terror attacs at the 11th September 2001
| Terrorist attacks on September 11, 2001 |
|
|---|---|
| date | September 11, 2001 (Tuesday) |
| time | 8:46 a.m. to 5:20 p.m. local time 2:46 p.m. to 11:20 p.m. CEST |
| country | |
| location | WTC 1 / North Tower ( AA 11 ) WTC 2 / South Tower ( UA 175 ) Pentagon ( AA 77 ) Shanksville ( UA 93 ) |
| Injured | more than 6,000 |
| Fatalities | 2,977 victims of attacks 19 al-Qaeda hijackers |
| category | Islamist Terrorism Jihad Airplane Hijacking Suicide Bombing |
The terrorist attacks on September 11, 2001 (short September 11 or English 9/11 [ nʌɪn ɪˈlɛvn̩ ]) were four coordinated aircraft hijackings with subsequent suicide attacks on symbolic civil and military buildings in the United States of America . The attacks were planned by the Islamist terrorist network Al-Qaeda under the leadership of Osama bin Laden and carried out by 19 of its members, including 15 citizens of Saudi Arabia , in which around 3,000 originally bystanders died within a short period of time. The attacks of September 11, 2001 are sometimes interpreted as a turning point in the history of the conflict between the Western and Arab world .
overview
On the morning of September 11th, the terrorists hijacked four passenger planes in three groups of five and one group of four. At 8:46 a.m. local time , American Airlines Flight 11 was first maneuvered into the north tower of the twin towers of the World Trade Center (WTC) in New York City . The subsequent impact of United Airlines Flight 175 into the south tower of the Twin Towers at 9:03 a.m. has already been broadcast live worldwide on TV . Both skyscrapers collapsed completely over the next hour and a half. Numerous surrounding buildings were destroyed by rubble or badly damaged. In the late afternoon of September 11th, WTC 7 finally collapsed . Not only the collapse of the 186 meter high office building, but also other circumstances of the attack became the subject of numerous conspiracy theories on September 11, 2001 .
At 9:37 a.m., a hijacking group drove American Airlines Flight 77 into the Pentagon , the headquarters of the US Department of Defense near Washington, DC The most recently hijacked United Airlines Flight 93 was after fighting with passengers by the hijacker's pilot near Shanksville in the US State of Pennsylvania crashed at 10:03 a.m. and was the only one of the four hijacked aircraft to miss the intended target. The attacks, classified as terrorist mass murder , claimed 2,996 lives from 92 countries, including eleven victims from Germany and two Swiss nationals. Numerous memorial sites have been created to commemorate, including the National September 11 Memorial and Museum , the Pentagon Memorial, and the Flight 93 National Memorial .
Immediately after the attacks, US President George W. Bush proclaimed the war on terror . As part of the military operation Enduring Freedom , a new war began in Afghanistan on October 7, 2001 , with the aim of overthrowing the Taliban government , which has ruled since 1996, and fighting al-Qaeda . A US special unit liquidated Al-Qaeda founder Osama Bin Laden as part of Operation Neptune Spear on May 2, 2011. The US government also referred to the attacks to justify the 2003 Iraq war , although there were doubts on the part of numerous NATO allies. According to a study by the IPPNW , well over a million people were killed in this "war on terror" by 2015.
The state of emergency declared on September 14, 2001 in the USA is still in force. Some authors therefore speak of a permanent state of emergency that has become normal. As a result of the 9/11 attacks, governments around the world enacted new counterterrorism laws, often at odds between individual freedom and collective security.
attacks
sequence
| Time (local time) |
occurrence |
|---|---|
| 8:46 a.m. | Flight AA 11 hits WTC 1 (north tower) |
| 9:03 a.m. | Flight UA 175 hits WTC 2 (south tower) |
| 9:37 a.m. | Flight AA 77 flies into the Pentagon |
| 9:59 a.m. | WTC 2 collapses |
| 10:03 a.m. | Flight UA 93 crashes near Shanksville |
| 10:28 am | WTC 1 collapses |
| 5:20 pm | WTC 7 collapses |
live recordings from 9:00 a.m. to 10:40 a.m.




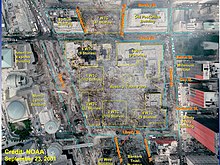

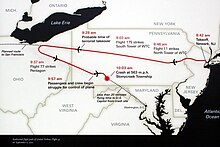
According to the investigation report of the 9/11 Commission , five members of the radical Islamic terror network Al-Qaeda hijacked American Airlines Flight 11 from Boston to Los Angeles on September 11, 2001 at 8:14 am local time . At 8:19 a.m., they set down the transponder of the Boeing 767-223ER with a total of 92 people on board. As a result, the passenger plane was only recorded by the primary radar . The flight controllers could no longer automatically assign flight altitude, speed and identifier. Also from 8:19 a.m., two flight attendants informed the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and their aviation company about the ongoing kidnapping. At 8:37 a.m., the FAA notified the North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD) military air defense command of the hijacking and asked for fighter jets to be launched. At first, there was confusion among the responsible air traffic controllers in the military, as NORAD orchestrated the large-scale anti-terrorist exercise Vigilant Guardian , which was also taking place at the same time and which also included aircraft hijackings. After the FAA had assured that the abduction was not part of the exercise, then started at 8:46 AM of the Otis Air Force Base , two F-15 . However, the pilots received no destination information and were initially directed into a military-controlled airspace off the coast of Long Island . They stayed in this corridor until 9:13 a.m.
At 8:46 a.m., AA11 flew into the north facade of the north tower (WTC 1) of the World Trade Center at a flight speed of around 750 km / h. TV stations around the world reported the impact live on location from New York City from 8:48 a.m. At first it was believed that there was an accident and the people in the neighboring south tower (WTC 2) were asked to keep calm and stay at work. According to the final report by NIST , the aircraft body between the 93rd and 99th floors severed a total of 35 of the 236 outer pillars and six of 47 inner pillars of WTC 1 and removed the fire protection coating on 43 of these pillars. All three stairwells collapsed and interrupted the elevator connections above the 60th floor. An estimated 15% of the 38,000 liters of kerosene on board went up in a fireball, about half of which leaked unburned in the building. The remaining fuel spread in fireballs through the elevator shafts, blew up doors and walls on several floors and shattered numerous windows in the lobby on the first floor. Immediately afterwards, countless victims called the emergency number.
Between 8:42 am and 8:46 am, United Airlines Flight 175 , which also took off from Boston for Los Angeles, was hijacked by another group of five terrorists. At 9:03 a.m. the Boeing 767-200 with 65 people on board flew into the south facade of the south tower. The aircraft impacted at 870 km / h between the 77th and 85th floors of WTC 2 and severed 33 of 236 outer pillars, including the southwest corner pillar, as well as ten of 47 inner pillars and replaced the fire protection coating on 39 of these inner pillars. Here, too, around 15% of the 34,500 liters of kerosene on board evaporated immediately upon impact, at least half of which leaked unburned in the building. With the second impact within a very short time, US authorities and contemporary witnesses recognized that apparently targeted terrorist attacks had been carried out. From then on, evacuations of the entire WTC complex including the auxiliary buildings WTC 3 , WTC 4 , WTC 5 , WTC 6 and WTC 7 were rung in. Nevertheless, FDNY firefighters and hundreds of other first aiders tried to get to the people trapped above the impact points.
The south tower collapsed completely 56 minutes after the impact at 9:59 a.m. WTC 3, which was used as a hotel, was destroyed by rubble from the collapsing south tower. WTC 4 with the world's largest commodity futures exchange for raw materials ( NYMEX ) and the world's largest trading floor for commodity futures trading in gold, silver, platinum, copper, aluminum, oil, gas, cotton and sugar at the time , Cocoa and orange juice concentrate was almost completely buried by the south tower. The 11 meter high St. Nicholas Greek Orthodox Church in the immediate vicinity of the south tower was completely destroyed . The neighboring Deutsche Bank Building was so severely damaged that it had to be removed floor by floor by 2011.
At 10:28 a.m., 102 minutes after the impact of Flight AA11, the north tower also collapsed completely. The collapse of the north tower caused severe damage to the buildings of the World Financial Center to the west due to debris being thrown out and almost completely destroyed WTC 5 and WTC 6. The 186-meter-high WTC 7 , which was evacuated shortly after the UA 175 impact , was damaged on the south facade and caught fire on several floors. Finally, WTC 7 also collapsed completely in the late afternoon at 5:20 p.m. The collapse of WTC 7 also caused considerable damage to surrounding buildings. There were no other injuries or deaths in the collapse of the 47-story office building.
The neighboring 32-story New York Telephone Building then had to be restored for $ 1.4 billion. The Fiterman Hall (30 West Broadway) to the north of the City University of New York was so badly damaged that it had to be demolished.
American Airlines Flight 77 was scheduled to fly from Washington Dulles International Airport to Los Angeles . The Boeing 757-223ER passenger plane was hijacked by five Saudi Arabian Al-Qaeda members between 8:51 and 8:54 am . The plane hit the Pentagon near Washington, DC at 9:37 a.m. and cut through three sections of the building on the west side. The exploded kerosene started a major fire. As a result, the affected facade collapsed around 10:10 a.m. At 9:42 a.m., FAA headquarters ordered all passenger planes in US airspace to land at the nearest airport.
United Airlines Flight 93 was the last to be boarded at 9:28 a.m. by a group of four, which was scheduled to lead with 44 people on board from Newark near New York to San Francisco . The Boeing 757-222 changed course to the east at 9:32 a.m. At 9:55 a.m., one of the hijackers entered the frequency of a navigation system at Ronald Reagan Airport into the on-board computer to enable navigation in the direction of Washington DC. The flight control confirmed the change of course. The White House , the Capitol or the country residence of the US President in Camp David were later suspected to be the target of the attack . In an interview with Al Jazeera editor Yosri Fouda in June 2002, Ramzi Binalshib of the Hamburg terror cell said that the fourth plane should hit the Capitol.
Some passengers on this flight found out about the attacks on the WTC when they called on board and tried to penetrate the cockpit from 9:57 a.m. and overpower the kidnappers. The pilot then steered the aircraft to the ground at 10:03 a.m. It shattered near Shanksville, about 100 kilometers east of Pittsburgh . NORAD did not find out about the hijacking of this flight until 10:15 a.m. The Northeast Air Defense Sector (NEADS) in Rome (New York) did not receive the order until around 10:30 a.m. to intercept and possibly shoot down hijacked aircraft.
Rescue operations
The coordination of the rescue operations was originally supposed to be headed by the New York City Office of Emergency Management (OEM), which has been located on the 23rd floor of WTC 7 across from the Twin Towers since 1999 . However, since WTC 7 was completely evacuated immediately after the plane impacts, this task fell to the New York Fire Department ( FDNY ) and the New York Police ( NYPD ) without further ado . They were supported by the Police Unit of the Port Authority of New York ( PAPD ), which was still responsible for the security of all buildings of the World Trade Center despite the leasing of the twin towers to Silverstein Properties in July 2001 . Due to the failure of the OEM, FDNY, NYPD and PAPD had to operate in an uncoordinated and autonomous manner with different communication systems during the rescue operations.
Rescue attempts began immediately after American Airlines Flight 11 hit the North Tower of the World Trade Center. Joseph W. Pfeifer , Head of Operations of the 1st Battalion of the FDNY, observed the approach and impact of the Boeing 767 from close by and reported it to the operations center. On the morning of September 11th, Pfeifer was accompanied by the two French filmmakers Jules and Gédéon Naudet . This was also where the rare film footage showing the impact of flight AA11 into the north tower was made.
The PAPD ordered the complete evacuation of the north tower just one minute after the impact. Six minutes after the impact, four fire brigade units were already on site, setting up a makeshift command post in the devastated lobby of the north tower. When the rescue work began, United Airlines Flight 175 crashed into the south tower. Originally, the fire brigade initially wanted to evacuate the 25,000 to 50,000 people suspected in the towers , rescue the injured and extinguish the fires around the point of impact. On the ground, however, the operations commanders realized that there was no hope of controlling the fire on the upper floors and it was decided to focus on evacuating the towers. Since all of the 99 elevators in the towers had failed, it would have taken too long to drag the heavy extinguishing equipment up the stairwells to the affected floors above the 77th floor. Each tower had two stairwells that led from the ground floor to the 110th floor. A third staircase reached from the 6th to the 107th floor. Each of the passage doors from the offices to the stairwells were designed so that they could be opened manually despite the fire. The doors to the roofs, however, were locked. An evacuation and rescue concept to rescue the injured from the roof by means of a helicopter did not exist, as the roofs were built by technical equipment in such a way that landing was impossible. Emergency drills had failed to inform World Trade Center staff that the roof doors were locked and that there was no plan to evacuate the roof platforms. Numerous people who were above the impact zones wanted to escape over the roof, but were standing in front of locked doors. As a result, they got stuck on the floors just below the roof as fire and thick smoke ate their way higher and higher through the upper floors of the twin towers.
While at the beginning of the rescue work the FDNY and the PAPD concentrated solely on the evacuation of the buildings, the NYPD first cordoned off the closer and then the wider area around the WTC, then supported the evacuation of the towers and began to determine the progress of the attacks . The police command received information about the situation in the towers via three NYPD helicopters, but this did not reach the fire brigade's operations management team.
