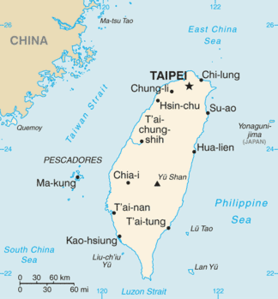
Taiwan (island)
| Taiwan 臺灣 |
|
|---|---|
| Satellite photo of Taiwan | |
| Waters | Pacific Ocean |
| Geographical location | 23 ° 43 ' N , 120 ° 51' E |
| length | 394 km |
| width | 144 km |
| surface | 35,801 km² |
| Highest elevation |
Yushan 3952 m |
| Residents | approx. 23,000,000 642 inhabitants / km² |
| main place | Taipei |
| Outline map of Taiwan | |
Taiwan ( Chinese 臺灣 / 台湾, Pinyin Táiwān , W.-G. T'ai-wan , Zhuyin ㄊ ㄞ ˊ ㄨ ㄢ , Taiwanese Tâi-oân , Hakka Thòi-vǎn ), in European languages also Formosa (福爾摩沙 / 福尔摩沙, called Fú'ěrmóshā ), is an island in the western Pacific off the mainland China , separated from it by the Formosa Strait . The island has formed the main part (99%) of the Republic of China in Taiwan since 1949. At the same time, Taiwan is being claimed by the People's Republic of China , which is reflected in the Taiwan conflict . The legal status of Taiwan is disputed.
Surname
The modern name "Taiwan" goes back to the name of an indigenous tribe in the southwest of the island, after which the Dutch colonial rulers named the area around Fort Zeelandia ( Tainan ), which they built between 1624 and 1634, as "Tayowan" or "Tayovan" in the 17th century “(There were different spellings) denoted. The name originally only referred to the city of Tainan, was later extended to the entire island and reproduced in Chinese as "Taiwan". The Chinese characters for “Taiwan” mean “Terrace Bay,” a meaning that is sometimes mistakenly given as an etymology.
The island is also known by the name Formosa, which was mainly used in the past and was given to it by Portuguese sailors (after "Ilha formosa", Portuguese for "beautiful island").
geography
The island of Taiwan extends over an area of 35,801 km² (for comparison: the area of Baden-Württemberg is 35,752 km²). The island is 394 km long, the maximum width is 144 km. It is separated from mainland China in the west by the Taiwan Strait, 130 km wide at its narrowest point , and in the south by the Strait of Luzon from the Philippines . The Philippines basin borders Taiwan to the east . In the northeast to include Taiwan Japan owned island chain of the Ryukyu Islands , which the flat East China Sea differentiate from the rest of the Pacific. To the southwest of the island lies the South China Sea , to the east lies the open Pacific.
Taiwan is shaped like a sweet potato on the map . That is why the descendants of newcomers from the mainland Chinese province of Fujian , who originally spoke Min Nan and who make up a large part of the population of Taiwan, also refer to themselves as the children of the sweet potato . Another interpretation of the shape is to imagine a whale in the sea.
Similar to Japan, Taiwan is often hit by earthquakes , which requires special safety standards for buildings and infrastructure .
climate
The Tropic of Cancer , which marks the climatic boundary between the tropics and the subtropics, runs through the island a little south of its highest peak at 3,952 meters, the Yushan . In the northern part there is a subtropical climate, the south is predominantly tropical , taking into account the climatic influence of the respective altitude . Due to the high mountains, there is also a moderate climate in the southern part of the altitude, which is mainly characterized by daily fluctuations.
