. In 1977 there was a large demonstration in Barcelona with over a million people demanding the restoration of Catalan autonomy as part of Spain's political renewal. This was established again shortly afterwards with the return of Josep Tarradellas - the President of the Generalitat in exile in France - and the law on the Statute of Autonomy of Catalonia, the Estatut de'Autonomia .
The development of Barcelona was promoted in the following years by two significant events: Spain's accession to the EU in 1986 and the 1992 Summer Olympics . The city developed into a popular tourist destination with steadily increasing numbers of visitors. As many families moved from the densely built-up city center to the suburbs, the population fell by 17 percent in the last two decades of the 20th century, and has increased since the turn of the millennium due to strong immigration (mainly from EU countries, Latin America and Morocco ) however again on. The urban development of the city has been characterized in recent years by numerous major projects aimed at improving the infrastructure and quality of life, such as the renovation of the beaches, the new construction of the Diagonal Mar district on the occasion of the 2004 International Forum of Cultures and the Construction of the AVE high-speed rail line from Madrid via Saragossa and Barcelona to France.
At least 15 people died in the terrorist attack in Barcelona on August 17, 2017 , which the terrorist organization Islamic State claimed.
politics
With Ada Colau i Ballano ( Barcelona en Comú ) is since 13 June 2015, the first woman in the history of Barcelona Mayor of the city.
administration
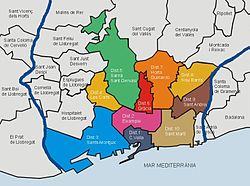
Since 1984, the city has been divided into ten administrative districts made up of 73 districts.
| No. | District | Area (km²) |
Residents |
Population density ( inh . / Km² ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ciutat Vella | 4.49 | 113.154 | 25.202 |
| 2 | Eixample | 7.46 | 262,485 | 35,186 |
| 3 | Sants-Montjuïc | 21.35 | 177,636 | 8,321 |
| 4th | Les Corts | 6.08 | 82,588 | 13,584 |
| 5 | Sarrià-Sant Gervasi | 20.09 | 140,461 | 6,992 |
| 6th | Gracia | 4.19 | 120,087 | 28,661 |
| 7th | Horta-Guinardó | 11.92 | 169.920 | 14,256 |
| 8th | Nou Barris | 8.04 | 164.981 | 20,521 |
| 9 | Sant Andreu | 6.56 | 142,598 | 21,738 |
| 10 | Sant Martí | 10.8 | 221.029 | 20,466 |
Culture and sights
Downtown
The center of the city forms the Plaça de Catalunya as a traffic junction , from here the Roman ruins, the medieval city and the modern planned city Eixample can be reached on foot , which for its square blocks with the beveled corners (cat. Xamfrans ) and the many Modernisme buildings is known. From Plaça de Catalunya, Passeig de Gràcia , a large shopping street, stretches northwards. Here you will find numerous Spanish chain stores as well as exclusive boutiques. In addition, there are two well-known buildings by the architect Antoni Gaudí, Casa Milà and Casa Batlló .
In the historic city center, the Barri Gòtic ('Gothic Quarter'), there are numerous beautiful architectural testimonies of the medieval royal and trading city such as La Catedral , the Cathedral of St. Eulàlia, the Plaça del Rei ('King's Square'), the city museum ( Museu d 'Història de Barcelona , MUHBA), the Frederic Marés Museum and the City Hall ( Ajuntament ). The most famous street in Barcelona is the promenade La Rambla (or plural Les Rambles ), a wide avenue that leads from the center to the port. There you will find numerous flower sellers, newspaper kiosks, street musicians, acrobats, cafes and restaurants as well as the famous market Mercat de la Boqueria and the Plaça Reial with its arcades and palm trees as well as typical bars and the famous Gran Teatre del Liceu . At the end of the Rambles facing away from the port is the Font de Canaletes drinking fountain , which is said to have made everyone return to Barcelona again and again after drinking from it.
