United States National Debt
The national debt of the United States refers to the total amount of all debt of the United States at the federal level, that is from the federal government owed total claims of the lending creditors. The national debt has grown steadily since the 1980s except for a brief period in the late 1990s, in the 2000s especially, by the conditions in Iraq and Afghanistan wars , the consequences and the global financial crisis from 2007 onwards . In November 2017 total public debt was 20.5 trillion US dollars , or 106% of gross domestic product .
history
Historically, the national debt of the United States almost always rose as a result of the war. Even when it was founded, the federation had debts from the previous American War of Independence and from the time of the articles of confederation . The first documented debt level on January 1, 1791 was $ 75,463,476.52. From 1796 to 1811 there were 14 budget surpluses and two budget deficits. The first major increase in national debt was to finance the British-American War in 1812. In 18 of the 20 years after the war, there were budget surpluses, so that 99.97% of the debt could be paid off.
The second major increase in national debt occurred in connection with the war of civil secession . While the debt level was still at 65 million US dollars in 1860, it exceeded the billion mark in 1863 and reached 2.7 billion US dollars after the end of the war. In the following 47 years, there were budget surpluses in 36 years and budget deficits in 11 years, which meant that around 55% of the national debt could be paid off. With the American participation in World War I , the national debt rose again and reached 25.5 billion US dollars by the end of the war. In each of the following eleven years there were budget surpluses, which reduced debt levels by 36%.
For the first time not due to the war, the national debt rose in the wake of the social reforms known as the New Deal , in particular the introduction of a pension and unemployment insurance in 1936 to combat the Great Depression that occurred in 1929 . They were closely followed by the entry of the United States into World War II in 1941. While the debt level in 1933 was around 20 billion US dollars (about 20% of the gross domestic product), it reached 33.7 billion US dollars in 1936 ( about 40% of the gross domestic product). In the years that followed, the debt level increased many times over until it reached $ 260 billion (about 94% of gross domestic product) in 1950.
During the era of the Bretton Woods system from 1944 to 1973, United States real debt steadily declined. The breaking of the dollar's nominal gold peg in August 1971 led to the Nixon shock and floating exchange rates .
By the beginning of the 1980s, the national debt tripled in step with inflation . During presidents Ronald Reagan and George Bush's terms in office, debt quadrupled with lower taxes, to $ 5.39 trillion in 1992. By the turn of the millennium, national debt rose again by 19% to 6.42 trillion US dollars. In relation to economic power, however, it fell in the course of the Reaganomics from 64% to 56.4% of gross domestic product, as there was a long period of growth in the United States in the 1990s. However, between 1960 and 1999 there was only a budget surplus in 1969.
In its budget projections in 2001, the Congressional Budget Office , the budgetary authority of Congress , projected budget surpluses of US $ 850 billion annually to persist through at least 2012. This means that the total debt could have been completely paid off after about eight years. In reality, however, budget deficits averaged $ 1.2 trillion a year through 2009. According to analyzes by the New York Times , this discrepancy can be attributed to the significantly worse than expected economic performance and the associated tax shortfalls (37%), the measures decided under President Bush (33%), including in particular tax cuts or an expansion of drug insurance as part of Medicare , but also the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq , the measures that were extended under President Obama (20%) and his new measures (10%). In addition, after the US real estate market bubble, the financial crisis from 2007 onwards led to a series of fiscal policy measures to prevent the financial sector and parts of American industry from collapsing. National debt rose 67% to US $ 10.71 trillion from 2001 to 2009 under the presidency of George W. Bush , accounting for about 84.2% of economic output.
In 2010, under President Barack Obama , further measures were taken to combat the ongoing economic downturn, so that national debt rose. In February 2011, the then legal upper limit of 14.2 trillion US dollars (around 96.9% of gross domestic product) threatened to be exceeded significantly. The legal limit was then set at $ 16.39 trillion. The US reached this level at the end of 2012 (around 102% of GDP in 2012). At the beginning of February 2013, Obama signed the law to suspend the debt ceiling until May 19, 2013. Debts borrowed up to this date will then be offset against the increase in the statutory ceiling, unless the deadline is extended indefinitely. This enables the government to borrow an unlimited amount, whereby the acceptance of the new upper debt limit, in order to avert national bankruptcy, is mandatory, at least in the amount of the new debt when the deadline expires.
President Barack Obama then reduced the annual public deficit back to $ 585 billion by the end of his second term in 2016.
Under President Donald Trump , the national debt rose and reached a national deficit of 984 billion dollars in October 2019 for the fiscal year 2018/19 compared to 779 billion dollars in the previous fiscal year. The US Treasury Department said spending on social affairs, defense and debt servicing increased, among other things. Experts blame, among other things, the after-effects of US President Donald Trump's tax cuts and higher military spending for the rise in the deficit. According to the US Treasury Department, national debt reached around $ 16.8 trillion in October 2019.
Calculation and evaluation
Third party loans and internal debts
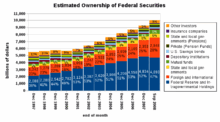
The official United States public debt figures consist of two numbers: debt held by third parties and debt incurred within the federal government between its institutions, such as government bonds, held as investments in government pension surpluses become. In February 2011, of the total debt of $ 14.2 trillion, approximately $ 9.6 trillion was held by third parties. The remainder, $ 4.6 trillion, went to federal institutions.