After a short time, the emergency lines were completely overloaded by thousands of emergency calls. Numerous emergency calls came from people in the twin towers who were locked in the upper floors and cut off from all escape routes. A head of operations of the FDNY decided to set up a provisional command and assembly point in the lobby of the Marriott Hotel ( WTC 3 ). The advantage of the location was that the main entrance of the hotel was in the direction of West Street, on which almost all fire and rescue vehicles congregated. In addition, one could get directly into the south tower from the hotel via a side entrance. Due to falling debris and people falling down, access through the main entrance of the south tower was too dangerous for the rescue workers. Numerous people were also evacuated via the entrances to WTC 5 and WTC 6 on Vesey Street. At 9:59 a.m., the south tower collapsed within ten seconds and tore all 630 employees and rescue workers in the building as well as numerous people on the streets to their deaths. The collapse created a violent storm and a cloud of dust and debris. Falling parts of the building destroyed WTC 3 and the temporary FDNY command post housed in it.
After the south tower collapsed, most of the operations commanders withdrew the rescue workers from the north tower. However, even 30 minutes after the collapse of the south tower, not all of the operations commanders who were on their rescue missions in the windowless stairwells of the north tower were aware of the collapse of the neighboring tower. At 10:28 a.m. the north tower also collapsed and buried all 1,355 people trapped on the upper floors, numerous first aiders and an unknown number of victims on the ground around the collapsing skyscraper. In an almost intact stairwell near the floor of the north tower, 12 firefighters, three PAPD officers and three civilians survived the collapse.
Around 87 percent of the 17,400 people who were in the World Trade Center buildings at the time of the first plane impact were able to save themselves or were evacuated by the emergency services. Of the total of around 1,000 rescue workers, the FDNY lost 343 firefighters, the PAPD 37 employees and the NYPD 23 police officers.
The forensic search of genetically usable remains of the victims was carried out as part of the World Trade Center Recovery Operation, which ran until July 2002, on the site of the former Fresh Kills construction waste site in Staten Island , NY. All rubble and remnants of the collapsed buildings, steel girders and more than 1,300 wrecked cars were previously transported to the island off Manhattan. Out of 4,257 human remains filtered out, 300 victims could be identified.
Around 65,000 emergency services were involved in the rescue and clean-up work at Ground Zero , which lasted until May 2002 . You and others were exposed to varying degrees with the numerous toxic pollutants in the air released by the collapse of the Twin Towers. The extent and management of the long-term health consequences have been increasingly discussed in the USA since around 2005. In November 2010, the City of New York approved an aid package worth US $ 625 million for ten thousand affected aid workers. In addition, US President Barack Obama signed the James Zadroga 9/11 Health and Compensation Act , approved on January 2, 2011 , in which almost 75,000 people are now cared for. Including around 65,000 emergency services at Ground Zero and another 10,000 survivors and those affected. Around half (37,305) of those enrolled in the health program have at least one disease associated with September 11th. Most of them suffer from diseases of the respiratory tract and gastrointestinal tract (32,291, including 27,613 emergency personnel) and mental illnesses such as post-traumatic stress disorder (12,500, including 9,465 emergency personnel). Cancer is now in third place with 5,441 cases (of which 4,692 among emergency services). In July 2019, the 200th FDNY firefighter died due to causes of death caused by ground zero.
Fatalities and injuries
According to official figures, 2,996 people were killed in the terrorist attacks on September 11th. Among the victims were eleven German citizens and two Swiss nationals. Austria had no dead to mourn. 372 fatalities from 92 countries were non-US nationals. The number of those acutely injured on September 11th is estimated at over 6,000. More than 3,200 children lost one or both parents to the attacks. Numerous memorial sites have been created to commemorate the victims of September 11, including the National September 11 Memorial and Museum , the Pentagon Memorial, and the Flight 93 National Memorial .
A total of 2,763 people died as a result of the plane impacts on the twin towers of the World Trade Center in New York. Including 127 passengers, 20 crew members and 10 hijackers of the two aircraft. Witnesses who resided as guests in the Marriott Hotel between the towers and photos released by NIST document that people were lying on West Street and the surrounding streets immediately after the plane crashes. 2,128 people died in the twin towers, mainly working in offices above and around the impact site. The investment bank Cantor Fitzgerald , located on the 101st to 105th floors in WTC 1, lost 658 employees on September 11th. The consulting firm Marsh Inc. had its offices between the 93rd and 100th floors of WTC 1 and was right in the center of the impact of Flight AA11, which struck between the 94th and 98th floors. 295 employees and 63 freelancers of the consulting company died in the attacks. In WTC 2, the insurance company AON , located on the 92nd and 98th to 105th floors, lost 175 employees. Before the towers collapsed, about 200 people fell to their deaths. They were cut off from escape routes on the upper floors and jumped to escape the unbearable heat, life-threatening burns or toxic smoke. In addition, 343 firefighters, 37 New York Port Authority officials, 23 police officers and 75 passers-by were killed. The Forensic Medicine Institute of New York worked for years on the genetic identification and mapping of body parts of the victims. In October 2019, the 1.645. Identified victim. Of 40 percent, i.e. 1,108 of 2,763 people killed in New York, there is still no forensic evidence.
189 people died in the attack on the Pentagon, including 125 officials, 53 aircraft passengers, 6 crew members and 5 hijackers. 44 people, including 33 passengers, 7 crew members and 4 hijackers, lost their lives near Shanksville.
| flight | Inmates (†) | Disaster | † at the scene of the accident | total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
American Airlines Flight 11 United Airlines Flight 175 |
92 65 |
WTC | 2606 | 2763 |
| American Airlines Flight 77 | 64 | Pentagon | 125 | 189 |
| United Airlines Flight 93 | 44 | Shanksville | - | 44 |
| total | 265 | 2731 | 2996 |
Shortly after September 11th, the September 11th Victim Compensation Fund was created with so-called Liberty Bonds to compensate victims and survivors of the attack . The US federal government authorizes the fund, under the direction of Kenneth Feinberg, to pay out a maximum of 7.375 billion US dollars from US government funds. In exchange for an individually determined amount of compensation, victims and survivors give their consent not to sue American Airlines and United Airlines .
Terrorists
Bin Laden & Al Qaeda

Immediately after American Airlines Flight 11 and United Airlines Flight 175 hit the twin towers of the World Trade Center, media representatives, politicians, and intelligence and terrorism experts spoke about Osama bin Laden (1957-2011) and the one he founded -Islamic terrorist organization Al-Qaeda speculated as the perpetrator of the attacks.
The US government also accused Osama bin Laden of having commissioned and co-financed the attacks because of the evidence gathered by its secret services. He welcomed the attacks as the will of Allah , but denied any involvement in them. In November 2001, the US Army found a video tape in Jalalabad in which bin Laden talked to members of his group about planning the attack, named some of the kidnappers, praised them and explained that he first told them about the attack targets in the USA and not with him total collapse of the WTC building expected. The US TV stations ABC and CNN reported on December 21, 2001 that Osama bin Laden named other aircraft hijackers besides Mohammed Atta on the video. The translators could have heard the names of a total of nine suspects. Commentators on American television said the US government likely omitted this passage in order not to snub the allied Saudis. The Hamburg orientalist Gernot Rotter and two independent sworn translators agreed , however, according to the ARD magazine Monitor , that in the English translation of the "confession" published by the Pentagon, references were formulated in serious places, from which a clear perpetration of Bin Laden can be deduced . For example, time references would be established that supposedly prove his prior knowledge, but did not appear in the original Arabic version. In addition, the amateur video is of extremely poor quality and sometimes incomprehensible.
FBI Vice Director Dale Watson told Congress in February 2002 that the evidence of bin Laden's 9/11 association was "clear and irrefutable." However, FBI director Robert Mueller said in April 2002 that no documents had yet been found supporting the bombers' plans.
On the basis of wiretapped telephone calls, money transfers and testimony, the US sees Khalid Sheikh Mohammed and Mohammed Atef as the main planners of the attacks. Muhammad Haidar Zammar is considered to be the recruiter for the assassins. Bin Laden selected the later assassins at the end of 1999, helped finance the attack plan and in November 1999 ordered the future hijackers from the Hamburg cell to fly to the USA to attend flight schools there.
On October 29, 2004, four days before the re-election of George W. Bush , bin Laden turned to the US people and explained when and why he had the idea of the attacks and that more of these would follow if they did USA did not change its policy. In further video and tape messages , he made his plans for the attacks clear. He and his most important co-planners always cited the US's support for Israel and its policy towards the Palestinians as the main motive for this .
In spite of bin Laden's confessional messages published by video, FBI spokesman Rex Tomb stated in 2006 that the FBI “does not have enough hard evidence” to link Bin Laden to the September 11, 2001 attacks. In addition, the Justice Department would not formally prosecute until there was enough evidence.
Assassin
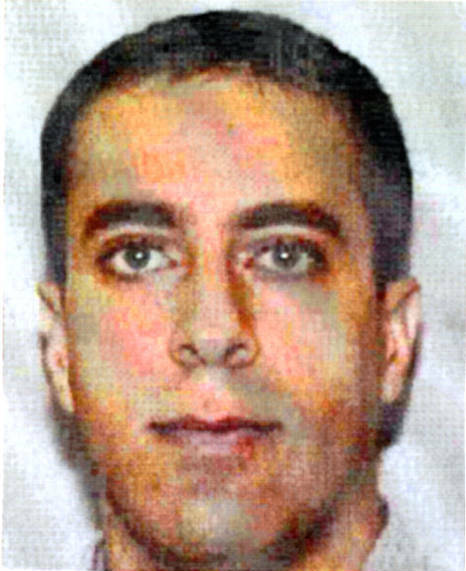
On September 13, 2001, the FBI announced the names of all hijackers, determined from passenger lists and seat numbers booked with real names. 15 of the 19 kidnappers identified by the FBI on September 11, 2001 were citizens of Saudi Arabia , two were from the United Arab Emirates , and one pilot each from Egypt and Lebanon . On September 27, 2001, the FBI released photos and personal information of the 19 people the FBI believed were the kidnappers. Since some names were confused with those of living people, the FBI also published alternative name spellings.
In 2002 the FBI released further biographical details of the kidnappers. All of the assassins came from wealthy, respected, more secular families and enjoyed an education that qualified them to study abroad. It was only there that they sought and found contacts with radical Islamic preachers who propagated jihad against the West. Its ideology included a belief in a world Jewish conspiracy , the image of an imperialist West colonizing and continuing to humiliate the Islamic world, and a hatred of the worldwide social injustice created by globalization .
- American Airlines Flight 11 : Mohammed Atta (pilot), Abdulaziz al-Omari , Satam al-Suquami, Wail al-Shehri, Waleed al-Sherhri
- United Airlines Flight 175 : Marwan al-Shehhi (pilot), Fayez Banihammad, Mohand al-Shehri, Ahmed al-Ghamdi, Hamza al-Ghamdi
- American Airlines Flight 77 : Hani Handschur (pilot), Khalid al-Mihdhar, Majid-Moqed, Nawaf al-Hazmi, Salem al-Hazmi
- United Airlines Flight 93 : Ziad Jarrah (pilot), Saeed al-Ghamdi, Ahmed al-Nami, Ahmed al-Haznawi.
By 2008, 13 of the 19 kidnappers could be identified with DNA analysis , nine of them through elimination procedures and four through comparison samples. The remains of six of the ten kidnappers in New York City could not be individually identified. In addition, the kidnapper's passport, Satam al-Suqami, was found a few blocks from the World Trade Center shortly after the impact. A passerby picked it up and handed it over to an NYPD detective just before the WTC twin towers collapsed.
On September 28, 2001, the FBI published a four-page handwritten letter , copies of which were found in three places, and assigned it to pilots on three of the four hijacked flights. Atta's copy was found in a late-checking bag at Boston Airport. In this will , combined with a “primer for suicide bombers” , said something like: “Open your heart, welcome death in the name of God ... because you are only a short moment away from the good, eternal life in the company of martyrs .” Abdelghani Mzoudi confirmed the authenticity of the document in October 2001.
In 2002, FBI counter-terrorism expert Dale Watson testified that the 19 attackers were linked to al-Qaeda and bin Laden. The FBI continued its investigation into approximately 7,000 out of 11,000 employees under the name PENTTBOM for years.
According to an article in the New York Times in December 2008, four of the future hijackers were identified as members of an al-Qaeda terrorist cell in the USA as early as 1999/2000 as part of the Able Danger program of the US military intelligence service SOCOM . Atta, al-Shehhi, al-Mihdhar and al-Hazmi were not reported as potential threats to the FBI until the spring of 2001, and their trail was not followed up until August 2001.
Hamburg terror cell
The three alleged suicide pilots and key figures in the attacks, Mohammed Atta , Ziad Jarrah and Marwan al-Shehhi, were enrolled as students at the Hamburg University of Technology and the Hamburg University of Applied Sciences at the time of the attack in September 2001 and had been living in Hamburg for years prior to the attacks . Together with a number of other radical Salafist allies, they formed the Hamburg terror cell, which was independent of Al-Qaeda until the end of 1999 . Atta, al-Shehhi and other like-minded people have lived in an apartment at Marienstraße 54 in Hamburg-Harburg since the 1990s , which served as the center and meeting point of the cell several times a week. They regularly visited the al-Quds mosque on Steindamm in Hamburg-St. George . According to the Bonn embassy of the United Arab Emirates, Marwan al-Shehhi was a "Armed Forces scholarship holder". At the end of January 1999, Mohammed Atta founded an Islam AG under the name Mohamed El-Amir at the TU Hamburg. In the same year, Atta, Jarrah, al-Shehhi and Ramzi Binalshibh, who is also part of the Hamburg terrorist cell, became increasingly radicalized and planned to travel to Chechnya as jihadist fighters to act against the Russian troops.