At the southern end of the Rambla on the Plaça Portal de la Pau there is a statue of Christopher Columbus with an outstretched arm pointing out to the Mediterranean Sea, the imaginary line goes just past Mallorca and hits the next mainland Algeria . Very close to the statue at the old port, the Port Vell , are also the medieval shipyards, the Drassanes Reials ('Royal Shipyards'), which today house the Maritime Museum Museu Marítim . It tells the story of the Catalan seafaring in the Mediterranean and exhibits, among other things, the 1: 1 replica of the hull of the Galley Real , the flagship of Don Juan d'Austria in the battle of Lepanto (1571).
The port houses the modern leisure center and shopping center Maremagnum , which in addition to numerous discos, boutiques and cinemas (formerly an IMAX cinema ) also contains the largest oceanarium dedicated to the Mediterranean . Barcelona was dubbed by its residents until the 1992 Summer Olympics as “the city with its back to the sea” (Catalan: “la ciutat d'esquena al mar”). Industrial areas blocked the view and access to the sea. In the course of the organizational measures for the 1992 Olympic Games, sufficient funds were then available to open up the city center in the area of the old port and the coastal strip to the northeast, beyond the old fishing district of Barceloneta, with a wide, attractive beach facing the sea. An older attraction is the Barcelona harbor cable car, which connects the Torre Jaume I with the Torre Sant Sebastià and goes up to the Montjuïc .
Barcelona and modernism
At the end of the 19th century, Barcelona developed its own form of Art Nouveau , Modernisme . Its most prominent representative is Antoni Gaudí , who lived in Barcelona and worked with the support of the industrialist Eusebi Güell . A number of famous buildings by him can be visited. These include the
- Casa Milà (La Pedrera)
- Palau Güell
- Park Güell
- Casa Batlló
- Casa Vicens
- Casa Calvet and
- the still unfinished Sagrada Família church , which has been under construction since 1882.
Since 1984 and 2005, these buildings are part of the World Heritage of UNESCO . Since 1997, with two buildings by Lluís Domènech i Montaner , Barcelona has had further World Heritage sites. These are the Hospital de Sant Pau and the Palau de la Música Catalana .
More Attractions
Important museums in the city include the Fundació Joan Miró , the Museu Picasso with numerous less well-known works by Pablo Picasso , the Museu Nacional d'Art de Catalunya (MNAC), which contains important Romanesque wall paintings and other medieval works of art, and that of Richard Meier designed the Museu d'Art Contemporani de Barcelona (MACBA).
Architecturally interesting are the television tower Torre de Collserola designed by Sir Norman Foster , the Torre Telefónica by Santiago Calatrava and the futuristic Torre Agbar with a height of 142 meters, which was only completed in 2004 and planned by the French architect Jean Nouvel . For the 1929 World Exhibition , Ludwig Mies van der Rohe designed the German pavilion , which was demolished at the end of the World Exhibition, but was then reconstructed again at the foot of Montjuïc from 1983 to 1986 , below Poble Espanyol , a small Spain that was also part of the former World Exhibition site. The Font Màgica , also located on Montjuïc, is very popular with visitors , a fountain system with fountains that are controlled and illuminated in the summer months in the evening with music. Also of interest is the Cementiri de Montjuïc municipal cemetery on the southern edge of Montjuïc with the graves of famous sons and daughters of the city, including those of Francesc Ferrer i Guàrdia and Francisco Ascaso and Buenaventura Durruti of the anarchist and anti-fascist fighters in the Spanish civil war .
To the east of the Barri Gòtic are the Arc de Triomf and the Parc de la Ciutadella , which was built here for the 1888 World Exhibition on the site of a demolished fortress. Part of the park is taken up by the zoological garden ( Parc Zoológic ).
The Bethlehem Church was completed in 1929.
