Australia (continent)
| surface | 8,600,000 km² |
|---|---|
| population | 36 million |
| Population density | 4.2 inhabitants / km² |
| countries |
Australia Papua New Guinea excluding Bougainville Western New Guinea part of Indonesia |
| Time zones | UTC + 8 ( Cape Inscription ) to UTC + 10 ( Cape Byron ) |
Australia as a continent comprises a mainland mass, the Australian mainland, and the offshore islands of Tasmania and New Guinea . Often the continent of Australia is also in conjunction with the in Pacific lying island states , in particular for cultural and political reasons Zealand summarized. This expanded region is known as Australia and Oceania .
The main land mass was formerly also called New Holland , the continent is counted as the fifth continent (from a European point of view) .
Historical geology

The continent of Australia lies on the Australian continental plate , which is seen as part of the larger Indo-Australian plate . In addition to Australia in the narrower sense and New Guinea, this includes the northern part of New Zealand as well as the eastern Indian Ocean , the Indian subcontinent and part of the Southwest Pacific . The Australian continent is now moving northeast at a rate of 73mm per year.
Originally, the continent of Australia was part of the southern major continent of Gondwana , which began to break away from the "primary continent" Pangea from the late Triassic around 230 million years ago .
In the Jurassic , about 180 million years ago, Gondwana also gradually began to disintegrate into today's “southern continents”. At the beginning of the Late Cretaceous about 95 million years ago, the continental blocks of South America , Africa - Arabia , Indo-Madagascar and Australo-Antarctica had largely separated from each other. However, the young ocean basins between these blocks were still relatively narrow. In the further course of the Late Cretaceous India broke away from Madagascar , drifted rapidly northeast in the Paleocene and collided with Eurasia in the Eocene around 50 million years ago . Madagascar, however, remained close to Africa. Although the earliest phase of the separation of the Australian continent from Antarctica began in the early Cretaceous, it remained near Antarctica until the Paleocene and did not begin to migrate rapidly northwards until the Eocene. The separation of Zealandias (with New Zealand) from Australo-Antarctica was already relatively advanced at that time. In the Oligocene , about 25 million years ago, the Australian continent collided with an arched island in the Southwest Pacific, the forerunner of today's Mariana Islands and the Palau Ridge, causing the New Guinea mountains to unfold. In the Miocene , around 15 million years ago, the Australian continent began to roam the southeastern tip of Eurasia (i.e. today's Southeast Asia ), and gradually the situation we see today emerged. During the Pleistocene , Australia, New Guinea, and Tasmania were a contiguous land mass, Sahul, due to the world's low sea levels . The Bass Strait was only flooded about 12,000 years ago, and finally the Torres Strait 8000 years ago and thus the land connections between Australia and Tasmania and New Guinea.
geography
The continent of Australia comprises a main land mass, the actual Australia, the offshore islands Tasmania , New Guinea , which is also called Papua or Irian, as well as several archipelagos and smaller islands such as Salawati , Misool , the Aru Islands , the Biak Islands , Yapen , the Lusancay Islands , Muyua ("Woodlark"), the D'Entrecasteaux Islands , the Kiriwina Islands ("Trobriand Islands") and the Louisiade Archipelago . The northernmost point is directly on the equator , on the island of Kabare, in the south the continent extends to the southeast cape on Tasmania at 43 ° south. The east-west extension extends from Cape Byron at 153rd longitude east to Cape Inscription at 113th longitude east.
With an area of 8,500,000 km² , the continent is almost as big as Europe. The land mass of Australia without offshore islands is about 7,600,000 km² and is still more than three times the size of the largest island on earth, Greenland . Therefore, Australia is rarely referred to as an island; the term island continent is also found . The following states are wholly or partially on the continent:
- Australia (whole)
- Papua New Guinea (whole)
- Indonesia (western part of the island of New Guinea )
Australia is characterized by its dry, flat hinterland. In the east, the flat center is bounded by the Great Dividing Range , which with Mount Kosciuszko reaches a height of 2228 m . This mountain range extends to Victoria in the southeast. In the sparsely populated west of the continent are the Australian deserts , such as the Nullarbor Desert . These flat landscapes are only occasionally interrupted by elevations like the MacDonnell Ranges . A striking landmark of the Australian mainland is the Inselberg Uluṟu , at the foot of which there are some sacred Aboriginal sites .