According to interrogation statements by Ramzi Binalshibh, the Hamburg cell's contact with Al-Qaeda came about by chance. (Note: In order to restrict the truthfulness, it must be said that Binalshibh's statements were made under alleged torture. ) During a train ride in Germany, al-Shehhi and Binalshibh were identified by a contact from Duisburg- based and the 9/11 Commission as " important Al Qaeda official ” Mohamedou Ould Slahi . At a subsequent meeting in Duisburg, Slahi was able to convince al-Shehhi, Binalshibh and Jarrah, who had traveled from Hamburg, that they would complete a training course specializing in jihad in Afghanistan before going to Chechnya. Slahi also instructed how to get Pakistani visas, travel to Quetta , Pakistan and which local Taliban fighters to contact.
Following the recommendations of Slahi, al-Shehhi, Jarrah and Atta first traveled to Quetta in Pakistan at the end of November 1999. Binalshibh followed two weeks later. From there, accompanied by Talibans, we went to Kandahar in Afghanistan . Al-Shehhi had already been sent to the United Arab Emirates from Binalshibh to prepare for the upcoming mission. Mohammed Atef told the remaining three men that they would be participating in a top-secret enterprise. Atta, Jarrah and Binalshibh took part in an initial preparatory course for the attacks during their stay at the Khaldan military training camp in the southeastern province of Paktia . Binalshibh and Atta met Al-Qaeda leader Osama Bin Laden during their stay. Bin Laden informed them that they would be martyrs. Mohammed Atta was chosen by bin Laden to lead the entire operation. During several meetings between Atta and Bin Laden, the targets of the World Trade Center , Pentagon and the United States Capitol were evaluated. Between the end of January and March 2000, the four members of the cell returned to Hamburg. Previously, they were instructed to apply to flight schools in the USA. In order to cover up their stay in Afghanistan, the members of the Hamburg cell reported their passports as lost or stolen. After their return to Germany, the four future assassins changed their appearance and behavior. They cut their beards, preferred a Western style of clothing, avoided visiting mosques known to be radical and distanced themselves from radical Islamists such as Muhammad Haidar Zammar in order not to be targeted by security forces.
In the spring, Ramzi Binalshibh, who had been designated as a terrorist pilot, was refused a visa to enter the USA by various authorities. Bin Laden then selected his Saudi Arabian compatriot Hani Handschur as a replacement, since Handschur was already studying in the USA. In May 2000, Atta, Al-Shehhi and Jarrah, who were also intended as pilots, received their entry visas for the USA. Immediately after their arrival in the United States in June 2000, Atta and Al-Shehhi attended a flight school in Florida and finally acquired their professional pilot licenses in December 2000 , which allow them to operate aircraft with a total weight of 5.7 tons and carry a maximum of 9 passengers entitled. Ziad Jarrah also attended the same flight school in Florida at the same time. In the meantime, however, he returned to Germany to his girlfriend, who was living in Bochum, and attended a flight school in nearby Mülheim an der Ruhr , in order to complete further hours of practice to acquire a private pilot's license . After the license was granted, the assassins began training on the simulator for passenger aircraft. Jarrah and Handschur booked small aircraft practice flights in the New York and Washington, DC area to learn about flight routes, air traffic and topography. Numerous exploration flights to Los Angeles and Las Vegas followed. At a meeting with Binalshibh in Europe in the spring of 2001, Atta received further instructions from Bin Laden and was the only one to learn about the targets of the attack. From then on, Atta coordinated all the assassins involved, whom Bin Laden had selected and who had entered the United States since April 2001. Atta is also said to have set September 11th as the attack date and the Capitol instead of the more difficult-to-reach White House as the attack target.
The 9/11 Commission stated that "in retrospect, it is remarkable how quickly the members of the Hamburg cell became the core of the 9/11 conspiracy." In particular, Mohammed Atta is mentioned again as head of the operation. The commission concluded that the new recruits from Germany possessed an ideal combination of technical skills and knowledge that the originally selected 9/11 assassins from the ranks of al-Qaeda lacked.
Unclear role of Saudi Arabia

15 of the 19 attackers on September 11, 2001 came from Saudi Arabia . However, the role of Saudi Arabia, the Saudi Arabian royal family and members of the Saudi Arabian secret service in the terrorist attacks regarding possible complicity and support of Al-Qaeda remains unresolved and is still part of serious diplomatic conflicts of interest and civil law claims for compensation by the survivors of the victims of the September 11.
The Saudi Arabian government in Riyadh has repeatedly denied suspicions that it supported the al-Qaeda attackers. In contrast, US politician Bob Graham revealed to CBS in April 2016 that the Saudi government, as well as Saudi charities and individuals, had provided “substantial aid” to the 9/11 bombers. The focus is on two of the Saudi kidnappers: Nawaf al-Hazmi and Khalid al-Mihdhar. The US secret services had already got on their trail in 1999 and were identified as members of al-Qaeda. Nevertheless, the two were able to enter Los Angeles unhindered in mid-January 2000 - under surveillance by the secret service. The almost destitute Saudis were supported by Fahad al-Thumairy and Omar al-Bayoumi after their arrival. Al-Thumairy was listed as a diplomat in the Saudi consulate in Los Angeles and was considered an extremist by the US secret services. Omar al-Bayoumi was listed by the FBI as an agent for the Saudi secret service and lived in San Diego, Southern California . In San Diego, the Saudi agent let the future kidnappers live in his apartment complex, helped them out with money and introduced them to several compatriots who, inter alia, the two. Got identification papers. The truth about Saudi aid to the terrorists remained under lock and key for a long time - apparently because even after September 11, 2001, relations with the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia were too important. In July 2016, the US government finally released the previously blackened 28 pages of the congressional report, which documented or suggested contacts between some of the attackers and the government of Saudi Arabia. Zacarias Moussaoui , convicted of terrorism, testified under oath that Saudi members of the royal family, including Bandar ibn Sultan , had donated to al-Qaeda and helped finance the 9/11 attacks. Declassified information from the edited portion of the 9/11 commission report shows that two of the kidnappers received $ 130,000 from Bandar's bank account. The publicist and historian Daniel Pipes said: "The attacks of 9/11 were based on Saudi ideology, Saudi financing, Saudi personnel and Saudi organization."
Until the fall of 2016, Saudi Arabia and the members of the Saudi Arabian royal family enjoyed extensive political immunity in the United States. That changed in September 2016 when the US Congress overruled President Barack Obama's veto of the Justice Against Sponsors of Terrorism Act (JASTA) and allowed civil lawsuits against Saudi Arabia related to September 11th. Without naming Saudi Arabia, the law was created specifically to bring lawsuits against Saudi Arabia from bereaved families. This created considerable tension in foreign relations between the US and Saudi Arabia. In the run-up to the passage of the law, Saudi Arabia threatened the US with the sale of US government bonds amounting to 750 billion US dollars and further financial restrictions.
On March 20, 2017, 1,500 injured survivors and 850 family members of 9/11 victims filed lawsuits against the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Plaintiffs allege that the Saudi Arabia government previously knew that some of its officials and employees were Al Qaeda activists or sympathizers. The complaint alleged that Saudi Arabia "knowingly provided material support and resources to the al-Qaeda terrorist organization and enabled the 9/11 attacks."
A federal court finally overruled Saudi Arabia's state immunity in March 2018. Since then, civil lawsuits against Saudi Arabia with reference to September 11th have been possible. The court finally rejected Saudi Arabia's request not to allow any lawsuits against Saudi Arabia. The government of the Arab state fears recourse payments in the billions if the involvement of the crime can be verified by a court.
Political Consequences
Initial reactions (USA)
Andrew Card , the then Chief of Staff of the White House , informed US President George W. Bush at a school lecture in Sarasota ( Florida ) around 9:00 a.m. local time of the first attack on the WTC and shortly afterwards of the second attack: "A second plane has it hit second tower. America is under attack. ”Bush continued the school event in front of the camera for seven minutes. After a brief discussion with his staff, he made an initial statement and then flew to various US Air Force bases on the Presidential Air Force One aircraft. At around 7:00 p.m., after a stopover, he reached Washington, DC and the White House. At 8:30 p.m., George W. Bush delivered a nationally broadcast speech to the American nation.
In the first days after the attacks, Muslims, Arabs or Arab-looking and turbaned people, often Sikhs , were insulted, attacked, threatened and some were murdered in the United States. There were also arson attacks on Islamic institutions. US President Bush then visited a mosque on September 17, 2001 , condemned the attacks, distinguished Islam from terrorism and called for tolerance towards Muslim US citizens.
Initial reactions (worldwide)
In the days that followed, many people around the world commemorated the victims of the attacks with a minute's silence and funeral ceremonies. Leading politicians in many countries condemned them and sent letters of condolence to the United States.
The German Federal President Johannes Rau declared on the evening of September 11, 2001: “Hate destroys the world and hate destroys people. That’s what it’s all about ...: To resist hatred and to make room for charity . Those who don't hate also say no to violence. Whoever says no to violence makes the lives of our children possible in the first place. ”On September 14, 2001, at a solidarity demonstration in Berlin attended by around 200,000 people, Rau said:“ Hate must not tempt us to hate. Hatred blinds. [...] The best protection against terror, violence and war is a just international order. ”This was seen as a contrast to the “ unrestricted solidarity ”and rejection of war that Chancellor Gerhard Schröder had previously declared.
A funeral service was held at St. Paul's Cathedral in London. The guards in front of Buckingham Palace played the US national anthem.
War in Afghanistan
On September 12, 2001, the UN Security Council unanimously condemned the attacks with Resolution 1368 and allowed the USA to engage in military self-defense. For the first time in its history, NATO declared an " alliance case ": A military attack on the territory of a NATO member state had occurred which, according to Article 5 of the NATO treaty, was to be assessed as an attack on all contracting parties and required their military assistance.
On September 20, 2001, in an extraordinary government statement before the US Congress , US President Bush first expressed his gratitude to the US for international solidarity and particularly emphasized its "loyal friend" Great Britain . He then named the international terrorist network al-Qaeda under Osama bin Laden as the organization responsible for the attacks, as indicated by all evidence, and demanded that bin Laden's immediate extradition by the Taliban regime in Afghanistan. Otherwise, he announced a " war on terror ". He emphasized the difference between the Afghan people and their government, whose human rights violations he criticized. He also called on all nations to ultimately decide to support the USA: "Either you are on our side or on the terrorists' side." Then he differentiated Islam from terror in the name of Allah : He respects the beliefs of Muslims; Al-Qaeda finds itself in blasphemous opposition to it. He called attacks on Muslims in the US “un-American.” The speech was welcomed across parties; the approval rates for Bush in the USA rose at times to over 90 percent.
While Secretary of Defense Donald Rumsfeld wanted to attack Afghanistan as soon as possible, Secretary of State Colin Powell managed to get the Taliban an ultimatum to extradite bin Laden. However, negotiations about an extradition ended without result. On October 7, 2001, the US Army began bombing Taliban positions and infrastructure in Afghanistan. The USA initially excluded its own ground troops. On November 13, the Northern Alliance, allied with them, took Kabul without a fight; Kunduz was occupied on November 25th and Kandahar on December 7th. By the end of the year, the regime under Mullah Omar was overthrown. Bin Laden escaped from the Battle of Tora Bora in December and spent the time until 2003 in a remote village in the Afghan province of Kunar .
From December 2001 onwards, several European countries, including the Federal Republic of Germany with Bundeswehr soldiers , supported the other security and reconstruction missions OEF and ISAF .
War in Iraq
In September 2002, Bush derived the United States' right to preventive strikes from the fight against terrorism (the so-called Bush doctrine ) and justified the Iraq war sought since the end of September 2001 on the one hand with an alleged collaboration between the dictator Saddam Hussein and Al-Qaeda, on the other with his alleged disposal of weapons of mass destruction that he could and wants to use against the US and US troops stationed in Saudi Arabia. Germany, France, Russia and China rejected this doctrine, the US justification for war and their participation in the Iraq war. In February 2003, the UN Security Council denied the United States the legitimacy of the Iraq war. The US government then formed a “ coalition of the willing ”, in which some NATO countries also participated, and began the Iraq war in March 2003 without a UN mandate. It led to the overthrow of Saddam Hussein, followed by years of terrorist attacks by a new Iraqi branch of al-Qaeda and other groups in Iraq.
International Relations
Political scientist Jochen Hippler classified the US war in Afghanistan and Iraq in 2003 not only as a reaction to the attacks, but also as a continuation of a unilateral US foreign policy. It used its position as the only remaining superpower after the Cold War to implement a neoconservative program that had existed since around 1995 to disempower “rogue states” and hostile regimes, to expand US power in the Middle East and Central Asia and to strengthen its global leadership role. Scientists in the USA, such as George Leaman , also take this point of view .
The terrorist attacks initially made this policy much easier, but the pretext overthrow of the Ba'ath regime has intensified violence and terror in Iraq enormously, widened the gap between the Arab dictatorships supported by the West and their people and thus increased the instability of the Middle East region. At the same time he had ended international solidarity with the USA, damaged the authority of the UN and international law and the relationship between the West and the Islamic world, created a gap between the USA and Europe and between supporter and rejection states in the EU and thus a unified foreign policy. and military policy of the EU made more difficult.
The wars that the USA waged following the attacks and the neoconservative project of "Benevolent Imperialism" to spread democracy and a market economy in the Middle East are now viewed as imperial overstretching and are no longer pursued by the USA.
Domestic politics (USA)
The attacks led to an unprecedented expansion of presidential power and a de facto abolition of the separation of powers in the United States. This was based, in addition to the role of the president as the constitutional head of the executive branch and commander in chief of the American armed forces, above all on the theory of the unitary executive . According to this, the executive stands legally above the legislative and judicial branches , its ability to fulfill its constitutional duty and to protect the American people should not be hindered by decisions of the Congress: According to this, it can decide autonomously whether and how to apply the law. Congress followed Bush in this interpretation of the constitution, only the Supreme Court of the United States insisted in several decisions since 2004 that principles of the rule of law such as habeas corpus and the separation of powers continue to apply .
