History of Oceania
The history of Oceania began with the immigration of the first humans at least 40,000 years ago, who came from Southeast Asia to the edge of Oceania and landed in Australia. Except for New Guinea and a few neighboring Melanesian islands, Oceania itself remained unpopulated.
The actual settlement began around 1500-1300 BC. BC presumably from the Philippines and Taiwan . In the course of many centuries the immigrants reached one island after another and expanded the settlement area further and further east. Above all, the Polynesians embarked on impressive voyages of discovery from their core area, the island triangle Tonga - Fiji - Samoa . With their outrigger canoes they reached Hawaii , New Zealand and in the east of the Pacific to Easter Island .
The history of this pre-European colonization is difficult to research because the peoples of Oceania had no writing. Only a few oral traditions have survived into modern times, such as B. the settlement of New Zealand by Tama Te Kapua . Written records only existed with the European voyages of discovery from the 16th century.
16th Century
The spirit of discovery of the 16th century is decisive for numerous expeditions. The first focus is on exploring a western route across the Pacific to the rich trading centers of Asia. Later, mainly Spanish and Portuguese adventurers search for the hypothetical southern continent Terra Australis Incognita or hope to find legendary riches such as the mines of King Solomon. Due to inadequate navigation techniques, some of the island groups discovered, e.g. B. the Solomon Islands , can no longer be found and fell into oblivion. At the end of the 16th century, the Dutch began exploring Oceania too.
Since the visits by Europeans were still comparatively rare, the negative effects on the local population were still limited.
| Timeline - 16th century | |
|
|
17th century
Much is still undiscovered in the Pacific and, above all, the stories of those returning home from Paradise attract more and more seafarers. The motivation to travel to new worlds is great, but goes hand in hand with the greed for the pristine natural resources of the new world. Meanwhile, the church worries about the "mixing" with the heathen peoples, but is nevertheless interested in the salvation of the "savages". She reacts by publicly discrediting the fornication with the inhabitants and delegating missionaries to assist with the trips.
| Timeline - 17th century | |
|
|
18th century
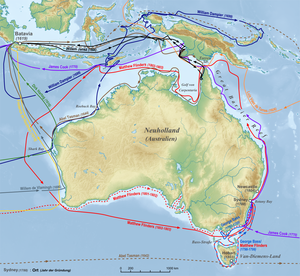
There is less and less available on undiscovered islands, but circumnavigators like Louis Antoine de Bougainville , James Cook and others still find some unexplored areas. In addition, some of the discoveries made in the 16th century were forgotten again. Some now set about mapping the islands using modern means.
| Timeline - 18th century | |
|
|
19th century
The mapping of the 18th century continues. The imperialism has started to be. Foreign island groups are increasingly being divided among the great powers. The colonization of the South Pacific is becoming a race. Above all Germans, British, French, Dutch and Americans fight over every island. The Spanish-American War leads at the end of the 19th century to a wild castling colonial territories.
| Timeline - 19th century | |
|
|
20th century
The First World War ended the German colonial power. German colonies around the world are divided among the victorious powers in the course of the creation of the League of Nations .
When the Second World War struck Oceania, it was the site of many naval battles between the United States of America and Japan. The war is carried as far as Australia through alliance politics. The imperial colonial power of Japan collapses shortly before its defeat.
At the beginning of the second half of the 20th century, the USA began to release their colonies into self-administration, subject to certain political intervention rights and military privileges - such as the construction and maintenance of military bases. Other island states later became independent from the British Commonwealth and the French overseas departments on similar terms . In rare cases the transition to self-employment occurs with bloodshed.
| Timeline - 20th Century | |
|
|




