History of south america
The history of South America began about 13,000 to 14,000 years ago with the colonization of America by humans . The written records of the South American cultures are very sparse until the discovery of America in 1492 and were even destroyed many times during the colonization .
The chronological table of human history offers a chronological and geographical overview of how South America is embedded in the history of mankind .
Prehistory and early history of South America
While the majority of archaeologists consider the Clovis culture to be the oldest human culture on the American continent around 13,000 years ago, this has been questioned by some researchers. Tom Dillehay dates the finds from the Chilean archaeological site of Monte Verde to an age of at least 14,000 years. He suspects immigration to South America by sea. This could have happened from Siberia across the North Pacific to North America or by Polynesian sailors across the Pacific to South America . Immigrants from Europe are also considered in some theories. None of these theses have been proven. Immigration probably took place in different waves.
The first reliable traces of a population around 8000 BC appear in South America. Chr. On. Stone tools and blades can be classified in this period. Cave paintings in the area around the city of Ayacucho in Peru and in the Lauricocha caves at the source of the Río Marañón also date from this period. The first cultivated cultivation of pumpkins and beans and the breeding of llamas are dated to about 4000 BC. Dated.
Pre-Columbian period
The oldest ceramics were found in Ecuador in the Guayas Basin . They are assigned to the Valdivia culture and date back to the 4th millennium BC. Chr. Dated. This oldest American culture already produced an urban organization with cults, rites and offerings at a time when the Sumer culture was developing on the other side of the world and historical records began in Egypt .
The city of Caral was discovered in 1996 and is the oldest known city on the American continent. The step pyramid was in 2001 to the year 2627 BC. Dated. Houses for at least 3000 people, amphitheaters and temples were found. Artificial irrigation systems ensured fertility in the middle of the desert area. Further finds prove that the population traded with the coastal and Amazon areas.
From the 2nd millennium BC Individual local cultures developed throughout South America. On the coast of Ecuador was created around 1600 BC. The Machalilla culture . They introduced the widespread ceramic vessels with handles that can still be found among the Chavín , Mochica and Chimú in the Andes .
The subsequent Chorrera culture was around the time from 1200 to 500 BC. Ceramics in human and animal form. Their houses were grouped around a large square and built on artificial embankments. They did a brisk trade with the Chavín.
Between 1000 BC BC and 500 BC The Arawak migrated along the Orinoco until they settled on the delta . They knew no ceramics, had canoes and lived from fishing, hunting and growing corn, beans, sweet potatoes , pumpkins and cassava . Peanuts, pepper, pineapple, tobacco and cotton were already known. After being discovered by the Spaniards, they fell victim to epidemics within a century.
The earliest advanced civilization still recognizable today was that of the Chavín , which began around 1800 BC. Until 300 BC Existed. The motifs of the Olmec culture, the big cat, bird and snake, suggest a connection. The ruins that have been preserved to this day are a magnet for tourism in northern Peru . The Paracas culture in the area around the Peruvian capital Lima falls in the same time frame . To this day, no one knows whether a separate culture existed or whether the dead were brought in from far away because of the dry, conservative air.
In Colombia , the Herrera culture existed in the highlands of Bogotá , as well as north of it and the Calima culture on the western cordillera around today's city of Cali. The period of these cultures is approximately between the 4th century BC. Estimated to 2nd century AD.
From the 4th century onwards, extensive tombs were laid out by the San Agustín culture and the terrain was deformed until the 7th century, probably for ritual reasons. The roots of the culture go back to the 7th millennium BC. BC back. Trade was conducted with both the coastal and Amazonian people.
Around Lake Titicaca developed from the 1st century BC BC to around 1000 AD, the Tiahuanaco culture. It is not clear whether there actually was a Tiahuanaco empire. The traces of this culture can be seen in Peru, Bolivia and the north of Chile . The Wari culture , which existed around the city of Ayacucho much later, is likely to be closely related .
Between 300 BC The Nazca civilization falls, which carved mysterious lines into the coastal soil and already knew irrigation channels. This culture was named after the nearby city of Nazca , about 500 km south of Lima.