In winter a strong monsoon blows from the northeast, in summer a strong monsoon from the southwest, which brings heavy rainfall with it. From May to October (most often in the months of July to September) the island is frequently hit by typhoons . In winter there is occasional snowfall at high altitudes - especially above 3,000 meters. One of the most famous places for this is Hehuanshan , located on a 3,275 meter high mountain pass in Nantou County . The average temperatures are 12 ° C in February and 25 ° C in July.
geomorphology
Around two thirds of the island consists of a mountain range, which is divided into five mountain ranges and extends from north to south over the eastern half of the island. These mountain ranges extend from north to south over about 330 km, the west-east extent averages 80 km. The west of the island is a flat, fertile and now heavily populated plain, traversed by valleys of the rivers rising in the mountains. To the east, this level rises to the central mountain range, which has over 200 peaks with a height of more than 3,000 meters. In the middle lies the Yushan , which at 3,952 m above sea level. d. M. highest point on the island. The valleys, which are mostly narrow in comparison to the Alps, are flanked by steeply rising slopes and have been made agriculturally usable by terracing up to an altitude of over 2,000 meters, especially for tea and fruit cultivation.
Along the central part of the east coast stretches the narrow, up to 1,682 m high Haian Coast Mountains , which are separated from the central mountains by the highly earthquake-prone Huatung Graben and slopes steeply towards the sea. Further north, the Central Mountains (Chungyang Mountains) extend directly to the Pacific. On this part of the east coast lies the Taroko Gorge , a river valley cut up to 600 meters deep into limestone cliffs, which is one of Taiwan's most important natural attractions. The mountain ranges further north, inland, are usually counted as a separate mountain range, the Xueshan Mountains (Snow Mountains ). A triangular coastal plain, the Yilan Plain, extends between the northern end of the Central Mountains and the Xueshan Mountains . The on the west side of the central mountains in the geographical center of the island at 762 m above sea level. d. The sun-moon lake is the largest inland body of water in Taiwan and, due to its altitude, is used as a storage power plant to generate hydroelectric energy.
geology
Taiwan lies on the western edge of the Pacific Ring of Fire , where the Philippine plate collides with the Eurasian plate . The resulting permanent friction is the cause of steep mountains, earthquakes and volcanoes. The volcanoes are all extinct today, but the magma herds are still active and the cause of numerous hot springs . Two small islands in the southeast - Lan Yu and Lü Dao - were originally volcanoes.
A major fault line runs straight along the east coast to the south, which is the cause of regular tremors. Every year there are several earthquakes of low strength (2-3) up to 8 on the Richter scale . Magnitude 8 was last reached in 1995 when a nighttime earthquake destroyed a school. Major damage in large parts of the island was caused by an earthquake with a magnitude of 7.6 on September 21, 1999 ( Jiji earthquake ), which killed over 2,400 people. The 2016 Kaohsiung earthquake killed 116 people. The risk of earthquakes of this magnitude reoccurring remains.
flora
Taiwan's flora includes 674 species of ferns , 4,596 species of bedspamers, and 34 species of nudibranchs . Due to the partly tropical and partly subtropical climate, Taiwan was an almost pure forest island until a few centuries ago. However, the forests were increasingly decimated during the Japanese rule , especially during the Second World War, as wood was used for military purposes. In addition, the wood was used for the construction of shrines and the associated burnt offerings during this time. Today, including the reforested areas, about 55 percent of Taiwan consists of forests and cultivated forests. Many originally endemic species have been introduced. In the mountains they usually consist of cypresses (especially false cypresses ), juniper , fir , pine , spruce , bamboo , azalea and deciduous trees . The camphor tree was almost wiped out by excessive deforestation, as camphor was Taiwan's main export in the past.
fauna
At least 120 species of mammals , 670 species of birds , 141 species of reptiles , 65 species of amphibians , 400 species of butterflies and 3100 species of fish have been described in Taiwan . Taiwan's fauna has been severely affected in the recent past. Industry has severely damaged the wetlands on the west coast that were once home to large numbers of birds and other animal species. Deforestation has had a negative impact on fauna. On the east coast, parts of the forests have been recultivated, which is causing the number of animals there to rise again.
