Demographics of Malaysia
The demographics of Malaysia is highly complex and difficult. The country of Malaysia comprises many ethnic groups alongside the politically dominant Malays who make up the majority.
The term Malaysian means a person with the citizenship of Malaysia, the adjective is "Malaysian". The term Malay, on the other hand, denotes belonging to a specific ethnic group. The adjective is "Malay".
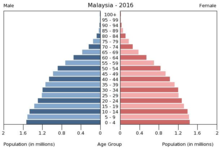
In 2008 Malaysia had a population of 27.2 million, of which around 5 million were in the two eastern states of Sarawak and Sabah . The Malaysian population growth rate is relatively constant at an annual rate of 2.4%. Malaysia is a young country in terms of its population profile: around 34% of the population is under 15 years old.
Malays
There is a constitutional definition for the Malays in Malaysia: According to Article 160 of the Malaysian Constitution, they are Muslims . These people, together with indigenous peoples of Austronesian origin ( Kadazandusun , Dayak , Melanau and other peoples mainly living in Sabah and Sarawak, as well as the Orang Asli ), are called Bumiputra , "sons of the earth".
The non-ethnic Malay indigenous peoples make up over 50% of the population of Sarawak and over 66% of the population of Sabah. They are divided into dozens of ethnic groups, but they share some general patterns of life and culture. They practiced animistic local religions until the 20th century , but most are now Christians or Muslims .
Minorities
The second largest ethnic group are Chinese , who historically played an important role in trade and commerce. Ethnic Indians make up the third largest ethnic group.
There is a small minority grouped in the state categorization known as the "other" category. This includes Malaysians who are (inter alia) of European descent or from the Middle East.
The population distribution is uneven: with around 20 million inhabitants, the majority is concentrated in the small flat land of the narrow Malaya peninsula. The rest of the population lives in northern Borneo in the Malaysian states of Sarawak and Sabah in a much lower population density.
There is no consensus on the ethnicity of children of different ethnic backgrounds. Some children choose to belong to the paternal race while others think they just fall into the "other" category. The majority choose to identify as a Malay as long as one of the parents is Malay, largely due to the legal definition and preference of Bumiputra.
Children from Sino-Indian mixed marriages are referred to as "Chindians". While this is not an official category in the state census, it is an increasing number of people especially in urban settings.
In Malacca there is a small community of descendants of the Portuguese colonial rulers who are Catholic and speak an ancient form of Portuguese (they say they can communicate with Brazilians without any problems).
In the border areas with Thailand there are Buddhist ethnic Thais, in the south of Thailand there are Muslim Malay. The border does not represent the border of the settlement areas.
Orang Asli
The indigenous people of the Malaya Peninsula are known as Orang Asli , which literally means "primitive man" and is a collective term for a variety of primitive people. They number about 60,000 people. 60 percent of them live in the country and 40 percent in the vicinity of cities. They were the first inhabitants of the Malaya Peninsula. Most of them are called Negritos and are related to the people of Papua New Guinea and possibly also to the Aborigines in Australia and peoples in East Africa. They came to the peninsula about 8,000 years ago and lived nomadically. The next largest group are the Senoi, who immigrated 6,000 to 8,000 years ago. They resemble mountainous tribes in Cambodia and Vietnam ; they are traveling farmers. The rest are Proto-Malayans of Sumatra who immigrated about 4,000 years ago. They are similar to the Malays. Many of them moved to the cities and knew how to assimilate with the Malays through marriage.