In contrast to the rest of the continent, New Guinea has strongly rugged mountains due to the collision with the Eurasian tectonic plate . A mountain range about 200 km wide runs through the entire island from west to east. Here are the highest mountains on the continent, the Puncak Jaya at 4884 m and Mount Wilhelm at 4509 m .
The most famous rivers in Australia include the Darling River , Murray River , Snowy River and the Sepik . The interior is poor in fresh water reservoirs, large salt lakes like Lake Eyre determine the landscape. At 15 m below sea level , Lake Eyre is also the lowest point in Australia.
climate

Climates
Due to its great north-south expansion, the continent has three different climatic zones from north to south . New Guinea in the far north lies entirely in the tropics . Due to its location just south of the equator, the island is exposed to heavy tropical rain all year round. Average temperatures on the coast are usually around 27 ° C. In the higher mountain regions, however, there can also be night frost, the highest peaks carry glaciers. The subtropical zone joins this climatic zone towards the south in the central area . This is only associated with significant rainfall on the east and west coast of the main land mass. Towards the interior of the land mass, the continent is characterized by a semi-arid and arid climate. Finally, in the far south, the continent extends into the temperate climate zone. This sequence can be easily traced along the east coast of the continent (see "Climate zones" on the right). The weather and climate, especially in the coastal areas, are mainly determined by three phenomena: the tropical low pressure belt , the trade wind zone and the subpolar westerly winds .
Rainfall
80 percent of the area of Australia are semi-arid and arid areas with less than 250 mm of precipitation per year. The center of the country remains largely dry all year round. Southeast trade winds bring uphill rain all year round in the mountains of the east.
In the summer half-year, which lasts from November to April, northwest monsoons and heavy rains occur in the coastal areas in the north due to a low heat level . In addition, it comes across the Timor Sea to hurricanes . At this time, South Australia lies in the subtropical high pressure belt and remains largely free of precipitation.
The winter half year follows from May to October. Then it is dry in northern Australia due to a high pressure area . The south and southwest of the continent are in the west wind zone , which is why they are exposed to precipitation in the winter half-year .
Temperatures
Since 1988 there has been a clear trend towards higher average temperatures .
According to the National Meteorological Service, 2005 will go down in Australian history as the hottest year since weather records began to be recorded in 1858. In the first ten months of 2005, the values were 1.04 ° C above the 30-year average .
January 1, 2006 was noted as the hottest start of the year in Australia. In Sydney, maximum temperatures of 44.7 ° C were measured at the official station on Observatory Hill at 4:24 p.m. The January temperature record of 45.3 ° C on January 14, 1939, however, remained unmatched.
Flora and fauna
On the Australian continent, which has been separated from the other continents by oceans for around 50 million years, its own great diversity of species and biodiversity has developed. Mainly due to the large number of endemic species, genera and families and the diverse ecosystems , Australia is one of the world's megadiversity countries . Within the animal world, Australia's marsupials are exemplary testimony to this isolated development. Marsupials are otherwise only found in North and South America .

Of the around 20,000 native plant species in Australia, around 85% are found exclusively on this continent. Typical of the Australian vegetation are the eucalyptus and acacia trees . There are over 600 types of both. The fast-growing and undemanding eucalyptus tree is found in a wide variety of environments, including hot and dry Central Australia. The size varies from the height of the bush to 90 m. In the southeast of Australia there are extensive forest areas, the densest vegetation is found in the tropical rainforests in northern Queensland . Heavy deforestation leads to a threat to the stock and threatens the biodiversity in the forests. The baobab tree, also known as the bottle tree, occurs in the arid regions of Western Australia . This tree can store water in its trunk. Large areas of the interior are characterized by grassland . The most important plant community here is the Spinifex grassland , which takes up about a quarter of the country's area.

The marsupials are typical representatives of the Australian fauna. Known representatives are the kangaroos with over 40 species of Koala , the wombat , the Tasmanian devils , the bag mouse and the genre of the Kletterbeutler (possums). Unique in the world are egg-laying mammals ( monotremes ), found only in Australia and New Guinea. In Australia, they are represented by the platypus (Engl. Platypus) and the echidna (Engl. Echidna).