Under the term Disaster Preparedness , the US government increased resources, personnel, competencies and tasks for disaster control , airport security and aviation security . A state of emergency was declared on September 14, 2001 .
In October 2001, Vice President Dick Cheney ordered eight domestic intelligence agencies to circumvent an existing law dating from the 1970s that prohibited trawls and dredging without a judicial order. On October 26, 2001, the USA PATRIOT Act came into effect, which defines "domestic terrorism" as intimidating or coercive influence on the government and allows federal agencies far-reaching encroachments on civil rights for counterterrorism investigations, such as monitoring suspects without a judge Order, the secret tapping of telephone calls, saving connection data and spying on e-mail contacts, obtaining personal information from insurance companies, financial institutions and employers, imprisoning and deporting foreigners suspected of terrorism without giving information and judicial review of suspicious facts and with more difficult judicial review rights. According to this, over 5,000 foreigners, mostly young male Muslims with contacts in Arab states, had been arrested by 2003, 531 of whom were deported, some detained for up to eight months, but none of them were charged. Although the Supreme Court ruled some of these provisions unconstitutional since 2004, in March 2006 the US Congress extended 14 of 16 provisions of the USA PATRIOT Act indefinitely. Bush broke the legal requirement to provide Congress with complete information on the implementation of the measures - in total, in addition to the central department for home security with 170,000 employees, 263 new security agencies were established or reorganized in the USA; 1200 state organizations and 1931 private companies have been dealing with security since then.
Other western states passed similar laws, tightened entry requirements and expanded personal surveillance. The Federal Republic of Germany reintroduced the computer search and leniency program from the fight against the RAF in the 1970s and passed two " anti-terrorism packages ". Draft legislation for the introduction of a preventive detention (2004), for telecommunications monitoring (2005), for permission kills hijacked airplanes and for preventive dragnet (2006), to the secret online searches of private computer (2008) and data retention (2010), the declared Federal Constitutional Court each unconstitutional.
Domestic policy (EU)
The European Council decided on 21 September 2001, terrorism in the territory of the European Union to fight (EU) priority. With Common Position 931 of December 27, 2001, the EU member states unanimously adopted additional measures to combat terrorism. In particular, with Regulation (EC) No. 2580/2001, a uniform list of persons, associations or bodies was adopted that may be subject to financial sanctions in order to combat and prevent terrorism (freezing of funds and economic resources, prohibition of the provision of funds and economic resources). With this and with the so-called EU terror list, the EU complied with UN resolution 1373 .
Judicial Consequences
Military proceedings
In the Afghan war and in the course of further investigations, the US Army captured over 1,000 suspects, mostly people of Arab or Asian origin. They were taken to Guantánamo Bay Detention Center , Bagram Military Prison, and other camps outside the United States, where they were isolated from the outside world and detained for years without charge or disclosure of their identity. Legally, the US government defined them as "irregular fighters" and tried to apply international law , such as Article 4 of III. Geneva Convention on the Treatment of Prisoners of War , and evade US criminal law. In addition, CIA interrogators have used some of the suspect prisoners' methods, such as sleep deprivation and waterboarding , which are defined as torture under international law . This led to sustained international protests by human rights organizations and allied Western states.
The torture practices and military exemption procedures to which the detainees were subjected and were also met with opposition in the United States. A public criminal lawsuit in US courts was dismissed on appeal. A ruling in June 2008 required the US government to treat these prisoners according to US legal standards. In November 2009, US Attorney General Eric Holder announced that the suspected masterminds of the terrorist attacks would be brought before a civil court in New York. Khalid Sheikh Mohammed and four co-defendants from the Guantánamo camp are said to answer for their actions near the former World Trade Center. The civil proceedings are intended to replace the previous military proceedings before the controversial special tribunals in Guantánamo, which had been set up by the former US President George W. Bush. Some victims' relatives criticized this decision.
Criminal proceedings
Mounir al-Motassadeq was involved in al-Qaida in the preparations for the terrorist attacks. Therefore, after several years of proceedings in Germany, he was found guilty of having participated in the hijacking of the aircraft and the murder of the passengers and crew members. He was not criminally charged with the destruction of the World Trade Center. He was therefore sentenced to a prison term of 15 years for aiding and abetting murder in 246 cases and membership in a terrorist organization on January 8, 2007, which became effective on May 2, 2007.
Since February 11, 2008, Chalid Sheikh Mohammed , Ramzi Binalshibh , Ali Abdel Asis Ali , Mustafa Ahmed al-Hausaui and Walid bin Attasch have been indicted by the United States in connection with planning and carrying out the attacks. The criminal case against another defendant was dropped in 2008.
Civil proceedings
Silverstein Properties , in cooperation with the shopping center operator Westfield America , leased the World Trade Center for 99 years six weeks before the attacks and insured it for 3.5 billion dollars. The real estate company and its fellow campaigners were awarded $ 4.6 billion in compensation after longstanding legal disputes with various insurance companies. Originally $ 7 billion and a little later $ 12.3 billion were sued. Nine insurance companies, including Allianz Global Risks US Insurance , ultimately had to pay double the amount of damage, as the plaintiff and the court believed that the two aircraft impacts were two different cases of damage. In addition, Silverstein received $ 861 million for the separately insured WTC 7 in June 2002 .
On September 5, 2012, another lawsuit by Silverstein subsidiary World Trade Center Properties LLC against American Airlines and United Airlines was admitted in the United States. The airlines were accused of negligently allowing the boarding of 19 terrorists on their aircraft due to inadequate security controls, whereby they are supposed to bear legal responsibility for the destruction of the buildings of the World Trade Center. The amount in dispute was $ 2.8 billion. In a 2015 settlement, plaintiffs accepted an amount of USD 95.2 million
In July 2016, the US government released the previously blacked-out pages of a congressional report that documented or suggested some bombers had contacts with the government of Saudi Arabia. (For the background, see 9/11 Commission # Unclear role of Saudi Arabia ). In September 2016, the House of Representatives passed the Justice Against Sponsors of Terrorism Act (JASTA), which allows the immunity of states suspected of terrorism to be lifted. As a result, a New York law firm filed a lawsuit for damages against the state of Saudi Arabia on March 17, 2017 on behalf of several thousand victims and their families. He is accused of providing financial and, in particular, logistical support to al-Qaeda, without which the attacks could not have been carried out.
The US judge George B. Daniels issued a default judgment requiring Iran to pay the victims of the attacks more than 6 billion US dollars. At the trial it was alleged that Iran provided training and other assistance to the kidnappers. Iran would be instructed to “US $ 12.5 million per spouse, US $ 8.5 million per parent or child, and US $ 4.25 million per sibling, with an annual interest rate of 4.96% (as of September 11, 2001 through the date of Judgment) ”to the families of the deceased, it said in the court records.
Economic consequences
Although the terrorists wanted to hit the American financial and economic power with the World Trade Center, the economic consequences of the attacks were comparatively small. The Dow Jones index lost after the reopening of York Stock Exchange New September 17, 2001, about seven percent. The proportion of jobs in the financial sector in New York fell from 25 to 20 percent within ten years. However, the relative importance of New York in the financial industry has been declining since the 1990s, so that the terrorist attacks cannot be seen as the only factor in this development. The disruption to American economic life caused by the attacks is estimated at just one percent of gross domestic product . The attacks did not trigger a recession , although this was precisely what was feared with a view to the bursting of the dot-com bubble in March 2000. The economic growth in the US and around the world moved to 2001 soon again, which is also on the massive spending deficit can be attributed to which the United States funded the subsequent wars. Whether the massive national debt of the United States (in 2001 it still had a budget surplus , in 2018 the national debt was over 22 trillion dollars) can be indirectly attributed to the attacks or whether it was caused by the Great Recession from 2007 onwards is controversial.
Investigations
FBI
Immediately after the attacks, the FBI began investigations into the perpetrators on September 11, 2001 under the code name PENTTBOM . It became the largest criminal investigation in US history involving 7,000 FBI agents and professionals. The FBI was able to identify the 19 hijackers in a matter of days because some suspects had made no effort to hide their real names on the flights, on their credit cards, or on other records. In addition, three passports of the attackers were recovered from the ruins of the attack sites. Another kidnapper's passport was found in Mohammed Atta's undamaged luggage.
Joint Inquiry
From February to December 2002, one committee each from the Senate and the US House of Representatives carried out the “Joint investigation into the activities of the secret services before and after the terrorist attacks on September 11, 2001” . In 2002 the “Joint report of the fire service management and the consulting firm McKinsey & Co” on management structures and operational guidelines appeared on September 11, 2001 and the consequences to be drawn from them.
9/11 Commission
At the urging of victims' associations, the House of Representatives set up the bipartisan 9/11 Commission in the fall of 2002, despite considerable opposition from the US administration under President George W. Bush . It consisted of five MPs each from the Democratic and Republican parties , chaired by ex-Governor Thomas Kean, and 78 staff members. It should clarify the history, course of the attacks and the reactions of the US authorities to them and propose security policy measures to prevent such attacks in the future. She was not supposed to investigate the physical causes of the WTC buildings collapsing. Working from January 2003 to August 2004, she interviewed approximately 1,200 witnesses, including 120 government officials including George W. Bush, Vice President Dick Cheney, and Security Advisor Condoleezza Rice . Their final report (July 22, 2004) showed serious systemic errors of the US authorities that had made the attacks possible: for example, a lack of screening of domestic passengers before checking in at the airport, lengthy and cumbersome procedural channels and command hierarchies that prevented NORAD from intervening quickly , failure to check flight schools in the US for flight students suspected of terrorism, failure to pursue al-Qaida members who have entered the US, failure to exchange information between the CIA and FBI about suspects and the Bush administration's passivity towards acute attack warnings. From May to August 6, 2001, it had received 40 short daily reports on Al-Qaeda, including several that warned of a multiple attack in the United States, possibly with hijacked planes and targets in New York. Coordination problems, misunderstandings, lack of information, non-disclosure of commands, unclear guidelines and wrong reactions at all levels were proven in detail. Persons responsible for this were not named and personal consequences were not requested. As a result of this analysis, the operational guidelines of the FDNY, the New York Police, the FBI and the CIA were changed. The Ministry of Internal Security was re-established and the city campaign “Preparedness” was set up.
The 9/11 Commission and the investigation report it produced was heavily criticized by parts of society. The focus of the criticism was the controversial interrogation testimony of alleged al-Qaida members made under torture, as well as a possible conflict of interest of Philip Zelikow , the chairman of the 9/11 commission. An analysis by NBC News found that more than a quarter of all footnotes in the 9/11 investigation report refer to CIA interrogations of al-Qaeda members who were subjected to controversial interrogation methods. In fact, the most crucial chapters of the report on the planning and execution of the attacks are essentially based on information from interrogations allegedly carried out under torture.
Philip Zelikow, head (“Executive Director”) of the 9/11 Commission has faced allegations of conflicts of interest raised by victims' associations and numerous members within the 9/11 Commission. Zelikow has been accused of being a "White House mole". In particular, Zelikow was shown his connections to the Bush administration, to US President George W. Bush's chief adviser Karl Rove and to the then National Security Advisor Condoleezza Rice . In addition, the commission chairman accused Thomas Kean and Lee H. Hamilton of the CIA claims to have impeded the investigation.
FEMA
Until May 2002, the disaster control agency FEMA examined the building security and structural problems that caused the collapse of the WTC buildings for the first time. After their report was criticized as inadequate, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) received a precisely defined research assignment, which it divided into individual tasks on its own initiative and delegated to experts from various disciplines.
NIST
The NIST issued several reports in the sequence. In September 2005 a detailed study of all relevant aspects of the collapse of WTC 1-6 was published. Over 300 experts and scientists were involved in the three-year research. Two fact sheets from August 2006 and December 2007 summarized NIST's answers to the most important questions about the technical process of the collapses and their explanation. The final report for WTC 7, which has been postponed several times, was published on August 21, 2008.
Scientists without a government mandate calculated the causes of the WTC collapse days after September 11th and published articles on it. Scientists at Purdue University ( Indiana ) developed simulation models and carried out the most detailed, high-precision simulations of the collapses to date. They show that 17 of the 47 load-bearing columns in the north tower were destroyed, so that the collapse became inevitable after a fire lasting almost two hours. The NIST had previously assumed that six pillars had been destroyed, which, together with the ongoing internal fires, would have been sufficient for the collapse of the floors above the impact zone.
Memorials and memorials


In the first days after the attacks, desperate relatives left their missing persons reports on barriers and wall surfaces around Ground Zero in New York. From this spontaneous memorial sites developed. By depositing photos, candles, letters and personal items, numerous people expressed their condolences and condolences for the missing and deceased victims. In the days after the attacks, there were numerous offers and campaigns to help the victims. Blood donations, free hotel use, medical care and medication for people without proof of residence or rent-free office space for group meetings were organized and provided. As a result, innumerable benefit concerts were held and the proceeds from CD sales were largely donated. New aid funds were launched or a new focus for affected families and children was established within existing aid funds. Became known z. B. the Coalition of 9/11 Families, Children of September 11th , the New York Police and Fire Widows' and Children's Benefit Fund or the New York Times 9/11 Neediest Cases Fund. In addition, many self-help groups were founded, the special focus of which arose from the group composition of the victims and the situation of the relatives.
On September 23, 2001, representatives of all New York-based groups and religions commemorated the dead and prayed together at a nationally televised memorial service from New York's Yankee Stadium . The funeral was accompanied by musical performances by Placido Domingo , Bette Midler and the Harlem Boys Choir.
Every year on September 11th, the victims of the attacks are remembered with numerous memorial services, especially in New York, at the Pentagon and in Shanksville. In New York, the names of the 2,791 people who were killed in the attack are usually read out by their relatives in alphabetical order.