El Peix construction by Frank Gehry at Port Olimpic
Font Màgica on Montjuïc
The beach and promenade of La Barceloneta
Events
- 1888: World's Fair
- 1929: World Exhibition , together with Seville
- 1982: Football World Cup a . a. held in Camp Nou and in the Estadio Sarriá
- 1988: First leg of the 1987/88 UEFA Cup final
- 1989: Final of the European Champion Clubs' Cup 1988/89
- 1992: Summer Olympic Games in Barcelona
- 1999: 1998/99 UEFA Champions League final
- 2003: World Swimming Championships
- 2004: From May to September the International Forum of Cultures
- 2010: European Athletics Championships
- 2013: Final of the 2013 Men's Handball World Championship
- 2013: Swimming World Championships , in the port of Moll de la Fusta, with cliff jumping for the first time
Squatter scene

Barcelona has had one of the most active squatter scenes in Europe for many years . One of the main reasons for this lies in the fact that over 80 percent of Barcelona's residential units are condominiums, making them unaffordable for teenagers and young adults.
In 2000, around 70 houses in the Barcelona area were occupied, mainly in the centrally located districts of Sants and Gràcia. Today there is talk of up to 200, of which only around a quarter are run as social, cultural and event centers - i.e. as open houses. In these, events take place regularly, which are also announced in a jointly managed, weekly updated and publicly displayed calendar and can be accessed on the Internet.
population
| rank | Country | Population (January 1, 2015) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. |
|
25,669 |
| 2. |
|
19,432 |
| 3. |
|
17,466 |
| 4th |
|
13,276 |
| 5. |
|
12,655 |
| 6th |
|
10,014 |
| 7th |
|
8,619 |
| 8th. |
|
8,551 |
| 9. |
|
8,530 |
| 10. |
|
8,038 |
According to official figures, there were just over 1.6 million people in Barcelona in 2015, including a marginal surplus of women. It is therefore the second largest city in Spain after Madrid and the most populous in Catalonia. About 62% of the population were born in Catalonia, and just under 24% are from other parts of Spain. The proportion of foreigners increased significantly from just under 4% in 2001 to 17% in 2015.
religion
Barcelona, like the rest of Catalonia, is one of the most secularized areas in traditionally Catholic Spain. The Roman Catholic Church is also the largest religious community in Barcelona. The number of believers is declining, however; in a 2011 survey, 49.5% for the first time, were less than half of the resident population Catholic, and only 45% in the 14 to 25 age group. According to the Catholic Church, however, in the same year 79.6% of the inhabitants of the Archdiocese of Barcelona , which is slightly larger than the urban area, are Catholics.
For Islam , most of them, however, are not Spaniards: about 6% of the population profess (2014 version). With 3,500 Jews there is the largest Jewish community in all of Spain, but this is only 0.06%. No figures are available for Protestants and non-denominationalists .
Economy and Infrastructure
Barcelona is the capital and the economic, cultural and political center of Catalonia, the strongest economic region in Spain. The city's GDP in 2012 was 64.2 billion euros, the GDP per capita was 40,100 euros, well above the EU average. According to a study from 2014, the Barcelona metropolitan area has a gross domestic product of 171 billion US dollars (KKB). In the ranking of the economically strongest metropolitan regions worldwide, he came 72nd. The GDP per capita was $ 36,157.
The city is an international business location. Outstanding sectors are in services of education, health, trade, and tourism and hospitality industry. The industrial sector contributes 8.1% to the added value. Important industrial sectors in and around Barcelona are the automotive industry and the pharmaceutical and chemical industries. The food industry and the development and manufacture of electronic components also occupy significant areas of the economy. Today the headquarters and a large factory of SEAT (the largest Spanish car manufacturer) are in one of its suburbs. With regard to the production facility of the vehicle manufacturer Nissan in the city's logistics and industrial area with approx. The permanent plant closure was announced to 3,000 employees at the end of May 2020. The factory of Derbi , a major manufacturer of motorcycles, scooters and mopeds, is also close to town.