Mammals such as the Taiwanese black bear (Ursus thibetanus formosus) , the sambar , the Chinese muntjak (Muntiacus reevesi) , the sika deer and the formosian gorale enjoy protection status. However, you can rarely find them in the wild. The only native primate species is the Formosa macaque . The Taiwan clouded leopard is believed to be extinct.
A great deal of attention is paid to birds in reforestation, so there is a great diversity of species, especially on the Penghu Islands. Some of them are the endemic species Swinhoe's Pheasant and Mikado pheasant that the corvids belonging Taiwan Blue Magpie ( Urocissa caerulea ), the white-tailed tropic bird , the snow egret , the spoonbill , the black-faced spoonbill ( Platalea minor ) and the Frigate .
The amphibian fauna is quite diverse with 65 species documented so far. These include several endangered species. Even the largest amphibian in the world, the Chinese giant salamander , is said to still occur in Taiwan - but this species is acutely threatened with extinction. Specifically, five tailed amphibians and 36 frog species belong to the animal world (three representatives of the angle-toothed newt family , one of the giant salamanders, one of the real salamanders , three toad species , one tree frog , four narrow-mouth frogs , 16 real frogs and twelve types of rowing frogs ). The cane toad is not originally an indigenous species, but was introduced by humans.
About 20 species of reptiles are endemic; that is, they only occur on Taiwan and some small offshore islands such as Lan Yu (Orchid Island). There are 16 venomous snake species in Taiwan, including six that can be potentially dangerous to humans: Taiwan cobra , multi- banded or Chinese krait , Siamese chain viper ( Daboia siamensis ), Chinese habu ( Trimeresurus mucrosquamatus ), Chinese pit viper ( Trimeresurus stejnegeri ) and Chinese nosed viper .
environmental pollution
Because of the high population density, many regions of Taiwan suffer from severe environmental pollution. The areas around Taipei and Tainan to Kaohsiung are worst affected. In the past, this pollution was particularly caused by cars, scooters and factories when lead was used without concern . This changed after the founding of an environmental agency, which has already achieved measurable effects in air quality.
The soil pollution is caused particularly by recent heavy industry. The increasing number of poisons in the soil is a steadily growing challenge and is directly damaging the economy with its high export of agricultural products. Water pollution is also a major problem. Around 90 percent of the wastewater is discharged untreated into rivers and the sea. It is estimated that cleaning the rivers would cost billions of dollars.
resources

55% of the land mass is covered by forests (mainly in the mountains), the agricultural area occupies 24%, another 5% is used as pasture land and 1% for permanent crops.
During Taiwan's industrialization, mineral resources such as coal, gold and marble, as well as wildlife, became scarce. Remaining forest stands were placed under nature protection and expanded through afforestation.
Agriculture
The Campherölgewinnung and sugar from sugar cane were the most important cash crops since the 19th century to the first half of the 20th century.
The main exports are fruits, rice, fish and tea. Since Taiwan's accession to the World Trade Organization in 2001, many agricultural products have been imported, so local agriculture has focused on specific products such as bananas , guavas , lychee and Java apples .
Water and energy
The water quality is average, but the government recommends boiling water from the tap. The lime content is an average of 10 ° dH (medium hard).
In 2019, 46 (11) percent of electricity was generated from coal, 11 (79) percent nuclear, 33 (23) percent from natural gas, 2 (1) percent from oil, 1 (17) percent from hydropower and 5 (6) Percent generated from renewable resources. Taiwan owned three nuclear power plants in 2019.
Oil and gas for transportation and power generation must be imported, making Taiwan's economy dependent on cyclical fluctuations in the energy market. In the meantime, some wind power plants have already been installed by German and American companies, and solar energy is also becoming more and more interesting for Taiwanese companies, especially since the technology of renewable energies is a possible export product for the island.