Before human colonization of Australia, placenta animals were represented only by bats , fruit bats , seals and rodents . Introduced by humans animals such as dogs , cats , rabbits , camels , foxes , cane toads are a strong threat to the Australian fauna, especially for smaller domestic mammals that are not up to the competition and the increased piracy. Livestock such as sheep and cattle make the native animals controversial for their habitat, as huge areas are required for their nutrition, especially in the steppe and desert-like areas. The bird world of Australia with the numerous parrots ( budgies , lories , cockatoos ) and the Australian kingfisher ( Kookaburra ) is very species-rich. Reptiles are mainly represented by snakes , turtles , crocodiles and lizards . Two-thirds of all snake species that are native to the Australian continent are poisonous.
The animals that can be acutely life-threatening to humans include a number of very different predators , all of them carnivores . On land it is mainly animals whose poison is dangerous. This includes not only the 25 toxic for humans snake species from the genera of Taipan and Tiger otters , but also various types of spiders as True Widows (Latrodectus hasselti) and Sydney funnel-web spider ( Atrax robustus ). In the coastal inland waters of Queensland , the Northern Territory and Western Australia , humans are also at risk from saltwater crocodiles . In addition to poisonous box jellyfish, sharks are a potential danger in the sea .
The Great Barrier Reef off the east coast of the state of Queensland , which is the largest coral reef on earth with its length of 2012 km, forms a unique habitat . The intensive industrial fishing in the surrounding waters as well as tourism can lead to a lasting disruption of the sensitive ecological balance .
Australia responded to the endangerment of its fauna and flora early on by setting up large-scale nature reserves both on land and in the form of marine reserves . The Royal National Park south of Sydney, founded in 1879, is the second oldest national park in the world after Yellowstone National Park . Around twelve percent of the country's area has been declared protection zones. Eleven areas belong to the world cultural heritage . These include the Uluṟu-Kata-Tjuṯa National Park with the Uluṟu (also: Ayers Rock), the Great Barrier Reef and the Blue Mountains .
Sea turtle on the Great Barrier Reef
Hard corals in the Great Barrier Reef
In the area of the main land mass, however, there are clear seasonal climatic differences. Three main phenomena determine the weather here, the tropical low pressure belt , the trade wind zone and the subpolar westerly winds. In the summer months from November to April, heavy rains occur in the north due to a low heat level . In addition, it comes across the Timor Sea to hurricanes . At this time, South Australia lies in the subtropical high pressure belt and remains largely free of precipitation. In the winter half-year, May to October, on the other hand, the north remains dry due to a high pressure area , the south and southwest of the country are in the westerly wind zone and are exposed to precipitation. Southeast trade winds bring uphill rain to the mountains of the east all year round.
The center of the country remains largely dry all year round, 80 percent of the area of Australia is semi-arid and arid areas with less than 250 mm of precipitation per year.
South Australia is the most populous area in the southern ozone hole area .
ecology

Due to its size and location, Australia has a remarkable diversity of ecosystems , from deserts , semi-deserts , steppes and savannahs , to temperate and tropical rainforests . These are protected by numerous Australian national parks and the Lorentz National Park in western New Guinea . The Mediterranean hardwood region of Southwest Australia is listed internationally as a biodiversity hotspot , as nature there - in contrast to all other mainland ecoregions of Australia - is particularly threatened. The 2,012 km long Great Barrier Reef is a unique habitat . This coral reef off the northeast coast of Australia was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1981 .
The Australian biogeographical region also includes the Indonesian islands east of Bali . The border to the oriental zone is formed by the Wallace line . Due to the long isolation of the continent, flora and fauna were able to establish themselves here that were largely unaffected by evolutionary developments on other continents. All recent species of monotremes occur only in Australia and New Guinea. The continent also has the world's highest diversity of marsupials . Special features of the bird world are, for example, the birds of paradise , a family restricted to tropical regions . The flora shows similarities to the floral elements of South America and to fossil finds in the Antarctic, an indication of the late separation of these continents.