On March 11, 2002 - six months after the attacks - the Tribute in Light lit up the New York night sky for the first time . Since then, the light installation has been repeated every year on September 11th between sunset and sunrise. From the Battery Park , the hard beams of light from 88 xenon headlights á 7000 watts emulate the twin towers.
In 2006, a memorial wall was inaugurated on Liberty Street at 10 Fire Station of the New York City Fire Department as an official memorial to the 343 New York firefighters who died on September 11th. In addition, a parade group of the FDNY takes part in commemoration of the annual “St. Patrick's Day parade, carrying 343 symbolic American flags.
Numerous memorial sites have been created to commemorate, including the Pentagon Memorial , Flight 93 National Memorial , Staten Island September 11 Memorial, and National September 11 Memorial and Museum .
- National September 11 Memorial & Museum
On the site of the old World Trade Center is the National September 11 Memorial, inaugurated on September 11, 2011, with the attached 9/11 Museum and Liberty Park. The memorial, known as the 9/11 Memorial, was designed by Michael Arad and the landscape architect Peter Walker with the support of the architect Max Bond. The center of the memorial is formed by two large rectangular cavities that recall the foundations of the destroyed twin towers and their loss. From there, the visitor can view the two water basins nine meters below. These in turn absorb falling water cascades. As Reflecting Absence (German: reflection of the absence of ) known pools are engraved with the names of all the victims of the attacks of 11 September 2001 and the bombing of the World Trade Center in 1993 surrounded.
On August 16, 2017, the large spherical caryatid NY by the German sculptor Fritz Koenig was inaugurated on the edge of Liberty Park . The 20-ton bronze sculpture with a diameter of almost eight meters had been on the forecourt of the World Trade Center since 1971 and was recovered from the rubble after the attacks. Since then, the work of art known in the USA as The Sphere has been transformed into an important symbolic monument of 9/11 commemoration.
Right next to The Sphere's new location , the St. Nicholas Greek Orthodox Church and National Shrine designed by Santiago Calatrava will be inaugurated on September 11, 2021 . The $ 85 million rebuilt house of worship with the national shrine will be another important part of the 9/11 Memorial.
Reconstruction World Trade Center
In addition to the twin towers, the remaining five buildings of the World Trade Center were also destroyed. 23 other buildings surrounding the WTC were damaged so badly that they were later demolished. The small St. Nicholas Greek Orthodox Church was completely destroyed . The buildings 90 West Street , 130 Cedar Street, the New York Telephone Building , 30 West Broadway ( Fiterman Hall ), three buildings of the World Financial Center and the winter garden in between were badly damaged . The badly damaged Deutsche Bank Building (also called 130 Liberty Street or Bankers Trust Building) was demolished by 2011 after a long insurance dispute. Previously, for years it was completely wrapped in black and carried a large US flag on the side facing Ground Zero . The St. Nicholas Greek Orthodox Church was built in place of the bank building. The building at 30 West Broadway ( Fitterman Hall ) was demolished from November 2008 to summer 2009 and replaced by a new building - the opening took place on August 12, 2012. Four subway stations on the New York subway were also destroyed and rebuilt
The building of the new World Trade Center began the real estate company Silverstein Properties on 7 May 2002 with the establishment of the new 7 World Trade Center on the site of the collapsed predecessor Bauwerkes World Trade Center 7 . The 226 meter high office tower on Greenwich Street opened on May 23, 2006.
On April 2, 2006, construction began on the One World Trade Center, originally known as the Freedom Tower , as a successor to the destroyed World Trade Center. The 1 WTC was after long disputes between the architect Daniel Libeskind and Larry Silverstein , the leaseholder of the WTC site, ultimately by architect David Childs designed. After seven years of construction, the skyscraper reached its final height of 541.32 meters in May 2013 and was opened on November 3, 2014. The symbolic height of the equivalent of 1776 feet is intended to commemorate the United States' Declaration of Independence in 1776 and goes back to the original first draft by Daniel Libeskind.
In addition to the One World Trade Center, the 329-meter-high Three World Trade Center , which opened in June 2018, and the 298-meter-high Four World Trade Center, which opened in November 2013, are already completed building blocks of the new WTC complex. Construction work on the Two World Trade Center has been at a standstill since 2013. The exact location for the construction of a Five World Trade Center is still unknown. In the center of the rebuilt World Trade Center complex is the National September 11 Memorial and Museum with the two commemorative water basins, the 9/11 Museum and Liberty Park.
Below the World Trade Center site , the by Spanish architect is Santiago Calatrava -designed subway station World Trade Center with shopping mall Westfield World Trade Center , the largest shopping complex in Manhattan. The building called Oculos , which opened in April 2016, is the most expensive train station in the world with construction costs of more than four billion dollars.
Social debates
sociology
There are various theories about the longer-term and deeper causes of Islamist terror: “ Anti-imperialist ” explanations make the West, especially the Middle East policy of the USA and Israel , responsible for the hatred and radicalization of many Muslims. Osama bin Laden was often seen as a product of the CIA and his attack planning as the result of a failed US foreign policy during the Cold War . This finally fell back on the USA itself ( blowback ).
The failure of the rich western industrialized countries to tackle the problem of poverty through unilateral globalization has also created a breeding ground for terror (but not for their masterminds). This view is often represented by left-wing intellectuals like Noam Chomsky or human rights activists like the Indian Arundhati Roy .
From a cultural sociological perspective, the phenomenon of so-called Islamic terrorism is also interpreted as the formation of a front against cultural modernization in the respective home country. The insecurity that goes hand in hand with the breakage of old, traditional structures and ideologies is compensated for by an increased focus on one's own roots (e.g. Salafism ) and lived out in the terrorist struggle against the western world. With the spectacular attack in the center of the western world, the perpetrators supposedly wanted to symbolically demonstrate the vulnerability of the “Jews and Crusaders ”. In this perspective, the ideology of the perpetrators is interpreted as " Islamic fascism " and the component of anti-Semitism is emphasized.
caesura
Whether the attacks of September 11, 2001 represent a historic turning point is a matter of dispute in journalism and specialist science. At first contemporaries clearly perceived them as such. The New York Times wrote on September 12, 2001 that it was "one of those moments when history divides and we define the world as 'before' and 'after'". In Germany, on that day, both the Bild-Zeitung and the Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung ran the headlines independently of each other: “Nothing will be as it was anymore”.
But just a few years later, historians and political scientists contradicted the perception of contemporaries in two volumes. They emphasized the continuity of the American hegemony vis-à-vis the Islamic world and the tendency to perceive international conflicts in Manichaean terms as a struggle between good and evil . On the left , too, emphasis was placed on the continuity of imperialism and the “American search for world domination ” (so the subtitle of a book by Noam Chomsky ).
In 2011 the Americanist Michael Butter published the volume 9/11, Not a Day That Changed the World . In it he argues that the concrete changes that have occurred in American politics since 2001 cannot be attributed monocausally to the attacks. These were not so much a trigger as a catalyst for developments that made them happen faster and more obviously. The historian Martin Sabrow, on the other hand, cites the attacks of September 11th as an example of a historical turning point, if only as an "orthodox turning point": In contrast to the "heterodox turning point" such as the fall of the Berlin Wall on November 9, 1989 , it still applies Basic norms and ideas intact and create "no new lines of sight and thinking horizons, but confirm previously known ones". For the social scientist Samuel Salzborn , the attacks were the "prelude to an anti-Semitic revolution that is currently underway around the world". It is not only directed against Jews, but also represents a general threat to the values of the Enlightenment , namely the promise that every individual can become a self-determining subject .
The historian Manfred Berg counterfactually weighs up which events would have to be considered unlikely without the attacks, because only if there are several of them can one speak of a turning point. The war on terror, the Afghan war and the Iraq war can clearly be traced back to the attacks, as can the enormous expansion of executive power in the USA. With increasing time lag, there could be no talk of a “ unipolar world”, which some commentators saw coming at the beginning of the millennium, given the American-Chinese rivalries. The danger of a repetition of the attacks does not shape the everyday life of the people in the USA and Europe either. Hence the prevailing impression “that '9/11' was not a historic turning point that decisively changed the long-term global political and global economic trends”.
conspiracy theories
There are numerous websites, books and films about the attacks on September 11, 2001, which discuss conspiracy theories about the acts. A variety of theories suggest that the US government and its intelligence services knowingly allowed or carried out the attacks. The reason for the doubts about the innocence of the US government are, among other things, warnings that there should have been about the flight training of the terrorists and targeted attack plans. These should not have been observed.
The collapsed World Trade Center in New York and the attack on the Pentagon remain grounds for speculation. The identified causes for the attack damage are doubted. A controlled demolition of the twin towers and WTC 7 is considered possible. Critics also claim that the damage to the US Department of Defense headquarters was too small to have been caused by an airplane. Supporters of the so-called 9/11 Truth Movement have been demanding a new investigation of the events since 2005. In addition to the experts from FEMA and NIST , numerous scientists also contradict your theses .
The US government continues to be accused by conspiracy theorists of needing a justification for the war in Iraq and therefore planning or permitting the attacks. The realization that Iraq had no weapons of mass destruction fueled critics' doubts about the credibility of the US government.
In 2010 the Süddeutsche Zeitung published the results of an international survey. Only in nine of the 17 countries surveyed were the majority of respondents convinced that Al-Qaeda was behind the attacks. The survey, which was carried out by researchers in the various countries and coordinated by the University of Maryland in the United States , also found that an international average of 46 percent of respondents believe that Al-Qaeda was responsible for the crimes. 15 percent are of the opinion that the US government initiated the attacks itself, seven percent suspected Israel as the originator and seven percent believed in other masterminds. One in four respondents said they did not know who was responsible for the terrorist attacks. According to the survey, 64 percent of people in Germany believed that Al-Qaeda had committed the acts, and 23 percent believed the US government was to be blamed. Especially in the Middle East, but also in countries like Mexico or Turkey, many citizens suspected that the US government or Israel were responsible for the attacks.
Artistic reception
music
Many musicians reacted to the attacks with special works. In many of these titles, concern, sadness, remembrance and the desire for tolerance were in the foreground.
In the US, the song was Only Time by Enya in the version with superimposed votes affected the unofficial anthem for the 11th of September. The American Hardcore Alliance's hardcore techno song We Will Never Forget commemorates the victims. The country musician Alan Jackson wrote the song Where were you When the world stopped turning? , Darryl Worley wrote the song Have You Forgotten? . Other topics works are the studio album The Rising by Bruce Springsteen , Let's Roll with respect to the resistance of the passengers on the flight UA-93 by Neil Young , "Believe" by Yellowcard , the instrumental title Darkness of Sept. 11th of guitarist Chris Mike and Towers On Fire by Brazilian thrash / death metal band Torture Squad . When the Eagle Cries by Iced Earth refers to the bald eagle, the heraldic animal of the USA, whose tears symbolize the grief of the USA. The German rapper Curse released the freetrack on September 16, 2001, nothing will be the same , in which he called for more tolerance and responsibility.
Others dedicated their appearances and recordings to the victims. Michael Jackson wrote the song What More Can I Give with the aim of raising $ 50 million for the victims' dependents. Paul McCartney was in New York on September 11, 2001 and then wrote the song Freedom for a tribute concert. Sting dedicated his concert, scheduled for September 11 in Tuscany, to the victims after his chosen concert guests spoke out against a cancellation. The concert recording was released as a live album entitled All This Time , the classic Fragile from it appeared on the album America: A Tribute to Heroes . The saxophonist Sonny Rollins gave a concert in Boston on September 15, 2001 , the live recording of which was released under the title Without a song: the 9/11 Concert . Melissa Etheridge dedicated her song Tuesday Morning to Mark Bingham and the other passengers whose moral courage had prevented the fourth hijacked plane from reaching its target.
Some musicians dealt with the consequences of the attacks: for example the band Tomte with their song New York or the Eagles with Hole In The World (2003). The Mono group for everyone! critically deals with the commemoration with her song September 11th . Heads Will Roll from Pro-Pain describes feelings of revenge and criticizes the development of the Iraq war. Techno musician Chris Korda combined media images of the attacks with pornographic film clips in a controversial music video I Like To Watch . With its title 9/11 Self-made, the Duisburg hip-hop band Die Spektrum criticizes previous US policies. Finally, in the song Jihad , the thrash metal band Slayer addressed the attacks from the perspective of the terrorists.
The Hungarian composer Robert Gulya , who lived in the USA from 2000 to 2002, wrote a new guitar concerto in autumn 2001, shortly after the 9/11 attacks. In the first movement of this concert, Gulya chose a theme that is reminiscent of that terrorist attack. The world premiere of this work was filmed and published on DVD Live in Budapest by the Austrian guitarist Johanna Beisteiner .
In 2002 the German composer Martin Christoph Redel wrote “Reflections on 'Ground Zero'” for violin and piano op. 52c, a meditation in memory of the victims of the terrorist attack in New York.
The important and esoteric composer Karlheinz Stockhausen caused a stir shortly after the attacks with his statements. Stockhausen said in a press conference: "Well, what happened there is of course - now you all have to rearrange your brain - the greatest work of art that has ever existed ..."
“So that ghosts can accomplish something in one act that we could never dream of in music, that people practice like crazy for ten years, totally fanatical, for a concert. And then die. [Hesitates.] And this is the greatest work of art there is for the whole cosmos. Just imagine what happened there. So these are people who are so focused on this one performance, and then five thousand people are chased into the resurrection. In a moment. I couldnt do that. We are nothing against it, that is, as composers. [...] It is a crime because people did not agree. They didn't come to the concert . That is clear. And nobody announced to them that you could get killed. "
Stockhausen's point of view met with incomprehension and rejection in the media and the general public. In a statement published on September 19, he defended his statements and pointed out that he had spoken in the spirit of his operatic character Lucifer , the fallen angel. Furthermore, Stockhausen distanced himself from the terrorist attack and wrote in the declaration that he included the victims in his prayers.