The government of Taiwan wants to establish a binding policy to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from Taiwan in the near future. According to the first information from the Deputy Prime Minister Qiu Yiren, the CO 2 emissions level of 2000 should be reached by 2025 . In 2000 Taiwan emitted 221 million tons of CO 2 ; in 2005, these emissions had increased by 25 percent to 276 million tons.
story
Early history
The first traces of settlement date from the Neolithic Age (around 4000 BC), another wave of settlements from mainland China can be traced back to around 2500 BC. Prove. This period was characterized by agriculture and a megalithic culture with erect large stones and graves made of stone boxes.
During the first half of the 1st millennium of our era, the indigenous cultures on the Chinese mainland and the islands off this area offered a culturally and linguistically similar picture (see Austronesian ). However, until the 17th century, there were little cultural ties between Taiwan and China. The indigenous peoples of Taiwan cultivated trade relations both with China and towards the south, e.g. B. with the Philippines .
During the Sui dynasty , there is said to have been the first Chinese expedition to Taiwan in 608. In the first Chinese representation of Taiwan published at the beginning of the 18th century (臺灣 府 志 / 台湾 府 志, Táiwānfǔ zhì - "Description of the district of Taiwan"), a trip by Admiral Zheng He in the 15th century is mentioned as the first expedition is not proven beyond doubt.
European powers
In 1583, the Portuguese were the first Europeans to reach the island and named it Ilha Formosa ("Beautiful Island"). In 1624 Dutch seafarers and the Dutch East India Company occupied the south of the island and in 1626 the Spaniards established branches at Keelung and Tanshui .
Until the beginning of the 17th century, the island was, apart from a small number of Chinese settlers, almost exclusively inhabited by Austronesian indigenous peoples . Then Chinese settlers immigrated from the mainland in several waves of immigration . Their descendants now make up the majority population of Taiwan. The indigenous people in the western plains were largely absorbed by the immigrant Han population, only in inaccessible mountain regions were some indigenous peoples able to maintain their independence into the early 20th century.
The first major wave of Chinese immigration goes back to the Dutch colonizers who recruited settlers from 1624. Around 1641 about a third of the island was under Dutch administration. The Dutch colonial administration also began Christian proselytizing the natives and set up the first public schools. The Latin alphabet introduced by the Dutch persisted into the early 18th century.
The Dutch colonial rulers were driven out by Koxinga (Zheng Chenggong), a warlord, pirate, merchant of Sino-Japanese descent and Ming loyalist . In 1683 the new rulers in Beijing , the Qing Dynasty (1644–1911) founded by the victorious Manchus , annexed the island.
Japanese rule

In the Peace of Shimonoseki , China had to cede Formosa (Taiwan) and the Pescadors to Japan after the lost Sino-Japanese War of 1894/95 . In response, the former provincial government of Taiwan proclaimed the Republic of Formosa and resisted the cession with the support of parts of the population, so that Japan had to conquer the island in a campaign lasting several months . Taiwan remained a Japanese colony until 1945.
The Japanese colonial administration also brought the indigenous people under its control and set up schools and police stations in the villages. The headhunting , which had been common with individual tribes until then , was stopped. Towards the end of their rule, the Japanese tried to introduce Shintoism as the state religion and ideology in Taiwan .
In 1919, the population was estimated to be approximately 3 million Han Taiwanese (Chinese) , 100,000 Japanese, and 120,000 indigenous peoples.
Republic of China
In 1945, following the Japanese defeat, Taiwan was incorporated into what was then the Republic of China under the leadership of Chiang Kai-shek in accordance with the Allied war aims ( Cairo Declaration ) , while the civil war between the ruling Kuomintang (KMT) and the Chinese communists flared up again on the Chinese mainland . The troops of the Republic were initially welcomed by the Taiwanese people excited, but it was because of pervasive corruption , runaway inflation and economic decline rapidly to tensions between Taiwanese and by-Kuomintang government administration used, which is the incident of February 28, 1947 one in bloody suppressed popular uprising .
In 1949, the Kuomintang government under Chiang Kai-shek fled to the island after its defeat in the Chinese civil war and made the city of Taipei their seat of government. In 1949, around 1.5 million refugees came to Taiwan with it from all parts of mainland China , who today make up around 14% of the population with their descendants and are referred to as Waishengren in Taiwanese society .