From the 1st century onwards, the Mochica culture existed in the north , which operated high-yield agriculture with sophisticated irrigation systems in the desert strip on the Pacific coast. Both ceramics and metalworking were highly developed. In addition to gold and silver, copper was also processed. The Mochica had several principalities, but the culture disappeared in the 7th century, probably as a result of an El Niño event.
From 850 to 1500 the Capulí culture is tangible in northern Ecuador and southern Colombia .
After that, the Chimu developed in the period from 1000 to 1470 with the capital Chan Chan (sun sun) in the area around Trujillo in Peru. Their skills in handicrafts were less developed than those of the Mochica. They put more emphasis on mass production and useful objects.
The Chachapoyas lived on the eastern edge of the Andes from 800 to 1600 . Very little is known about them. The warlike people were tall and fair-skinned. The remnants of their culture are completely atypical for South American Andean peoples. The rock tombs that they left on the high cliffs are famous. In the 16th century, introduced diseases wiped them out.
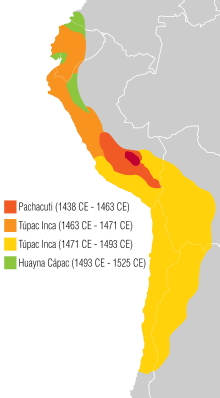
From 1438 to 1532 the Incas ruled over large parts of South America and created a huge empire. The arrival of the Spanish conquerors put an abrupt end to this.
Colonial times
conquest
Already in 1494 South America was in the Treaty of Tordesillas by Pope Alexander VI. split between Spain and Portugal . The eastern part, large parts of today's Brazil , was awarded to Portugal. Panama and the rest of the continent fell to Spain. The Spanish conquest came from Central America and the Caribbean in search of the legendary gold country El Dorado . The history and information about the settlement of the Portuguese part can be found in the history of Brazil .
The first settlements of Spanish immigrants emerged as early as 1520 in what is now Venezuela , Colombia and Argentina . Driven by the rich gold sources in Mexico , Francisco Pizarro explored the Pacific coast of South America from Panama for the Spanish crown in search of riches. In 1526 he came to what is now Ecuador and Peru. In the two years 1532/1533 he knew how to exploit the turmoil of the fratricidal war between the Inca Huáscar and Atahualpa and subjugated the huge Inca Empire . The diseases brought by the immigrants, which had devastating consequences for the original population, came to his aid.
In the Caribbean in particular , the population was almost completely wiped out within a very short time. Other conquests, especially Peru, resulted in excessive massacres. A comprehensive ideological conflict arose over the question of the treatment of the indigenous peoples with the exponents Bartolomé de Las Casas as “general defender of the Indians” and Juan Ginés de Sepúlveda , who viewed the Indians as a kind of subhuman. This dispute led to the enactment of the Leyes Nuevas ("New Laws") of 1542, which, although partially protected the Indians, were often ineffective and partially withdrawn. Later attempts by the Spanish crown to develop legislation to protect the Indians also failed due to a lack of will to implement it and the reality of colonial society in view of the profitability of exploitation. The silver mines of Potosí achieved sad fame , in which countless Indians worked under unbearable conditions during the colonial period and well over a million perished. Forced labor as part of the encomienda also led to desolate conditions for the indigenous population, as well as social disruption through the destruction of indigenous culture in the name of religion and civilization. In addition, the Indians occupied the lowest and weakest rank in the colonial caste society. The persecution of the Indians was particularly radical in those areas that were wrested from the Europeans in the 19th century, in the famous Indian Wars, but also during the conquest of Patagonia . Here it came to the deliberate extermination of entire tribes, so that one has to speak of a deliberate genocide .
administration
Christopher Columbus was the supreme authority in the New World until around 1500 . Only with the stabilization of the huge empire and the establishment of the viceroyalty of New Spain (Mexico and Venezuela) and the viceroyalty of Peru (Spanish part of South America and Panama) in 1543, with Lima as the capital, there were two representatives of the king on the continent. The viceroy of Peru was considered to be of higher rank because of the silver deposits in Potosí . The empire was divided into provinces, each headed by a governor with administrative and judicial powers.
In Europe separate institutions have been set up for the administration of the overseas territories. They drafted laws and took on political tasks. In the Cedulario Indiano , at that time the most important reference about the laws in the new areas, there are about 3500 laws.