The Avinguda de la Llum was an underground shopping street from 1940 to 1990 .
tourism
In 2014, 7.878 million tourists officially registered in hotels came to Barcelona, compared to 1.7 million in 1990. The number of overnight stays rose from 3.8 to 17 million during this period and the number of international passengers has increased tenfold since 1990. Barcelona ranks fourth among Europe's most visited cities, after Paris, Rome and London, but with a comparatively much smaller number of inhabitants, which is known as overtourism (“Venice principle”).
traffic
Public transport
Barcelona is an important hub for RENFE , the Spanish state railways . The main station for suburban trains is Sants-Estació . The AVE - Madrid-Barcelona high-speed rail line went into operation in 2008 fully and from the timetable change in December 2013. high-speed lines even after Paris Gare de Lyon , Lyon , Marseille and Toulouse . RENFE and the Catalan state railway Ferrocarrils de la Generalitat de Catalunya (FGC) operate an extensive S-Bahn network (called Rodalies) .
The transport company of Barcelona, Transports Metropolitans de Barcelona (TMB), the operator of a very dense network consisting of metro Metro Barcelona and local bus lines. The Barcelona tram, which opened in 2004, has two different, not yet interconnected sub- networks, called Trambaix and Trambesòs . These will be connected and expanded through the center of Barcelona over the next few years (currently in planning). The old tram network was closed in 1971.
The public transport in the metropolitan region is combined in a tariff system that is coordinated by the transport association Autoritat del Transport Metropolità (ATM).
Since 2007 there with bicing also a network of bicycle rental stations. However, these can only be used by people who are registered in Spain, as you have to register on the relevant website beforehand and only a Spanish address is accepted. In 2015 the first electric bicing stations were put into operation. However, there are many bike rental shops near Placa Catalunya. In addition, tours with three-wheeled bicycles from private providers can also be booked in the city center.
Private transport
The motorway network around Barcelona is extremely dense and (apart from a section of the C-16 towards Terrassa ) there is no toll. The road network in the city center has a chessboard structure. One of the most important streets is Avinguda Diagonal , which runs diagonally from northeast to southwest across the city. However, Barcelona has significant problems with traffic density. Barcelona is therefore trying to reduce car traffic in the city by 20 percent by 2018 with a new concept called “Superilles” (“Superblocks”). Nine blocks are combined and the traffic is diverted.
A considerable part of the road network is laid out as a system of one-way streets , alternating in opposite directions.
In the city center, parking spaces are very limited and the many underground garages can only be used by cars. The parking fees are accordingly higher than average. A park-and-ride offer enables parking outside of the city as an alternative.
Airport
Barcelona is easy to reach mainly via its own El Prat airport , but also via the airports of Girona , Reus and Lleida-Alguaire . All airports outside of Barcelona have access to the AVE high-speed train for quick access to Barcelona (city), as well as access to highways to the Catalan capital.
port
The port of Barcelona is one of the largest ports in Europe and the Mediterranean. It is divided into three areas: the Port Vell ('old port'), the large industrial port below the local mountain Montjuïc, the Port Franc de Barcelona - here the ferry and cruise ships operate , but also container ships - and the small marina , built in 1992 Port Olímpic ('Olympic Port ').
education
Barcelona has five public universities:
- Universitat de Barcelona (UB) (founded 1450)
- Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) (founded 1968)
- Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC) (founded 1971)
- Universitat Pompeu Fabra (UPF) (founded 1990)
- Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC) (founded 2000)
There are also various private universities ( see also the list of universities in Barcelona ).
Education for immigrants and exchange students
Barcelona is home to many German immigrants and therefore also has the German School Barcelona , where the general university entrance qualification can be acquired according to the Bavarian curriculum. There is also a Swiss school in Barcelona that offers all levels up to and including grammar school.
For a semester abroad in Barcelona, for example at the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya or the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (in Cerdanyola del Vallès ), knowledge of the Catalan language is an advantage, as most of the courses are held in Catalan. However, lectures are also offered in Spanish and French, and increasingly in English.