Since 1957, the amount of debt held internally has increased steadily. The largest share of this is due to surpluses accumulated over decades from social security, which are used for other purposes. To compensate for this withdrawal from the insurance systems, they will be credited with federal debt securities, which like all other debts must be financed from future budget funds.
The national debt is also divided into marketable and non-marketable debt securities. In February 2011, the total of all marketable debt securities was $ 9 trillion, compared to non-marketable debt securities of $ 5.2 trillion. Most of the marketable instruments are Treasury Treasury securities held by investors and other countries around the world. In particular, non-marketable debt includes state pension accounts, which were $ 2.5 trillion in 2010.
State mortgage lender liabilities
When looking at US national debt, the liabilities incurred by the state mortgage financiers Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac are traditionally not included. The background to this is that these two institutions were founded as autonomous and independent institutions, so their activities cannot be attributed to the federal government. As a result of the financial crisis, however, a political guarantee was issued for these liabilities, which is why they are now partially included. In 2008 they totaled about $ 5 trillion.
Private guarantees
One of the measures taken after the financial crisis from 2007 onwards was the issuing of payment guarantees for liabilities of private companies, banks and investment funds. The scope of these guarantees is not added to the national debt, regardless of the actual probability of default. However, direct investments in financial institutions, such as those incurred under the Troubled Asset Relief Program , are taken into account.
Future commitments
The federal government has committed itself to future payments under a number of social insurance schemes, including in particular pension payments to nearly all current American workers. In the pay-as-you-go system , payments due are financed from taxes collected in the same period. According to projections by the Government Accountability Office , a congressional investigative agency, these payments will exceed the revenue from the levies in the next 75 years and a subsidy from other budget funds will therefore be necessary.
The total value of these non-levy future obligations in 2009 was $ 45.8 trillion. This sum should have been made available to cover future payments through 2084 from capital and interest. Of that, $ 7.7 trillion would go to retirement and $ 38.2 trillion to health. If these obligations were added to the national debt, the total debt would be $ 62 trillion, or 4.4 times the gross domestic product.
Debt ceiling
Under the Constitution of 1787 , Congress has the authority to legislate for borrowing. Until the First World War, Congress decided on every single loan to be borrowed. In order to flexibly finance American participation in the war, the federal government was granted the right to independently decide on borrowing up to a specified limit. This approach was generalized in 1939 and 1941 by new legal regulations. Since then, the federal government has been able to decide on its own authority when to take out loans to finance expenses within the annual budget laws. As with World War I, however, there is a strict debt ceiling that can only be changed by law. The refusal by Congress to raise this limit in 2011 led to a political budget crisis . The debt ceiling in the fall of 2013 was US $ 16.7 trillion (EUR 12.3 trillion).
creditor
Federal bonds are held by a large number of people and institutions around the world. According to estimates by the Treasury Department, in September 2008 47% of the bonds were from federal institutions, led by the Federal Reserve Bank , 28% from foreign investors and other states, 5% from states and their subdivisions, 6% from investment funds, and 4% held by pension funds.
Most of the national debt held by foreign investors is accounted for by China , Japan , the United Kingdom , Brazil and Switzerland . China's share of the United States' total national debt was 7.9% in May 2011.
Web links
- Website of the Bureau of the Public Debt (English)
- Website of the Bowles-Simpson Commission to reduce the national debt (English)
- USdebtclock.org , detailed United States debt clock
- Debt clock for the national debt of the USA
Individual evidence
- ^ US National Debt Clock. USDebtclock, accessed November 20, 2017 .
- ↑ Summary of Receipts, Outlays, and Surpluses or Deficits (-): 1789–2013. ( MS Excel ; 27 kB) (No longer available online.) Government Accountability Office, archived from the original on February 19, 2011 ; accessed on July 24, 2011 (English). Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ America's Sea of Red Ink Was Years in the Making. In: New York Times. June 2, 2009, accessed July 24, 2011 .
- ↑ Handelsblatt.com: Almost a trillion minus: USA with highest budget deficit in seven years , accessed on October 26, 2019
- ↑ Handelsblatt.com: Almost a trillion minus: USA with highest budget deficit in seven years , accessed on October 26, 2019
- ↑ Spiegel.de: US Treasury Secretary Mnuchin reports the highest deficit in the US budget for seven years
- ↑ Treasury Department-Monthly Statement of the Public Debt of the United States-February 2011. (PDF; 36 kB) United States Treasury Department , February 28, 2011, accessed July 24, 2011 .
- ^ Social Security Trust Fund 2010 Report Summary. Social Security Administration , accessed July 24, 2011 .
- ↑ Paulson readies the 'bazooka'. (No longer available online.) CNN September 8, 2008, archived from the original March 14, 2012 ; accessed on July 24, 2011 (English). Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ The federal government's financial health: a citizen's guide to the 2008 financial report of the United States government. (PDF; 1.1 MB) Accessed July 24, 2011 (English).
- ↑ Obamacare plunges USA into budget crisis on Tagesanzeiger.ch
- ^ Ownership of Federal Securities. (No longer available online.) United States Department of the Treasury, June 30, 2011, formerly original ; accessed on July 24, 2011 (English). ( Page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Major Foreign Holders of Treasury Securities. United States Department of the Treasury, July 18, 2011, accessed July 24, 2011 .