An important means of colonization was the founding of cities. They served to consolidate claims to power. At first only intended for the Indian population, they later also served against the claims of other European powers. Every foundation was carefully checked. They were administered by a city council, which was composed of two city judges and councilors. In addition, the Spanish king appointed a person who was directly subordinate to him and who had the task of establishing order and royal authority.
In 1717 Ecuador, Colombia and Venezuela broke away from the viceroyalty of Peru and formed the viceroyalty of New Granada . Bolivia, Chile, Argentina and Paraguay followed suit in 1776 and created the new viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata .
Population change
Only the Inca, with their tightly organized infrastructure, made it possible for the Spaniards to bring the huge empire under their rule in a short time and to reshape the situation according to their interests. Smaller cultures, the forms of which were based on kinship rules, such as existed in southern Chile and Argentina, could never be brought under the control of the colonial regime due to a lack of centralized political organization. In return, however , the Indian tribes acquired agricultural techniques , cultivated plants and, above all, the horse.
With the many different peoples in the Amazon region , contact was limited to trade and missionary purposes, also because of the sparse population . In the steppes and savannahs of Paraguay , northern Argentina and the eastern part of Bolivia, nomadic hunters and gatherers lived in groups of barely more than 100 people. Colonization was more opposed to displacement and extermination through disease.
After the Spanish conquest, the population decline of the indigenous population was dramatic. The reasons for this lay in the diseases that were introduced, the warlike events, the deaths from the enslavement of the Indians and the change in eating habits. Due to the large-scale cultivation of sugar cane and the introduced grazing animals, there was no space left for the cultivation of conventional foods. This also increased soil erosion . The labor shortage caused by the population decline of the natives eventually led to the importation of slaves from Africa in large parts of South America.
By mixing the various population groups, a three-part social stratification finally developed. At the top of the list were the Spanish immigrants, followed by their descendants, the Creoles mixed with the local population . The lowest stratum was made up of the indigenous population.
Effects of Spanish Colonial Policy
Due to the numerous military undertakings, the mother country needed enormous financial resources, which the American possessions provided in the form of goods, gold and silver. This made the Spanish kings more independent of the estates in their own country, which the Habsburgs did well. Charles V consumed almost 3 billion ducats for his Tunis campaign alone , which the new world had to raise. The successors followed his example. From the 17th century, money deliveries from the New World decreased steadily, which went hand in hand with the decline of Spain as a hegemonic power in Europe, which, in addition to the lack of silver and gold deliveries from the American colonies, was also due to the decline in domestic economic output and increasing inflation was.
The colonization of South America took place at the expense of the local population with the loss of people and cultures, while in Europe the great power politics of Spain would never have been possible without the funds from the new world.
Decolonization
Encouraged by the French Revolution and the independence of the British colonies in North America, but mainly caused by deficiencies in the Spanish colonial system and the Spanish trade monopoly, the rebellion against the Spanish motherland developed. The decisive role was played by the Creole upper class, which initiated and drove the independence movement on the basis of economic interests, the pursuit of power and the economic pressure caused by Spanish expropriation measures. The demand for independence had been discussed since 1808 and in 1809 the first uprisings broke out in the Real Audiencias Chacras (now Bolivia ) and Quito , which the rest of the states in Spanish America joined in the following year. The self-government implemented first, followed by the declaration of independence only later, was in the spirit of the Spaniards occupied by Napoleon Bonaparte and was further promoted by the constitution of Cádiz in 1812. The final detachment from the motherland was not undisputed in the ranks of the Creoles, so that in addition to the clashes with the colonial troops, there were also internal battles. The massive fighting among each other, especially in today's Colombia, prevented quick and sustained victories against the Spaniards, whose attention was tied up in their own country because of the French. Only in Argentina did the separatists hold out. An Argentine expedition failed in Paraguay in 1811, but the patriots there prevailed against the royalists that same year. In 1813 the country broke away from Argentina and became an independent republic.
