subcontinent
A subcontinent is a large, coherent part of a continent that is clearly delimited geographically and can therefore be viewed as a self-contained unit. This geographical delimitation has its cause in the geological history of the area concerned and can be given by high mountains or a land bridge .
Examples
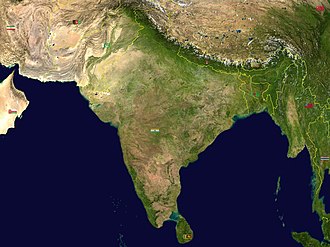
In common parlance, the term is primarily used for the Indian subcontinent , which is separated from the rest of Asia by a series of highlands and mountain ranges, including the Himalayas . These mountains were formed when India collided with Eurasia after a long period as a minor continent during the Paleogene .
Depending on the definition of the term continent , Europe is also classified as a subcontinent or peninsula in western Eurasia. The geographical delimitation is only clear in the south with the Mediterranean , Black Sea , Caucasus and Caspian Sea . Towards the east, the Ural Mountains as low mountain ranges and the Ural River do not represent a barrier that would justify a demarcation based on the pattern of India (see also Inner Urasian border ).
If North America and South America are not counted as independent continents, then they are considered subcontinent of America , which are connected by the land bridge of Central America . Other subcontinent are Madagascar and the Arabian Peninsula .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Gerhard Heck, Manfred Wöbcke: Arabian Peninsula . DuMont book publisher . P. 14. ISBN 978-3-7701-7994-7 .
- ^ Jörg Berchem: Elements of an Afro-Austronesian cultural syncretism . P. 300. ISBN 978-3-9210-0813-3 .