With the composition WTC 9/11 (2009-10) Steve Reich created a 16-minute work for string quartet and two quartets on tape, written for the Kronos Quartet . The three-movement work is played at a steady tempo without a break; the tape also contains documentary material on the attack.
The American media company Clear Channel Communications drew up the 2001 Clear Channel Memorandum for its radio stations after the attacks , a list of songs that were considered inappropriate during the period of national remembrance.
Movie
- September 11th - The last hours in the World Trade Center (French / American documentary by Jules and Gédéon Naudet , 2002) Originally the filmmakers had planned a film about a "firefighter in training" at the FDNY . The film team got involved in the rescue operation of the fire brigade, and they got dramatic pictures of the disaster and the way people dealt with it.
- 11'09 "01 - September 11 , 2002, ARTE F. Rather a film about the meaning and perception of September 11 worldwide. 11 short films by eleven directors from different countries.
- 9/11 - The last minutes in the World Trade Center - docu-drama, USA and GB 2006 (reconstruction of the inferno, also based on statements of survivors, police reports, recordings of telephone calls. Director: Richard Dale; Original title: 9/11: The Twin towers)
- Twin Towers (American documentary, USA, 2003, director: Bill Guttentag ) about two brothers who died on September 11th.
- DC 9/11: Time of Crisis (feature film, Canada / USA, 2003, director: Brian Trenchard-Smith ) about the political adaptation of September 11th by the president.
- Fahrenheit 9/11 (2004, critical and sarcastic documentary film by director Michael Moore , which describes the policies of the US government before and after the destruction of the WTC)
- Land of Plenty (2004, fictional film directed by Wim Wenders about the general paranoid sense of threat that divides the United States, two years after the attacks)
- Flight 93 (feature film, USA, 2006, director: Paul Greengrass )
- The Path to 9/11 (Feature Film, USA, 2006, Director: David L. Cunningham )
- World Trade Center (Feature Film, USA, 2006, director: Oliver Stone )
- Remember Me (Feature Film, 2010, Director: Allen Coulter )
- Extremely loud & incredibly close (2011 feature film, director: Stephen Daldry ): Here the loss of a loved one through the attacks is discussed
- The love in me (2007 feature film, director: Mike Binder ): Here the loss of loved ones due to the attacks is discussed
- The world will be different (feature film 2021, director: Anne Zohra Berrached ): Inspired by the biography of the assassin Ziad Jarrah
In May 2019, 441 titles on this topic are listed in the IMDb .
theatre
The Mercy Seat (dt. Day of grace ) by Neil LaBute is about the fictional story of a married man who has worked in the World Trade Center, however, survived the attacks because he secretly met his mistress. The play, which takes place on September 12, 2001, deals with the two considerations of how to deal with this lie. Itpremiered on Broadway in2002 with Liev Schreiber and Sigourney Weaver under the direction of the author; the German premiere took place in 2003 at the Deutsches Theater Berlin . Theattack on the World Trade Center is re-enacted with the use of white fogin the four-hour play Reich des Todes by writer Rainald Goetz , whichpremiered on September 11, 2020 at the Deutsches Schauspielhaus in Hamburg under director Karin Beier .
novel
In his 2003 novel Windows on the World , Frédéric Beigbeder meticulously tells of a father and two sons who were in the Windows on the World restaurant in the north tower of the World Trade Center during the attacks .
Jonathan Safran Foer's novel Extremely Loud and Unbelievably Close , published in 2005, tells the story of a traumatized nine-year-old boy whose father was killed in the attacks.
The protagonist of Don DeLillo's 2007 novel Falling Man is a survivor of the attacks. The theme of the novel is the appearance of a performance artist named Falling Man, who is hanging on a rope and recreating the famous photograph The Falling Man by Richard Drew .
The novel Die habenichtse by Katharina Hacker , published in 2006, is set against the background of the terrorist attacks and the beginning of the Iraq war. In the novel Das Hohe Lied by writer Nell Zink , which was published by Rowohlt Verlag in August 2020 , the September 11 attack is a driving force behind the plot.
Painting and sculpture
After the terrorist attacks on September 11, 2001, Eric Fischl designed the ten breaths series of works with gouaches and sculptures depicting falling and fallen people. The Tumbling Woman sculpture , which depicts a woman in free fall, has been the subject of controversy in the United States. The series of works processes the press photos of the desperate, who fell from the windows of the burning towers of the World Trade Center after the attacks in order to avoid death by fire.
By Gerhard Richter , the image "September" has been made in dealing with the event. The artwork To the Struggle Against World Terrorism is dedicated to the victims of the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001 and that of 1993 .
Satire and comedy
More or less black humor under the motto Where was King Kong when we needed him? as well as jokes spread online in particular emerged the day after the attack. They have also found expression in folklore research.
The British-Pakistani comedienne Shazia Mirza became known nationwide when she appeared in a hijab on her first stage appearance after the terrorist attacks and began with the words:
“My name is Shazia Mirza. At least, that's what it says on my pilot's license. "
“My name is Shazia Mirza. At least that's what it says in my pilot's license. "
In 2011, Wiglaf Droste interpreted the attacks on the Twin Towers as a satirical critique of architecture in an article for the Marxist newspaper Junge Welt :
“The collapse of two ugly and very dispensable towers has only national folkloristic significance. For me, September 11, 2001 will be the hour of birth of the manned, flying architecture criticism. The engineering office bin Laden & Erben could continue to do a lot to beautify the world. Against blind and deaf brains / the wrecking ball helps quite well. To put it presidential: also and especially in Germany. "
The feature film Postal by the German director Uwe Boll deals with the subject.
literature
course
- Stefan Aust , Cordt Schnibben (Ed.): September 11, 2001. History of a terrorist attack. Dtv , Stuttgart 2003, ISBN 3-423-34026-6 .
follow
- Manfred Berg , September 11, 2001 - a historic turning point? In: Zeithistorische Forschungen / Studies in Contemporary History 8 (2011), pp. 463–474.
- Michael Butter , Birte Christ, Patrick Keller (Eds.): 9/11. Not a day that changed the world. Schöningh, Paderborn 2011, ISBN 978-3-506-77097-4 .
- Bernd Greiner : 9/11. The day, the fear, the consequences. CH Beck, Munich 2011, ISBN 978-3-406-61244-2 ( review ).
- Till Karmann, Simon Wendt et al. (Ed.): The turning point of 9/11? A transatlantic balance sheet. Verlag Barbara Budrich, Opladen, Berlin & Toronto 2016, ISBN 978-3-8474-0562-7 .
- Hans Vorländer : Political culture: “Rally round the flag ”. The USA after September 11th, in Peter Lösche (Ed.): Country Report USA. History, politics, economy, society, culture. Federal Agency for Civic Education BpB, 5th neub. Edition Bonn 2008 ISBN 978-3-89331-851-3 , pp. 196-236.
Background, causes
- Tore Bjørgo (Ed.): Root Causes of Terrorism: Myths, Reality and Ways Forward. Taylor & Francis, 2005, ISBN 0-415-35149-9 .
- Michael Bothe : September 11th - causes and consequences. Winter, Heidelberg 2003, ISBN 3-8253-1546-0 .
- Christoph Kucklick : September 11, 2001. The day that changed the world. The planning, the process, the consequences. All the backgrounds of the disaster . Gruner + Jahr, Hamburg 2001, ISBN 3-570-19350-0 .
- Lawrence Wright : Death will find you. Al-Qaeda and the road to September 11th . Deutsche Verlags-Anstalt, Munich 2007, ISBN 978-3-421-04303-0 (English: The Looming Tower. Al-Qaeda and the Road to 9/11 . New York 2006. Translated by Stephan Gebauer and Hans Freundl).
Individual aspects
- Helga Embacher / Margit Reiter: Europe and September 11, 2001. Böhlau Verlag, Vienna 2011, ISBN 978-3-205-78677-1 .
- Clément Chéroux: Diplopia. September 11th image policy. Konstanz University Press, Konstanz 2011, ISBN 978-3-86253-007-6 .
- Brian A. Monahan: The shock of the news. Media coverage and the making of 9/11 . New York University Press, New York et al. 2010, ISBN 0-8147-9554-4 .
Web links
Image and sound documents
- Live TV coverage of the TV stations ABC, NBC, CBS, CNN, FOX and BBC from September 11th to 13th, 2001 (English)
- ARD Tagesschau: September 11, 2001 Live TV coverage by ARD
- NIST Archives: Thousands of Photos and Videos from September 11, 2001
- The September 11 Attacks & Aftermath: Image and sound archive as of September 11, 2001
- ARD Planet Schule: The attack: September 11th and the consequences
sequence
- Multimedia Timeline: September 11, 2001 (English)
- The 9/11 Commission Report: Report of the 9/11 Commission, July 2004 (PDF)
Causes of collapse
Reactions
- September 11 Television Archive: A library of world perspectives Concerning September 11th, 2001 (english)
- Information portal on political education: 10 years September 11, 2001
follow
- Balancing conference on the 10th anniversary of the terrorist attacks of September 11th with a focus on the transatlantic perspective.
- Analysis of the domestic and foreign policy consequences
- Works of art that were destroyed or damaged on September 11 (English)
Arts
- Fritz Koenig's Ball - The Sculptor and the September 11th Documentary by Percy Adlon about the sculptor Fritz Koenig and his large ball caryatid NY
Commemoration:
- Memorial list of the victims of the 9/11 attacks
- Homepage of the Museum of the National 9/11 Memorial in New York
See also
Individual evidence
- ^ Brad Plummer Nine facts about terrorism in the United States since 9/11 Washington Post, September 11, 2013
- ↑ Remembering 9/11: 'The Death Toll Was Too Staggering to Whisper' New York Presbyterian Hospital, 2017
- ↑ Chris Bell: The people who think 9/11 may have been an 'inside job' BBC News, February 1, 2018
- ↑ NIST: Videos of the collapse of WTC 7 (Youtube)
- ^ About 9/11 American Studies University of Notre Dame
- ↑ Integrated United States Security Database (IUSSD): Data on the Terrorist Attacks in the United States Homeland, 1970 to 2011 - Final Report to Resilient Systems Division, DHS Science and Technology Directorate National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism, p December 26, 2012
- ↑ Hans Joachim Schneider: International Handbook of Criminology: Fundamentals of Criminology, Volume 1. 1. Edition, De Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 3-89949-130-0 , p. 802.
- ↑ Body Count. Number of victims after 10 years of "war on terror". (PDF) In: IPPNW . Retrieved November 18, 2020 .
- ^ "Letter from the President on the Continuation of the National Emergency with Respect to Certain Terrorist Attacks". In: Whitehouse.gov. September 10, 2010, accessed September 4, 2016 .
- ^ "Letter - Continuation of the National Emergency with Respect to Certain Terrorist Attacks". In: Whitehouse.gov. August 30, 2016, accessed September 4, 2016 .
- ↑ Johannes Thimm: From the state of emergency to the normal state: The USA in the fight against terrorism . Science and Politics Foundation Study 16, August 2018.
- ^ A permanent emergency: Trump becomes third president to renew extraordinary post-9/11 powers . In: Milwaukee Journal Sentinel . ( jsonline.com [accessed November 11, 2017]).
- ↑ 10 years 9/11 Federal Agency for Civic Education, September 11, 2011
- ↑ The 9/11 Commission Report , 1.2 IMPROVISING A HOMELAND DEFENSE, p. Eite20 (incl. Footnote 116; PDF, English).
- ↑ Michael Bronner: 9/11 Live: The NORAD Tapes Vanity Fair, October 17, 2006
- ^ Katie Lange (US Department of Defense): 9/11 Air Defense Stories You Might Not Know , Military.com (English).
- ↑ The 9/11 Commission Report 1.2 IMPROVISING A HOMELAND DEFENSE, page 20 (incl. Footnote 116)
- ^ NIST, Final Report on the Collapse of the World Trade Center Towers: 2.3 The Immidiate Damage , pp. 22-24 and 2.5, p. 26
- ^ NIST, Final Report: 2.4 The Jet Fuel , pp. 20 to 24; 2.5, p. 25
- ^ NIST, Final Report: 3.2, p. 38 ; 3.4 The Jet Fuel , p. 42.
- ↑ Gold Rises Above $ 400; 5-Month High New York Times, August 18, 1990
- ^ The Commodities Exchange Center Commodities Exchange Center Inc .; Brochure (PDF)
- ↑ Herculean Effort to Restore a Landmark Battered on 9/11. New York Times, January 6, 2003
- ↑ Verizon Building Restoration for 1.4 billion US-Dollar ( Memento of September 26, 2007 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ Ground Zero building to be razed. Badly damaged CUNY building will be replaced. Crains New York, November 13, 2008
- ^ The 9/11 Commission Report, Chapter 1: We have some Planes , p. 29; P. 457, footnote 85; P. 461, footnote 164 (PDF; 7.2 MB)
- ↑ David Ballingrud: Day of terror shatters confidence of a nation. In: St. Petersburg Times , September 12, 2001.
- ↑ The Pentagon was the "art academy". In: Spiegel Online . September 13, 2002, accessed December 23, 2014 .