The Kuomintang (KMT) ruled the island for four decades as an authoritarian one-party state . In 1987 the KMT repealed martial law and the first opposition party , the Democratic Progressive Party (DFP), was founded. The local languages, especially Taiwanese , long banned from schools, authorities and radio , experienced a renaissance. Efforts have also been made since the mid-1990s to preserve the culture and languages of the indigenous people.
See also
bibliography
- James Wheeler Davidson: The Island of Formosa. Past and Present. History, people, resources, and commercial prospects. Tea, camphor, sugar, gold, coal, sulfur, economical plants, and other production . London / New York 1903. (online at Internet Archive)
- Oskar Weggel : History of Taiwan. From the 17th century until today. Edition global, Munich 2007, ISBN 978-3-922667-08-7 . (1st edition. Böhlau, 1991, ISBN 3-412-02891-6 )
- NTU : Flora of Taiwan Volume 1. 2nd edition. 1994, ISBN 957-9019-52-5 . Online edition
- NTU: Flora of Taiwan Volume 2. 2nd edition. 1996. Online edition: photocopy / pdf
- NTU: Flora of Taiwan Volume 3. 2nd edition. 1993. Online edition: photocopy
- NTU: Flora of Taiwan Volume 4. 2nd edition. 1998. Online edition: photocopy
- NTU: Flora of Taiwan Volume 5. 2nd edition. 2000. Online edition: photocopy
- NTU: Flora of Taiwan Volume 6. 2nd edition. 2003. Online edition: pdf
Web links
- Country and travel information from the Federal Foreign Office
- official tourist website of Taiwan (English)
- Bertelsmann Stiftung Transformation Index Taiwan
- CIA World Factbook to Taiwan (English)
- Link catalog on Taiwan at curlie.org (formerly DMOZ )
Individual evidence
- ^ Victor H. Mair: How to Forget Your Mother Tongue and to Remember your National Language. Pinyin.info website, accessed January 1, 2017
- ^ Kang Chao, Marshall Johnson: Nationalist Social Sciences and the Fabrication of Subimperial Subjects in Taiwan. In: positions: east asia cultures critique. Volume 8, no. 1, 2000, pp. 151-177.
- ↑ Executive Yuan (ed.): The Republic of China Yearbook 2016 . 2016, ISBN 978-986-05-0041-7 , ISSN 1013-0942 , 1. Geography & Demographics, pp. 42 (English, pdf ).
- ↑ a b 2018-2019 Taiwan at a glance. January 10, 2019; Retrieved November 30, 2019 (Taiwan Government Leaflet).
- ^ Amphibiaweb.org
- ↑ Taiwan's Reptiles in The Reptile Database , as of January 17, 2016.
- ^ Alison Hsiao: Snakes coming out with the arrival of spring, CDC warns. In: Taipei Times. March 27, 2013, accessed December 28, 2017 .
- ^ Snakes of Taiwan. Retrieved December 28, 2017 (English).
- ^ Executive Yuan , ROC: The Republic of China Yearbook 2014 . Taipei 2014, ISBN 978-986-04-2302-0 , pp. 304 ( gov.tw [PDF; accessed June 11, 2016]).
- ^ Executive Yuan , ROC: The Republic of China Yearbook 2014 . Taipei 2014, ISBN 978-986-04-2302-0 , pp. 160–168 ( gov.tw [PDF; accessed June 11, 2016]).
- ^ Water Quality. ( Memento of July 13, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) at: www.sinica.edu.tw/
- ↑ Energy Statistics from Bureau of Energy, Ministry of Economic Affairs
- ↑ CO 2 emissions are to be reduced to the level of 2000 by 2025. ( Memento from July 9, 2012 in the web archive archive.today ) In: Radio Taiwan International . December 21, 2007.
- ↑ Tapenkeng site, Encyclopedia of Taiwan .