Under the resistance of the royalists, the early republics in Bolivia, Ecuador and even twice in Venezuela collapsed. In Bolivia, repeated expeditions by the Argentines did nothing to change that. In Peru, in which the viceroy reacted with a mixture of harshness and courtesy, the patriots could not get beyond isolated, ultimately fruitless uprisings. This gave the Spaniards of Peru the opportunity to start a campaign to Chile, which ended the republic there between 1814 and 1817. In 1815 Ferdinand VII , who had returned to absolute rule in Spain, sent an expeditionary army to recapture the colonies in South America. Since this was almost at full capacity with the reconquest of Colombia and Venezuela, which was subjugated as early as 1814 but could not really be pacified, there were not enough troops for the other countries, Argentina ahead, to be really successful.
After the repulsed Spanish attempt at reconquest, the Argentines prepared a campaign to liberate Chile, which was successful. In the north , after unsuccessful attempts, Simón Bolívar , who had won the second republic in Venezuela and lost it again, was able to establish himself on the lower Orinoco in late 1817. His efforts to conquer Caracas were unsuccessful until he led a campaign into less guarded Colombia, by means of which he was able to defeat the Spaniards there in 1819. While the patriots were preparing the liberation of other countries, Ferdinand VII did not remain idle either. A second army, almost twice as strong as the first, was supposed to finally secure its colonies in early 1820, but its leader, Rafael del Riego , turned against his king and forced him militarily to recognize the constitution of 1812. Even if this phase was only lasted until the end of 1823, as it gave the Republicans of South America time to complete their work.
While the Argentine José de San Martín , who had liberated Chile with Bernardo O'Higgins , set out for Peru in 1820 to end Spanish rule, Bolívar prepared the overthrow of the Spaniards in his Venezuelan homeland, as well as in today's Ecuador. The colonial troops frustrated by the events in Spain lost Venezuela in 1821 and Ecuador in 1822. The " Greater Colombia " aimed at by Bolívar had thus become a reality. Meanwhile in Peru, San Martín was depriving himself of the fruits of his good work and was forced to seek help from Bolívar. However, he preferred to snatch Peru from the Spaniards on his own responsibility. In 1824 this was finally achieved by Antonio José de Sucre , who had already given Ecuador independence on behalf of Bolívar. With the fall of Peru, today's Bolivia was isolated and the Spaniards there fought each other, so that Sucre could finally lead the country out of colonial dependency without a battle in 1825.
Uruguay, which had been part of the viceroyalty of La Plata, gained independence from the United Provinces of Rio de la Plata (Argentina) in 1828 after fighting. In Brazil, the Portuguese had been more adept at dealing with their colonists. In 1822 they officially released the country into independence, but with Emperor Pedro I, a son of the Portuguese king remained in power. Therefore, one can only speak of real sovereignty in 1889, when the monarchy in Brazil was abolished. Guiana was granted independence by England in 1966, Suriname by the Dutch in 1976. French Guiana is still an overseas department to this day.
History of nation states
After independence, democracies were gradually built. In the 19th and 20th centuries, especially after the Second World War , almost all countries in South America were ruled by right-wing military dictatorships . Serious human rights violations occurred in almost all of the affected countries in the context of so-called dirty wars against political opponents of all kinds, especially in the 1970s and 1980s. This period was characterized by the secret disappearance and murder of tens of thousands of people ( Desaparecidos ) by state organs, which is a burden on the societies of Chile and Argentina to this day. All South American countries had been democratically ruled since 1990, but Venezuela has slipped into dictatorship since President Nicolás Maduro took office in 2013 . The foreign policy of the USA has always been an important factor influencing the political development of South America . Since the early 2000s, left-wing governments have come to power through elections in many South American countries.
| Timeline of the political direction of the governments in South America | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| country | 50s | 60s | 70s | 80s | 90s | 2000s | 2010s | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | 5 | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | 5 | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | 5 | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | 5 | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | 5 | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | 5 | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | 5 | 6th | ||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
██ Left / Socialist ██ Center-Left ██ Independent / Liberal / Centrist ██ Center-Right ██ Dictatorship or military regime
Web links
- http://www.indianer-welt.de/sued/
- From the Valdivia culture to the Inca
- Latin American Travelogues , Collection of Digitized Travel Reports, Center for Latin American and Caribbean Studies, Brown University, Rhode Island