Sports
The most important sports club is FC Barcelona , whose Camp Nou stadium is considered the largest stadium in Europe. The Espanyol Barcelona sports club , which played in the Olympic Stadium on Montjuïc until 2009 and has now moved to the newly built Estadi Cornellà-El Prat in the Cornellà district, is the second largest sports club in Barcelona.
Formula 1 races have been held regularly on the Circuit de Catalunya north of Barcelona since 1991 . Before that, the Circuit de Montjuïc and the Circuit de Pedralbes served as the venue for the Spanish Grand Prix .
The handball division of FC Barcelona is still the most successful club team in the world, and has won the Champions League nine times . The home games are played in the Palau Blaugrana , an arena with a capacity of 8,250.
Barcelona is known as the “Mecca for skateboarders” and skateboarding events take place here on a regular basis .
In 2014 and 2015, Barcelona hosted the figure skating Grand Prix final .
music
sons and daughters of the town
Twin cities
-
 Antwerp , Belgium (1997)
Antwerp , Belgium (1997) -
 Athens , Greece (1999)
Athens , Greece (1999) -
 Boston , USA (1983)
Boston , USA (1983) -
 Busan , South Korea (1983)
Busan , South Korea (1983) -
 Dubai , United Arab Emirates (2006)
Dubai , United Arab Emirates (2006) -
 Dublin , Ireland (1998)
Dublin , Ireland (1998) -
 Gaza City , Palestine (1998)
Gaza City , Palestine (1998) -
 Havana , Cuba (1993)
Havana , Cuba (1993) -
 Isfahan , Iran (2000)
Isfahan , Iran (2000) -
 İstanbul , Turkey (1997)
İstanbul , Turkey (1997) -
 Kobe , Japan (1993)
Kobe , Japan (1993) -
 Cologne , Germany (1984)
Cologne , Germany (1984) -
 Monterrey , Mexico (1977)
Monterrey , Mexico (1977) -
 Montevideo , Uruguay (1985)
Montevideo , Uruguay (1985) -
 Montpellier , France (1963)
Montpellier , France (1963) -
 Rio de Janeiro , Brazil (1972)
Rio de Janeiro , Brazil (1972) -
 Saint Petersburg , Russia (1985)
Saint Petersburg , Russia (1985) -
 São Paulo , Brazil (1985)
São Paulo , Brazil (1985) -
 Sarajevo , Bosnia and Herzegovina (2000)
Sarajevo , Bosnia and Herzegovina (2000) -
 Shanghai , China (2001)
Shanghai , China (2001) -
 Tel Aviv-Jaffa , Israel (1998)
Tel Aviv-Jaffa , Israel (1998) -
 Valparaíso , Chile (2001)
Valparaíso , Chile (2001) -
 Wenzhou , China (2011)
Wenzhou , China (2011)
In addition to these twin cities, Barcelona also has cooperation agreements with a large number of other cities around the world.
See also
literature
- Emil Huebner : Barcino . In: Paulys Realencyclopadie der classischen Antiquity Science (RE). Volume III, 1, Stuttgart 1897, Col. 7.
- Juan Maluquer de Motes: BARCINO (Barcelona) Barcelona, Spain . In: Richard Stillwell et al. a. (Ed.): The Princeton Encyclopedia of Classical Sites. Princeton University Press, Princeton NJ 1976, ISBN 0-691-03542-3 .
- hiCat Research territories . ACTAR, Barcelona 2004, ISBN 84-95951-40-1
- Barcelona 1979-2004. Del desenvolupament a la ciutat de qualitat . Ajuntament de Barcelona, 1999, ISBN 84-7609-926-6
- Joan Busquets: Barcelona. La construcción urbanística de una ciudad compacta . Ediciones del Serbal, Barcelona 2004, ISBN 84-7628-458-6
- Ulrike Fokken: Barcelona, literary forays . Artemis & Winler, Düsseldorf 08/2007, ISBN 978-3-538-07249-7
- Robert Hughes: Barcelona . Droemer / Knaur, 1995, ISBN 978-3-426-77114-3
Web links
- Link catalog on Barcelona at curlie.org (formerly DMOZ )
- Col. Barcino in the Pleiades Database
- barcelona.cat: Official Barcelona website
- poblesdecatalunya.cat: Attractions in Barcelones / Barcelona (Catalan)
- How Barcelona is planning an open "Smart City" in the service of the common good
Individual evidence
- ↑ Cifras oficiales de población resultantes de la revisión del Padrón municipal a 1 de enero . Population statistics from the Instituto Nacional de Estadística (population update).