- ↑ The 9/11 Commission Report, Section 9.2, p. 13 f. (PDF; 7.2 MB)
- ↑ 9/11 Commission Report Report of the National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Upon the United States, p. 282, published July 22, 2004
- ^ 9/11 Commission Report Report of the National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Upon the United States, pp. 281-284, published July 22, 2004
- ↑ 9/11 Commission Report Report of the National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Upon the United States, p. 292, published July 22, 2004
- ↑ 9/11 Commission Report Report of the National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Upon the United States, pp. 279-280, published July 22, 2004
- ↑ 9/11 Commission Report Report of the National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Upon the United States, p. 295, published July 22, 2004
- ↑ 9/11 Commission Report Report of the National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Upon the United States, p. 300, published July 22, 2004
- ↑ 9/11 Commission Report Report of the National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Upon the United States, p. 305, published July 22, 2004
- ^ Summary of Findings About the NIST World Trade Center Disaster Investigation, NIST, June 30, 2011
- ↑ 9/11 Commission Report Report of the National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Upon the United States, p. 311, published July 22, 2004
- ↑ 8.4.2: Evacuation. (PDF) (No longer available online.) In: Final Report on the Collapse of the World Trade Center Towers. United States Department of Commerce , Technology Administration, National Institute of Standards and Technology , September 2005, pp. 188ff , archived from the original on April 24, 2011 ; accessed on April 24, 2011 .
- ↑ 9/11 Commission Report Report of the National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Upon the United States, p. 317, published July 22, 2004
- ^ The World Trade Center Recovery Operation at Fresh Kills The New York State Museum, 2003
- ↑ Isabell Chapman A landfill in their backyard CNN, September 11, 2020
- ↑ Claudia Pieper: 9/11 - The Suffering of Helpers 15 Years After the Terror, Ärztezeitung, September 9, 2016
- ↑ Obama blesses billions in aid for 9/11 rescuers. In: Spiegel Online . January 3, 2011, accessed December 23, 2014 .
- ↑ Doug Stanglin 343 NYC firefighters died on 9/11. Since then, 200 have died from Ground Zero-related illnesses USA Today, July 19, 2019
- ^ About 9/11 University of Notre Dame American Studies
- ↑ Integrated United States Security Database (IUSSD): Data on the Terrorist Attacks in the United States Homeland, 1970 to 2011 - Final Report to Resilient Systems Division, DHS Science and Technology Directorate National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism, p December 26, 2012
- ↑ Hans Joachim Schneider: International Handbook of Criminology: Fundamentals of Criminology, Volume 1. 1. Edition, De Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 3-89949-130-0 , p. 802.
- ↑ Bradley Jontzen (April 24, 2011): Tributes, September 11, Tributes and Memorials to the Victims, Families and Heroes of September 11, 2001.
- ↑ a b Reuters, September 11, 2007: FACTBOX: Attacks of Sept. 11, 2001
- ↑ Gudrun Dometeit Wie Puppen vom Himmel Focus Magazin, No. 38, September 15, 2004
- ^ The victims on 9/11 Boston Globe, September 11, 2001
- ↑ Tom Junod: The Falling Man - 9/11 Suicide Photograph. In: Esquire , September 8, 2009.
- ↑ New York City identifies 1645th victim of September 11 attacks at World Trade Center ABC News New York, October 19, 2019.
- ↑ Ground Zero Forensic Work Ends. CBS News, Feb. 23, 2005; Anemona Hartocollis: First New Identification of 9/11 Victim Since 2009. In: NY Times, May 12, 2011.
- ↑ Drew Angerer How Many People Died in 9/11 Attacks? History.com, August 25, 2018
- ↑ September 11th Victim Compensation Fund: Compensation of Claims Federal Register, Issue 83, No. 192, October 3, 2018
- ^ Martin Z. Braun: New York's Post-9/11 Liberty Bond Program Gets Mixed Grades. In: bloomberg.com. September 11, 2006, accessed February 28, 2015 .
- ↑ Robbyn Swan, Anthony Summers: The Eleventh Day. The Full Story of 9/11 and Osama bin Laden. Random House Publishing, 2011, ISBN 0-345-53125-6 , p. 165 f. Limited preview in Google Book Search
- ↑ Confessional video by Osama Bin Laden: New translations and interpretations. In: uepo - the translator portal. December 22, 2001, accessed August 28, 2021 .
- ↑ New quotes from Bin Laden video decrypted ( Memento from November 22, 2011 in the Internet Archive ), Netzeitung, December 21, 2001
- ↑ Bin Laden's "confession video" is said to be incorrectly translated. In: Spiegel Online . December 20, 2001, accessed December 23, 2014 .
- ↑ Christopher C. Yang and others: Intelligent Systems for Security Informatics. Elsevier Science, 2013, ISBN 0-12-405902-3 , p. 130 ; Oktay F. Tanrisever: Afghanistan and Central Asia. Ios Press, 2013, ISBN 1-61499-178-2 , p. 193 .
- ↑ Eric Lichtblau, Josh Meyer: Details of Sept. 11 Plot Elude US Investigators. Los Angeles Times, April 30, 2002
- ↑ Robbyn Swan, Anthony Summers: The Eleventh Day. The Full Story of 9/11 and Osama bin Laden. 2011, p. 286. Limited preview in Google Book search
- ↑ Bernd Greiner: 9/11: The day, the fear, the consequences. Munich 2011, p. 40.
-
↑ Peter Bergen : The Rise and Fall of Osama bin Laden . Simon & Schuster, New York 2021, ISBN 978-1-982170-52-3 , pp. 185 (English, limited preview in Google Book Search). Full transcript of bin Ladin's speech. In: Al Jazeera , November 1, 2004 (English).
- ↑ Robbyn Swan, Anthony Summers: The Eleventh Day. The Full Story of 9/11 and Osama bin Laden. 2011, limited preview in Google Book Search
- ↑ Peter Phillips and others: Censored 2008: The Top 25 Censored Stories of 2006-074. Seven Stories Press, 2011, p. 93 f. Enver Masud: FBI: Bin Laden Not Wanted for 9/11? The Milli Gazette, June 11, 2006
- ↑ September 13, 2001: FBI publication on the 19 suspects ( Memento of March 5, 2008 in the Internet Archive ); see also 9/11 Commission Report pp. 2-4 (PDF; 7.2 MB)
- ↑ Official: 15 of 19 Sept. 11 hijackers were Saudi , USA today, February 6, 2002
- ↑ CNN Editorial Research September 11 Hijackers Fast Facts CNN, August 20, 2020
- ↑ The FBI Releases 19 Photographs of Individuals Believed to be the Hijackers of the Four Airliners that Crashed on September 11, 2001 (Washington, DC September 27, 2001)
- ↑ Chronology of the Hijackers on 9/11, part 1
- ↑ Bernd Greiner: 9/11. The day, the fear, the consequences. Munich 2011, pp. 32–37.
- ↑ Sean D. Hamill: 7 Years Later, 9/11 Hijackers' Remains Are in Limbo. The New York Times, September 20, 2008; Riva Kastoryano, Cynthia Schoch: Burying Jihadis: Bodies Between State, Territory, and Identity. Oxford University Press, 2018, ISBN 0-19-093486-7 , p. 104
- ↑ Information letter from the US government agency National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Entry of the 9/11 Hijackers into the United States: Staff Statement No. 1 page 1/2
- ^ FBI publication of a letter
- ↑ Bernd Greiner: 9/11. The day, the fear, the consequences. Munich 2011, p. 33.
- ↑ Cordula Meyer, Dominik Cziesche: "Atta was so soft." Spiegel Online , October 6, 2001
- ^ Dale L. Watson, Executive Assistant Director, Counterterrorism / Counterintelligence Division, FBI ( February 17, 2007 memento on the Internet Archive ). Tested before the Senate Select Committee on Intelligence on February 6, 2002; see Dale L. Watson ; FBI - Facts and Figures on "Counterterrorism", 2003 ( Memento from July 9, 2008 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ Federal Bureau of Investigation - FBI, website ( March 11, 2008 memento in the Internet Archive ); FBI's 9/11 Team Still Hard at Work , Washington Post, June 14, 2004
- ↑ The secret service saw Atta as a threat as early as 2000 Süddeutsche Zeitung, December 6, 2008
- ↑ Marc-Oliver Rehrmann 9/11: Where the "death pilots" of the terrorist attacks were at home, NDR, September 9, 2011
- ↑ Klaus Brinkbäumer Dear, nice and never angry Der Spiegel, issue 39/2001
- ↑ FBI timeline of the kidnappers, page 36
- ↑ Marc-Oliver Rehrmann 9/11: Where the "death pilots" of the terrorist attacks were at home, NDR, September 9, 2011
- ^ 9/11 Commission Report: THE HAMBURG CONTINGENT The 9/11 Commission Report, page 165
- ↑ Marc Pitzke: US torture report "Nashiri responds well to harsh treatment" , Spiegel Online, December 10, 2014
- ^ 9/11 Commission Report: THE HAMBURG CONTINGENT The 9/11 Commission Report, page 165
- ↑ Lawrence Wright: Death Will Find You. Al-Qaeda and the road to September 11th . Deutsche Verlags-Anstalt, Munich 2007, ISBN 978-3-421-04303-0 , p. 383–386 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ^ 9/11 Commission Report: THE HAMBURG CONTINGENT The 9/11 Commission Report, pp. 165-167
- ↑ FBI timeline of the kidnappers, page 122
- ↑ Bernd Greiner: 9/11. The day, the fear, the consequences. Munich 2011, pp. 40–45.
- ↑ National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Upon the United States: 7. The Attack looms
- ↑ 9/11 Commission Report: THE HAMBURG CONTINGENT , The 9/11 Commission Report, p. 166 (PDF, English).
- ↑ Stefan Aust, Dirk Laabs: This is how Saudi agents helped the 9/11 terrorists Die Welt (online), April 16, 2016
- ↑ Jim Sciutto, Ryan Browne, Deirdre Walsh: Congress releases secret '28 pages' on alleged Saudi 9/11 ties. CNN, July 16, 2016; Mark Mazzetti: In 9/11 Document, View of a Saudi Effort to Thwart US Action on Al Qaeda. New York Times, July 15, 2016; Erica Werner: Congress releases once-classified pages of 9/11 report. Boston Globe, July 15, 2016
- ↑ Jim Sciutto: New allegations of Saudi involvement in 9/11 CNN, February 4, 2015
- ^ Pre-9/11 Ties Haunt Saudis as New Accusations Surface New York Times, February 15, 2015
- ↑ Daniel Pipes in an interview with Ramon Schack: The Islamic debate in the West is primitive Neue Zürcher Zeitung, November 10, 2010
- ↑ Caleb Hannan: One Man's Quest to Prove Saudi Arabia Bankrolled 9/11. Politico, April 7, 2017; UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT SOUTHERN DISTRICT OF NEW YORK: Case 1: 17-cv-02003 Document 1 Filed 03/20/17 ( Indictment , PDF)
- ↑ UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT SOUTHERN DISTRICT OF NEW YORK: Case 1: 17-cv-02003 Document 1 Filed 03/20/17 ( Indictment , PDF)
- ↑ Jonathan Stempel Saudi Arabia must face US lawsuits over Sept. 11 attacks , Reuters, March 28, 2018
- ↑ 'The President Will Never Forget 9/11'. In: Spiegel Online . September 15, 2008, accessed December 23, 2014 (interview with Andrew Card ).
- ↑ a b Garrett M. Graff: 'We're the Only Plane in the Sky' In: Politico , September 9, 2016 (English).
- ↑ Justus Bender: Mr. President, it's going to be an easy day. In: Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung . September 5, 2011, accessed December 23, 2014 .
- ↑ amnesty.org: The backlash - human rights at risk throughout the world ( Memento of October 14, 2007 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Dana Milbank, Emily Wax: Bush Visits Mosque to Forestall Hate Crimes , Washington Post, September 18, 2001
- ↑ September 11, 2001: International Responses: Listing by Country , Patriot Resource
- ↑ Helsinki, September 11, 2001: Statement by Federal President Johannes Rau at the reception in honor of the President of the Republic of Finland in the Swedish Theater
- ↑ Rau: "We have to fight terrorism". In: welt.de . September 15, 2001, accessed December 23, 2014 .
- ↑ Ralf Beste, Ulrike Demmer, Christoph Hickmann, Marc Hujer, Christoph Schwennicke, Holger Stark, Rainer Staudhammer, Klaus Wiegrefe : A German War . In: Der Spiegel . No. 36 , 2011 ( online - September 5, 2011 ).
- ↑ Paul Kelso: US anthem played at changing of the guard. In: theguardian.com. September 14, 2001, accessed November 9, 2014 .
- ↑ UN Security Council Condemns 'In Strongest Terms' Terrorist Attacks On United States , United Nations Press Release, September 12, 2001. Retrieved June 7, 2008.
- ↑ NATO press release 124/2001 of September 12, 2001
- ^ Address to a Joint Session of Congress and the American People , Address by George Bush to Congress on September 20, 2001. Retrieved June 7, 2008.
- ↑ Ahmed Rashid: Descent into Chaos. The US and the Disaster in Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Central Asia . Penguin Books, New York 2009, ISBN 978-0-14-311557-1 , pp. 77 (English, limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Bernd Greiner: 9/11. The day, the fear, the consequences. Munich 2011, pp. 89–90.
- ↑ Peter L. Bergen : The Hunt for Osama Bin Laden. A story of disclosure . Deutsche Verlags-Anstalt, Munich 2012, ISBN 978-3-421-04551-5 , pp. 73–74 (English: Manhunt. The Ten-Year Search for Bin Laden - from 9/11 to Abbottabad . New York 2012. Translated by Helmut Dierlamm, Norbert Juraschitz, Thomas Pfeiffer, Heike Schlatterer and Karin Schuler).