Species introduced by humans endanger the ecological balance, especially on mainland Australia . So have foxes , cats and dogs helped several small marsupial species to extinction, ungulates destroy the sensitive tiles and imported for hunting wild rabbits compete successfully with the domestic herbivores.
population
With around 28.5 million inhabitants, the continent of Australia is the second poorest in population after Antarctica .
Indigenous population
The indigenous population of the continent consists of the Aborigines and the Torres Strait islanders of the main land mass, the Papuans and the Melanesian peoples of New Guinea and the offshore islands. However, these groups do not form uniform cultures, but rather form a multitude of linguistic and culturally delimitable units. The population of New Guinea in particular is considered to be one of the most heterogeneous in the world. While a large part of the population in Papua New Guinea and almost half of the population in Western New Guinea are of indigenous origin, the Aborigines make up just under two percent of the Australian population. The Tasmanians were almost completely annihilated after the European colonization.
immigration
Due to the different colonial histories of the Australian regions, the immigration patterns are also very different. The majority of the population of the Australian Federation is of British descent, but immigration from Asia has been increasing since the 1970s . Immigration has never played a significant role in Papua New Guinea, while the Indonesian government's Transmigrasi program has resulted in the relocation of around 1.2 million people, mostly from Sumatra and Java , to Western New Guinea.
languages
Several hundred Papua languages are still spoken in New Guinea, but Tok Pisin has established itself as the lingua franca here . The official language of Australia and Papua New Guinea is English , in Western New Guinea Bahasa Indonesia .
religion
The majority of the population belongs to Christian religious communities (79%), especially in Papua New Guinea the proportion is very high at 96% due to successful proselytizing . The practice of the faith among the indigenous peoples often takes place in combination with traditional beliefs with an animistic background. In Western New Guinea, Muslims make up around 20% of the population, mostly Indonesian immigrants.
history
→ For the history of the Commonwealth of Australia, see History of Australia
→ For the history of Oceania, see History of Oceania
→ For a chronological and geographical overview, see the chronological table of human history
colonization
The Australian continent was settled from Southeast Asia at least 50,000 to 60,000 years ago. By 35,000 years ago, the population had spread to Tasmania via the continuous land connection. The first human communities are believed to have inhabited the coast. The first settlements emerged in the New Guinea highlands around 30,000 years ago.
discovery
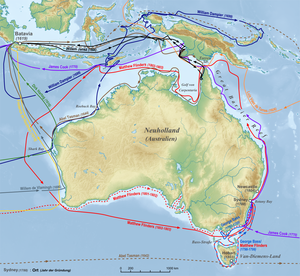
Even in ancient times, a southern continent , as Ptolemy mentions it in the 1st and 2nd centuries AD as terra australis incognita ( Latin for unknown southern land ), was assumed as a necessary counterweight to the land mass in the northern hemisphere. But the idea that everywhere in the equatorial latitudes there was a hostile heat that would make it impossible to overcome, initially prevented serious attempts to explore the southern hemisphere. The name of Australia is derived from the Latin name of the unknown southern land of the ancient scholars.
In the 15th century, Portuguese navigators crossed the tropics along the West African coast and finally advanced into the Indian Ocean . It was also a Portuguese, Jorge de Meneses , who was the first European to discover land that belongs to the Australian continental block in the 16th century: in 1526/27 he sailed past the north coast of New Guinea within sight. After taking possession of the island for the Spanish crown by Íñigo Ortiz de Retez in 1545 exotic woods and other luxury goods to Europe were shipped from there.
The main part of the continent was discovered in 1606 by the Dutchman Willem Jansz . In the following decades, other Dutch merchant ships reached the Australian north and west coasts, but did not attach any particular importance to this discovery. In 1642, however, the Dutch East India Company decided to explore the continent. Abel Tasman discovered what is now Tasmania. In an expedition led by Willem de Vlamingh from 1696, large parts of the west coast were mapped. Since the landscape looked dry and barren, the Dutch showed no interest in colonizing "New Holland" .