- ↑ Most visited cities in the world: London in first place , according to the MasterCard Global Destination Cities Index; ForgSight.com on June 15, 2015, accessed August 26, 2015
- ↑ Mercer's 2018 Quality of Living Rankings. Retrieved July 30, 2018 .
- ↑ Global Wealth and Lifestyle Report 2020. Julius Baer, accessed April 4, 2020 .
- ↑ aics-usa.org ( Memento from June 1, 2006 in the Internet Archive ), pages 26–30
- ↑ Anarchism . In: Brockhaus Konversations-Lexikon 1894–1896, 1st volume, pp. 576–579 (here p. 578).
- ↑ nytimes.com
- ↑ The Anarchists Chapter 7
- ↑ Ute Müller: Peace - but not forgetting. Spain is still reluctant to face its past. In: Neue Zürcher Zeitung of August 16, 2016, p. 9.
- ^ Terrorist militia IS claims the attack in Barcelona for itself . Spiegel Online, August 17, 2017
- ↑ Ada Colau, nueva alcaldesa gracias a los votos de los ediles de izquierda , ABC.es of June 13, 2015, accessed on June 13, 2015
- ↑ 73 Barris. Ajuntament de Barcelona, accessed September 26, 2019 .
- ↑ High Diving as a World Cup spectacle - premiere for High Diving , ORF.at from August 1, 2013
- ↑ zuender.zeit.de In: Zeit online
- ↑ Life in the Gap . ( Memento from June 10, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) In: Online weekly newspaper Jungle World , October 25, 2000
- ↑ Info Usurpa - Butlletí setmanal de contr @ informació des del 1996 . No. 486, July 11th to 17th, 2007 (since 1996 a weekly updated calendar of events for squatted houses and autonomous centers in Barcelona)
- ↑ usurpa.squat.net (click below)
- ^ "De la población de Barcelona" ( Memento of March 9, 2016 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ "Barcelona Demographics" , accessed March 7, 2016.
- ↑ Spain experiences decline in Catholicism ( Memento of October 5, 2017 in the Internet Archive ), CBN July 7, 2011 (Spanish)
- ^ Alan Berube, Jesus Leal Trujillo, Tao Ran, and Joseph Parilla: Global Metro Monitor . In: Brookings . January 22, 2015 ( brookings.edu [accessed July 19, 2018]).
- ↑ "Main economic indicators for the Barcelona area" , accessed on October 28, 2016.
- ↑ 1950 - SEAT starts moving. Retrieved May 8, 2020 .
- ↑ Nissan plant in Barcelona in front of the AUS report in the daily DIE WELT on May 28, 2020, accessed on May 31, 2020
- ↑ Peter Schelling: Barcelona is an imposition that is flooded by tourists . In: Die Welt from September 30, 2015.
- ↑ New TGV route Perpignan - Barcelona completed in 2012. Retrieved August 1, 2010 .
- ↑ https://www.deutschlandfunknova.de/beitrag/superblocks-in-barcelona
- ↑ Catalonia Economy
- ↑ dsbarcelona.com
- ^ Website of the Swiss School in Barcelona
- ↑ www.wenzhou.gov.cn: City friendships . Retrieved July 11, 2019.
- ↑ Barcelona's twin cities ( Memento of August 5, 2009 in the Internet Archive ), website of the city administration
- ↑ City Cooperation ( Memento of February 12, 2009 in the Internet Archive ), website of the city administration