Iberians
The Iberians were an ethnic or tribal group who inhabited the Iberian Peninsula in prehistoric times and at times also areas outside of it.
swell
The Roman historian Marcus Terentius Varro ( Pliny the Elder Nat. Hist. III, I, 8) reports that the Iberian Peninsula was settled successively by the Iberians, Celts , Phoenicians , Greeks and Carthaginians .
history
The Iberians were pre-Roman inhabitants of the east and south of the Iberian Peninsula, including what is now Catalonia . The oldest date is from the 6th century BC. And the last are dated around the 1st century AD. The Iberians initially lived in closed tribal communities. They practiced agriculture and had knowledge and skills in metalworking, including working with bronze . In later years the Iberians developed a complex culture with urbanized settlements (over 30 of these poblados have been studied) and social stratification.
The Phoenicians established in the 8th century BC With Gadir or Gades (today Cádiz ) one of their most important trading bases on the Iberian Peninsula and probably made contact with the Iberians at this point in time or a little later. Greek colonizers gave in the 6th century BC The first historical references to the Iberians. The Greeks also dubbed a different tribe than Iberians, the Caucasian Iberians . The reason for these names being the same is unknown.
The Iberians established trade contacts with the Phoenicians and Greeks, where the silver found on the Iberian Peninsula was a sought-after product. This period of trade, which reached into the 5th century BC, also represents the heyday of the Iberian culture. The Iberians spread from the predominantly southern Spanish core areas to the northeast, to what is now southern France ( oppida von Ullastret and Ensérune ). The Iberian culture is proven by numerous archaeological finds (see for example the exhibition in the art and exhibition hall of the Federal Republic of Germany ). The Iberian sites in Catalonia , such as the Puig de Castellet near Lloret de Mar , are united in the Ruta dels Ibers , which is organized by the Museu d'Arqueologia de Catalunya .
External influences
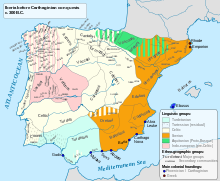
The Ligurians mainly settled north of the Pyrenees , but also in the east of the Iberian Peninsula. In the 5th and 4th centuries BC, the Celts migrated west and ousted the Ligurians. The Celtic culture then predominated in the north and west of the peninsula, while the Iberians held the south. The Iberians in today's Spain retained their independence or mixed with the Celts to form the Celtiberians . The tribal divisions into Celtiberians, Lusitanians (today's Portugal ), Asturians and Cantabrians (north-west Spain ) and Turdetans (near Tartessos ) date from this time .
The Iberians and the Celtiberians traded extensively with other Mediterranean cultures. Iberian pottery has been found in France, Italy, and North Africa. Iberians also had close contact with the Greek colonizers, who shared their cultural skills with them. The Iberians may have adopted some of the artistic skills of the Greeks.
At the time of the Punic Wars , the Iberians came into the focus of traditional history. Between the first and second Punic wars, they came under the rule of the Carthaginians for a short time . Both ethnic groups also provided troops for Hannibal's army. Then they were militarily oppressed by the Roman Empire and finally occupied. The subsequent Romanization meant the end of an independent culture or politics.
After the fall of the Roman Empire , the Iberian era finally ended with the invasion of the Vandals (406), the Visigoths (415) and finally the Moors (712).

Language and writing
The Iberian language probably belongs to the group of ancient Mediterranean languages . The hypothesis of a relationship with Basque (including Aquitaine) is now largely rejected. The assumption that Iberian served as the starting language for modern Basque went back to Manuel Larramendi's La antigüedad y universalidad del Bascuenze (1728) and Wilhelm von Humboldt's examination of the causes of the native inhabitants of Hispania using the Vaskan language (1821). However, Basque did not offer any help in deciphering Iberian texts.
Iberian texts date from the 5th and 1st centuries BC. BC, mainly consecration and grave inscriptions, the majority of which come from Andalusia. Four writing systems were used to record Iberian: The Northeast Iberian script , which is closely related to the South Lusitan , the Southeast Iberian and the Celtiberian script , is a mixed system of letters and syllables; an influence of the Cypriot syllabary is therefore discussed. In the area of today's provinces of Murcia and Alicante, the Graeco-Iberian alphabet was also used to record Iberian .
origin
There are a number of assumptions about the origin of the Iberians: One opinion is that they immigrated from North Africa to today's Spain in the Neolithic . Their arrival is dated around the 4th millennium BC. Most of the scholars who support this theory believe, based on archaeological, anthropological and genetic evidence, that the Iberians came from an area in the eastern Mediterranean. Others believe that the Iberians may have been native to North Africa itself and were related to the ancestors of the Berbers . The Iberians would then have initially settled along the Spanish east coast and possibly later spread over the entire Iberian Peninsula.
Another view regards them as part of the indigenous people of Europe and as the creators and heirs of a great megalithic culture in this area. Genetic evidence also supports this theory. Accordingly, there are closer relationships with those tribes that were subjugated by the Celts in the first millennium BC in what is now Ireland, Great Britain and France.
At the beginning of the 20th century, the French archaeologist Louis Siret equated the producers of Neolithic finds in southeastern Spain with the Iberians, presumably based on the information provided by Varros .
art
The artistic legacy of the Iberians consists mainly of sculptures. It is believed that statues such as the Dama de Elche , the Dama de Guardamar or the Dama de Baza were created by Iberian artists with a fairly high (probably Greek) training in sculpture and aesthetics. The main artefacts of Iberian art can be found in the Museo Arqueológico Nacional de España in Madrid , the Museo Internacional de Arte Íbero in Jaén , the Museo Arqueológico y Etnológico de Córdoba and the Museo de Albacete .
literature
- Michael Koch (Ed.): The Iberians . (Exhibition catalog Paris, Galeries Nationales du Grand Palais, October 15, 1997 - January 5, 1998; Barcelona, Center Cultural de la Fundación "La Caixa", January 30 - April 12, 1998; Bonn, Art and Exhibition Hall of the Federal Republic of Germany , May 15 - August 23, 1998) Hirmer Verlag , Munich 1998. ISBN 3-7774-7710-9
- Michael Art: Zambujal. Madrid contributions 5 (Mainz 1987), 9-17 on the history of the term “Iberians” in Spanish archeology.
Web links
- Iberian language areas around 200 BC BC (ethnographic map)
- Iberian arts and crafts in the Museo Arqueológico Nacional de España (Spanish)
- Iberian arts and crafts at the Museu d'Ullastret (Spanish)
- Iberian settlement of Puig Castellar
Individual evidence
- ^ Bonn Art and Exhibition Hall ( Memento from November 6, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Harald Haarmann : Lexicon of the undergone languages , CH Beck, Munich 2002, p. 98
- ↑ Indoeuro ( Memento of the original dated February 11, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Iberians . In: Encyclopædia Britannica . 11th edition. tape 14 : Husband - Italic . London 1911, p. 216 (English, full text [ Wikisource ]).