The interior of Australia, the so-called outback , was only explored by white settlers from the middle of the 19th century. Among the early explorers counted Charles Sturt , who from 1828 to 1830 the river system of Darling and Murray River explored. Other discovery expeditions failed. The natural scientist Ludwig Leichhardt died trying to cross the continent from east to west. Only a competition between the colonies of Victoria and Melbourne finally led to successful expeditions to cross Australia. Melbourne offered 2000 pounds in 1859 for a crossing to the north or northwest coast , whereupon Victoria provided 6000 pounds in 1860 for its own expedition. Robert O'Hara Burke then left Melbourne on August 20, 1860 equipped with 26 camels . On February 10, 1861, Burke had to turn back just a few kilometers from the Gulf of Carpentaria . Burke's competitor, John McDouall Stuart, on the other hand, was the first European to cross Australia between 1860 and 1862. His route ran from Adelaide to Port Darwin .
colonization
On April 28, 1770, James Cook reached the fertile east coast in Botany Bay and took part of the land for England as the British colony of New South Wales . This was planned as a convict colony. The first ships with settlers and convicts arrived in Sydney Cove on January 26, 1788. Further colonies were established by 1836, bringing all of Australia, with the exception of New Guinea, under British control.
In 1828, with the acquisition of the Vogelkop peninsula by the Dutch, the colonization of New Guinea began. The rest of the island was divided between the Netherlands, Great Britain and the German Empire in 1884 . The western part went to the Netherlands, Great Britain received the southeast, Germany the northeast. In 1906 the British part was transferred to Australia, the German part came under Australian control in 1919.
Aspirations for independence
Between 1855 and 1890, the individual British colonies on the main continent were given the privilege of Responsible Government and thus greater independence from the British Empire . For the time being, however, London retained control over foreign policy, defense and foreign trade. In the colonies, the planning for a merger of the individual states began.
On January 1, 1901, the once independent colonies on the mainland with Tasmania formed the Commonwealth of Australia. On September 26, 1907, the Australian Confederation was granted almost complete independence from the mother country of Great Britain with Dominion status . This allowed the domestic policy of Australia to be shaped according to one's own wishes, while foreign policy was still primarily conducted by the British Foreign Office. It was not until the Statute of Westminster (1931) that the state of Australia was formally fully independent. So was z. For example, Australia did not declare World War I , but it was able to sign the Versailles Peace Treaty (1919).
During the Second World War , northern New Guinea was occupied by Japan from 1942 to 1945 . The Australian mainland was also threatened by Japanese invasion during this period.
Indonesia, independent since 1949, laid claim to the western part of New Guinea, but this remained Dutch for the time being. In 1957, the Netherlands and Australia began developing plans for the independence of a united New Guinea in the 1970s. In 1961 an assembly was held in Dutch New Guinea and a parliament, the Nieuw Guinea Raad , was established. Indonesia then invaded and a little later began to drive the Papuans out of areas in which settlers from Indonesia were to be settled. In 1963, Western New Guinea officially became an Indonesian province. Despite ongoing efforts to achieve autonomy, Indonesia has not yet recognized the province's independence. The eastern part of the island gained complete independence from Australia in 1975.
The Commonwealth of Australia
Australia joined the League of Nations, founded in 1920, as a founding member. This allowed a League of Nations mandate for the former German colonies Kaiser-Wilhelms-Land , the northeastern part of New Guinea, and the Bismarck Archipelago to go to Australia. After the Second World War, Australia became a member of the Commonwealth of Nations .
From a military point of view, Australia was not only involved in the two world wars, the Korean War and the Vietnam War. During the Malaysian state of emergency ( Malayan Emergency ) (1948-1960) sent Australia in 1955 troops. Also in the subsequent Indonesian-Malaysian confrontation (1962–1966), from 1965 onwards, Australian soldiers were involved at the Malaysian request.
Another troop deployment of great importance in 1999 was the participation in the international peacekeeping force in East Timor , which led to East Timor's independence from Indonesia.
Papua New Guinea
A civil war erupted in 1988 on the state's easternmost island, Bougainville , when a denied claim for compensation for the environmental damage caused by a copper mine. About 20,000 people are said to have died. In 1990 the government army withdrew and ordered the island to be blocked. Government troops marched in again in 1992, but it was not until 1997 that a ceasefire and negotiations came about, which were successfully concluded in 2001 with a peace agreement.
economy
Natural resources
Mineral resources include gold, silver, diamonds, hard coal, iron ore, bauxite, copper, nickel, tin and uranium. In 2002, 55% of all Australian exports were raw material exports, with coal being the most important export product at 11.1%. For Papua New Guinea, raw material exports were even more important, accounting for 70% to 80% of total exports. The most important raw material products were gold, petroleum and copper. The largest copper mine in the world is located in Western New Guinea. There are also gold mines and the timber trade in particular is of great economic and ecological importance.