- ↑ Bundestag printed paper 14/7296 of November 7, 2001; Bundestag printed paper 14/7913 of December 21, 2001
- ↑ George Leaman: Iraq, American Empire, and the War on Terrorism. In: Marlene and Thomas Rockmore: The Philosophical Challenge of September 11. John Wiley & Sons, 2004, p. 5. limited preview in the Google book search
- ↑ Jochen Hippler: The Consequences of September 11, 2001 for International Relations ( From Politics and Contemporary History 3–4, 2004)
- ↑ Jens von Scherpenberg: Imperial Overstretch? The US and the rising costs of the "war on terror" . In: swp-berlin.org , September 2003; Manfred Berg : September 11, 2001 - a historic turning point? . In: Zeithistorische Forschungen / Studies in Contemporary History , online edition, 8 (2011), issue 3, p. 472; Accessed both times on September 23, 2019.
- ^ Franz-Josef Meiers: The Return of the Imperial Presidency? The President, Congress, and US Foreign Policy after September 11, 2001 . In: Amerikastudien / American Studies 55, No. 2 (2010), pp. 249-286.
- ^ "Letter - Continuation of the National Emergency with Respect to Certain Terrorist Attacks". In: Whitehouse.gov. August 30, 2016, accessed September 4, 2016 .
- ↑ Bernd Greiner: 9/11. The day, the fear, the consequences. Munich 2011, p. 163 f. And 228–235.
- ↑ Bernd Greiner: 9/11. The day, the fear, the consequences. Munich 2011, p. 233.
- ^ Annual Report 2003: United States of America , Amnesty.de
- ↑ ACLU, May 28, 2002: Federal Court to Hear Arguments May 29 in Battle Over Government Secrecy About Sept. 11 Detainees ( Memento of November 16, 2005 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ "9/11" -Terroristen come to New York to court. In: welt.de . November 14, 2009, accessed December 23, 2014 .
- ↑ Historic Port Authority Agreement to privatize World Trade Center Press release from New York and New Jersey Port Authority signing the lease, July 24, 2001
- ↑ Unlocking Land Values to Finance Urban Infrastructure George E. Peterson, The World Bank, 2009, p. 53
- ^ WTC tenant Silverstein: A dream of a skyscraper Der Spiegel, August 29, 2011
- ↑ WTC leased to Silverstein Westfield, CNN, September 12, 2001
- ^ Silverstein Will Get Most of His Cash Back In Trade Center Deal New York Times, November 23, 2003
- ↑ Developer Sues to Win $ 12.3 Billion in 9/11 Attack New York Times, March 27, 2008
- ^ Verdict in 9/11 insurance battle CNN, April 30, 2004
- ^ Silverstein and the eternal construction site manager-magazin, October 19, 2006
- ^ Even as Foundation Is Set, a New 7 World Trade Center Faces Barriers New York Times, January 13, 2003
- ↑ Real estate company is suing airlines over 9/11. In: welt.de . September 5, 2012, accessed December 23, 2014 .
- ↑ Jonathan Stempel: World Trade Center developer settles with United, American over 9/11 , at businessinsider.com
- ↑ Jim Sciutto, Ryan Browne, Deirdre Walsh: Congress releases secret '28 pages' on alleged Saudi 9/11 ties. CNN, July 16, 2016; Mark Mazzetti: In 9/11 Document, View of a Saudi Effort to Thwart US Action on Al Qaeda. New York Times, July 15, 2016; Erica Werner: Congress releases once-classified pages of 9/11 report. Boston Globe, July 15, 2016
- ↑ Caleb Hannan: One Man's Quest to Prove Saudi Arabia Bankrolled 9/11. Politico, April 7, 2017; UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT SOUTHERN DISTRICT OF NEW YORK: Case 1: 17-cv-02003 Document 1 Filed 03/20/17 ( Indictment , PDF)
- ↑ US judge: Iran must pay $ 6bn to victims of 9/11 attacks , at aljazeera.com
- ^ Chronicle: Black stock exchange days since 1929 . spiegel.de , January 21, 2008, accessed on December 23, 2019.
- ↑ Norbert Kuls: Wall Street does not come to rest. In: FAZ.net . September 11, 2011, accessed December 23, 2014 .
- ↑ Manfred Berg: September 11, 2001 - a historic turning point? . In: Zeithistorische Forschungen / Studies in Contemporary History, online edition, 8 (2011), issue 3, p. 470; Jana Puglierin and Christoph Schwarz: The end of the American superpower after “9/11”? In: From Politics and Contemporary History 27 (2011); the information on national debt according to Bruno Urmersbach: National debt of the USA until 2018 , statista.com, August 9, 2019, accessed on December 23, 2019.
- ↑ The FBI's 9/11 Role by the Numbers Information from the FBI
- ↑ Federal Bureau of Investigation - FBI History ( Memento October 3, 2006 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Federal Bureau of Investigation - Facts and Figures 2003 ( Memento of August 16, 2006 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ According to a statement by Susan Ginsburg, a contributor to the 9/11 Commission Report , on January 26, 2004 during a public hearing
- ^ Joint Inquiry into Intelligence Community Activities before and after the Terrorist Attacks of September 11, 2001 (final report 2002)
- ↑ McKinsey and Co., report on the operation on September 11, 2001 ( Memento from June 8, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF)
- ↑ Thomas H. Kean, Lee H. Hamilton (Eds.): The 9/11 Commission Report. WW Norton & Co, New York 2004, ISBN 0-393-32671-3 ( full text online, PDF; 7.2 MB )
- ^ 9/11 Commission controversy. In: NBC News Investigations. January 30, 2008, accessed August 29, 2021 .
- ↑ Marc Pitzke: US torture report "Nashiri responds well to harsh treatment" , Spiegel Online, December 10, 2014
- ^ The White House Mole. In: Washington Post. February 4, 2008, accessed August 29, 2021 .
- ^ 9/11 Commission controversy. In: NBC News Investigations. January 30, 2008, accessed August 29, 2021 .
- ^ The White House Mole. In: Washington Post. February 4, 2008, accessed August 29, 2021 .
- ↑ FEMA, May 2002: World Trade Center Building Performance Study ( Memento of September 18, 2010 on WebCite )
- ↑ NIST study concept 2002
- ^ NIST WTC Investigation website National Institute of Standards and Technology, 2002
- ↑ NIST: Final Reports of the Federal Building and Fire Investigation of the World Trade Center Disaster (Parts NCSTAR 1-1 to 1-8)
- ^ NIST: Investigation of the World Trade Center Disaster FAQ
- ↑ Final Report on the Collapse of World Trade Center Building 7 ( Memento of September 28, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF, 7.5 MB)
- ↑ Examples: Zdeněk P. Bažant, Jia-Liang Le, Frank R. Greening, David B. Benson (May 2007; revised March 2008): What Did and Did not Cause Collapse of WTC Twin Towers in New York (PDF; 728 kB ); Zdeněk P. Bažant, Yong Zhou: Why Did the World Trade Center Collapse? - Simple Analysis. (PDF; 146 kB); Oral Buyukozturk, Franz-Josef Ulm (Massachusetts Institute of Technology): Materials and structures (PDF; 1.41 MB)
- ↑ Markus Becker: Simulation shows the end of the World Trade Center. In: Spiegel Online . June 18, 2007, accessed December 23, 2014 .
- ↑ Nick Hopkins: At Yankee Stadium, a tearful farewell to victims The Guardian, September 24, 2001
-
↑ Reporting of the Tagesschau 2008, ard ( Memento from October 22, 2008 in the Internet Archive )
* The commemoration in the USA 2009 , NZZ from September 12, 2009 - ^ New York Times, 'Tribute in Light' Will Keep Shining, This Year and the Next , September 10, 2010, accessed May 17, 2012.
- ↑ Michael Arad, Peter Walker: Reflecting Absence (English; undated). In: World Trade Center Site Memorial Competition. Retrieved May 20, 2010.
- ↑ Sharon Otterman: Battered and Scarred, 'Sphere' Returns to 9/11 Site New York Times, November 29, 2017
- ^ The Sphere, a Symbol of Resilience After 9/11, Is Unveiled at Liberty Park Official homepage of the 9/11 Memorial
- ↑ Michael Young: First Marble Panels Installed on Santiago Calatrava's St. Nicholas Greek Orthodox Church in the Financial District New York Yimby, February 17, 2021
- ↑ David Bjorkgren St. Nicholas Greek Orthodox Church and National Shrine Now on Solid Ground as Construction Restarts Hellenic News of America, August 11, 2018
- ↑ Lowermanhattan.info (December 2013): 130 Liberty Street ( Memento from December 11, 2013 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ BMCC: Fiterman Hall timeline. (No longer available online.) In: BMCC. cuny.edu, August 27, 2012, archived from the original on April 23, 2012 ; accessed on February 8, 2015 .
- ↑ Kate Hinds: Photos That Will Make You Want To Ride The PATH Train. In: WNYC Transportation Nation Blog. February 25, 2014, accessed February 27, 2014 .
- ↑ “One of those moments in which history splits, and we define the world as 'before' and 'after'”. The War Against America; An Unfathomable Attack . New York Times of September 12, 2001, quoted by Manfred Berg: September 11, 2001 - a historic turning point? . In: Zeithistorische Forschungen / Studies in Contemporary History , online edition, 8 (2011), issue 3, p. 464.
- ↑ Sandra Poppe: Introduction. In: the same, Thorsten Schüller and Sascha Seiler (eds.): 9/11 as a cultural turning point. Representations of September 11, 2001 in cultural discourses, literature and visual media . transcript, Bielefeld 2009, ISBN 978-3-8394-1016-5 , pp. 9–17, here p. 9 (accessed via De Gruyter Online).
- ↑ History and September 11: A Special Issue (= The Journal of American History 89, No. 2, [2002]); Mary L. Dudziak (Ed.): September 11 in History. A watershed moment? Duke University Press, Durham 2003.
- ^ Noam Chomsky: Hegemony or Survival: America's Quest for Global Dominance. Metropolitan Books, New York 2003.
- ↑ Michael Butter, Birte Christ and Patrick Keller: 9/11. Not a day that changed the world . Schöningh, Paderborn / Munich / Vienna / Zurich 2011.
- ↑ Martin Sabrow: Caesuras in Contemporary History , Version: 1.0. In: Docupedia Zeitgeschichte , June 3, 2013, accessed on December 23, 2019.
- ^ Samuel Salzborn: Global anti-Semitism. A search for traces in the abyss of modernity. Beltz Juventa, Weinheim 2018, p. 28 (here the quote).
- ↑ Manfred Berg: September 11, 2001 - a historic turning point? . In: Zeithistorische Forschungen / Studies in Contemporary History , online edition, 8 (2011), issue 3, pp. 468–474, the quotation on p. 472 f.
- ↑ International survey: Who is to blame for 9/11? Süddeutsche Zeitung, May 17, 2010
- ^ Christian Speicher Invitation to speculate about 9/11 Neue Zürcher Zeitung, September 16, 2016
- ↑ International survey: Who is to blame for 9/11? Süddeutsche Zeitung, May 17, 2010
- ↑ Melissa Etheridge: Lucky. February 23, 2004, accessed February 27, 2021 (American English).
- ↑ Robert Gulya talks about his collaboration with Johanna Beisteiner and the guitar concerto that he wrote for her. Video, Gramy Records , 2010. (Hungarian with English subtitles) Interview with Robert Gulya on YouTube
- ↑ Stockhausen interview during the press conference (MP3; 1.6 MB) on September 16, 2001 in Hamburg. Danskmusiktidsskrift.dk ( Memento from August 29, 2006 in the Internet Archive ).
- ↑ The transcription of the entire press conference: “Huuuh!” The press conference on September 16, 2001 in the Senate room of the Hotel Atlantic in Hamburg . ( Memento of February 5, 2018 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF; 74 kB) In: MusikTexte No. 91 (2002), pp. 69–77, here p. 77.
- ^ Message from Professor Karlheinz Stockhausen, September 19, 2001. Stockhausen.org ( Memento of September 24, 2001 in the Internet Archive ).
- ^ The 164 songs that were banned from American radio after 9/11. Kerrang , September 10, 2021, accessed September 11, 2021 .
- ↑ IMDb: Films for September 11, 2001 , accessed on September 16, 2013
- ↑ World premiere of Rainald Goetz '"Reich des Todes" in Hamburg by dpa on the homepage of the daily Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung at www.faz.net ( Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung ), September 12, 2020, accessed on September 15, 2020
- ↑ Culture time . TV cultural broadcast, September 14, 2020, 36 min. Moderation: Peter Schneeberger . A production by 3sat
- ↑ Culture time . TV cultural program, September 15, 2020, 36 min. Moderation: Peter Schneeberger . Contains an interview with author Nell Zink. A production by 3sat
- ↑ On Gerhard Richter's picture “September” , Kölner Stadtanzeiger, June 4, 2008
- ↑ Giselinde Kuipers: "Where Was King Kong When We Needed Him?" Public Discourse, Digital Disaster Jokes, and the Functions of Laughter after 9/11 . In: Wiley (Ed.): The Journal of American Culture . 28, No. 1, March 2005, pp. 70-84. doi : 10.1111 / j.1542-734X.2005.00155.x .
- ↑ Bill Ellis: A Model for Collecting and Interpreting World Trade Center Disaster Jokes. Archived from the original on September 6, 2013. In: NewFolk (Ed.): New Directions in Folklore . No. 5, October 2001. Retrieved May 26, 2019.
- ↑ Veiled humor Shazia Mirza was supposed to be a teacher and marry a nice Muslim man - but she prefers the loneliness of the mostly-male comedy circuit. Why? By Geraldine Bedell, The Observer, April 20, 2003
- ↑ Wiglaf Droste: From Beckenbauer to Atta - Another eleventh September is possible. Junge Welt from September 10, 2011, accessed on September 11, 2018. online , category focus, p. 3. Complete article requires online subscription.