Agriculture
In Australia, agriculture can only be practiced on the coasts, although even the best areas, e.g. B. the predominantly in the southeast lying wine-growing areas, occasionally have to be irrigated artificially. For this reason, the bulk of agriculture is extensive livestock farming.
With around 100 million domestic sheep in 2003, 25 percent of world wool production is in Australia. The sheep graze in the partially fertile areas of the outback on farms with an average of 3,000 animals, with individual farms also housing over 100,000 animals. In addition, the production of lamb and sheep meat is of economic importance. Almost all of the merino wool produced today comes from the Australian merino sheep . The agriculture of Papua New Guinea and Western New Guinea are mainly geared towards local needs.
politics
The state of Australia
Elizabeth II is currently Queen of Australia and thus the head of state of Australia. There is a governor general and a governor for each of the six states of Australia to represent them.
In addition to the close foreign policy ties associated with membership in the Commonwealth of Nations, Australia maintains intensive political and military contacts with the USA. As a result of the Pacific War , the ANZUS Agreement was created in 1952 . In this mutual military support between the USA, Australia and New Zealand was agreed. The first serious incident was the terrorist attacks on September 11, 2001 , which led to Australia's participation in the war in Iraq, initially with 2,000 soldiers and 300 commandos in the war in Afghanistan .
The military involvement of Australia in the Indonesian-Malaysian confrontation led to the establishment of the Five Power Defense Arrangement (FPDA) between Great Britain, Australia, New Zealand, Malaysia and Singapore in 1971 , which provides that the first three should be transferred to the two Southeast Asian states in the event of an attack Help come. Since 1997 the naval and air forces of the five countries have been carrying out joint maneuvers on a regular basis.
After the attack in Bali in 2002 and the terrorist attack on the Australian embassy in Jakarta , cooperation with Indonesia on security issues increased.
In trade policy, Australia is increasingly representing its interests in favor of its export-oriented raw materials industry. These include, for example, the non-ratification of the Kyoto Protocol and the many disputes with the EU within the framework of the World Trade Organization . Australia is also trying to represent its interests through membership in APEC , which wants to set up a free trade area in the Pacific region .
A free trade agreement, called Closer Economic Relations , has existed between New Zealand and Australia since 1983 , which includes a free labor market. This has created an almost completely free market of around 22 million people. Australia is talking to China about a free trade zone, as this way the Chinese demand for raw materials and the Australian demand for cheap consumer goods could be covered at low cost.
Papua New Guinea
Elizabeth II is the head of state of Papua New Guinea , represented by a governor general. The country has been a member of the Commonwealth of Nations since its independence from Australia in 1975 and of the APEC since 1993. Political ties exist with the states and dependent areas of Oceania through membership in the Pacific Community and the Pacific Islands Forum .
In 2005 there were elections for the first autonomous provincial government in Bougainville , the easternmost island in the country, which temporarily pacified the civil war there. Only with the agreed referendum on the island's independence will the issue be finally resolved.
Western New Guinea
- Western New Guinea (until 2002 Irian Jaya) is divided into the Indonesian provinces of Papua and West Papua .
Armed and unarmed independence movements are committed to the independence of the area from Indonesia. An autonomy law has been in force for the region since 2002, institutionalizing a representation of interests for Papua for the first time and allowing a larger part of the profits generated locally from the timber trade and mining operations to benefit the residents. However, so far the law is only on paper.
See also
Web links
literature
- Robert Hall: The plate tectonics of Cenozoic SE Asia and the distribution of land and sea. In: Robert Hall, Jeremy D. Holloway (Eds.): Biogeography and Geological Evolution of SE Asia. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden (The Netherlands) 1998, pp. 99-131
Individual evidence
Coordinates: 25 ° S , 135 ° E