Total population
29,179,952 (July 2012, estimated)

-
age structure
- 0-14 years: 29.6% (male 4,374,495 / female 4,132,009)
- 15-64 years: 65.4% (male 9,539,972 / female 9,253,574)
- 65 years and older: 5% (male 672,581 / female 755,976) (2011, estimated)
statistics
- Growth rate : 1.54% (2011, estimated)
- Birth rate : 20.74 births / 1,000 population (2011, estimated)
- Mortality rate : 4.95 deaths / 1,000 population (2011, estimated)
-
Net migration rate : −0.37 migrant (s) / 1,000 population (2012, estimated)
- Note: these figures do not reflect the net outflow of the unknown number of illegal immigrants from other regions
-
Gender ratio :
- Birth: 1.07 male / female
- under 15 years: 1.06 male / female
- 15-64 years: 1.03 male / female
- 65 years and older: 0.89 male / female
- Total population: 1.01 males / females (2011, estimated)
- Child mortality : 14.57 deaths / 1,000 live births (2010)
-
Life expectancy at birth:
- Total population: 74.04 years
- male 71.28 years (2012, estimated)
- female: 76.99 years (2012, estimated)
- Total fertility : 2.64 children born per woman (2012, estimated)
nationality
- Name: Malaysian
- Adjective: Malaysian
Ethnic groups
| Ethnolinguistic assignment | Population (2005 census) |
|---|---|
| Abai Sungai | 500 |
| African | 1,000 |
| Albanians | 50 |
| Anglo- Americans | 11,000 |
| Australian | 20,000 |
| New Zealanders | 1,210 |
| Arab speaking Malay | 400,000 |
| Arabs, others | 12,662 |
| Arakan | 12,000 |
| Bajau | 203,320 |
| Bajau , Bukit | 1,140 |
| Bajau, Kagayan | 33,000 |
| Bajau from the west coast | 52,000 |
| Balau | 8,980 |
| Balinese | 5,065 |
| Banjarese | 1,187,734 |
| Bateq | 700 |
| Bengal , Bangladeshi | 200,000 |
| Bengal, Malaysian | 101,840 |
| Bidayuh | 210,000 |
| Bosniaks | 200 |
| British | 39,594 |
| Bugis | 718.435 |
| Burmese | 25,325 |
| Butonese | 15,195 |
| Champa | 10,000 |
| Chechens | 10 |
| Chin , Myanmar | 15,000 |
| Chinese, Baba | 417.673 |
| Chinese, Cantonese | 1,376,386 |
| Chinese from Fujian | 222,441 |
| Chinese from Guangxi | 186.211 |
| Chinese from Hainan | 386,636 |
| Chinese, Hakka | 1,813,631 |
| Chinese, Hokchiu | 379.077 |
| Chinese, Hokkien | 2,021,000 |
| Chinese, Hoklo | 59,572 |
| Chinese, Hsiang | 70,446 |
| Chinese, Hui | 15,000 |
| Chinese, mandarin | 973.207 |
| Chinese, Min Bei | 214,000 |
| Chinese, Min Dong | 253.248 |
| Chinese from the People's Republic of China | 172.972 |
| Chinese, Pu-Xian | 75,974 |
| Chinese, Teochew | 989.559 |
| Eurasier , Malayo-Portuguese | 6,035 |
| other Eurasier | 50,650 |
| Philippines , non- Tagalog speakers | 645.783 |
| German | 2,431 |
| Gujarati , Bania | Unknown |
| Gujarati, Bohra | 1,000 |
| Gujarati, Khoja | Unknown |
| Gujarati, others | 25,325 |
| Hindus | 50,560 |
| Iban | 650,000 |
| Indian citizens | 114.174 |
| Indonesian (language) | 253.248 |
| Japanese | 12,662 |
| Javanese , speaking Malay | 1,214,931 |
| Javanese, others | 785.069 |
| Jews | 10 |
| Kadazandusun | 500,000 |
| Canarian | 50,650 |
| Kayan | 75,000 |
| Khmer | 11,381 |
| Malays from Brunei | 56,000 |
| Malays, Cocos Islanders | 6,197 |
| Malaccers, Malays from Malacca | 37,987 |
| Malay from Negeri Sembilan | 311,000 |
| Malays of the East Peninsula | 2,100,000 |
| Malays of the West Peninsula | 7,579,000 |
| Malays from Riau | 101,299 |
| Malays from Sabah | 126,624 |
| Malay from Sarawak | 259,000 |
| Malay from Tioman | 50,650 |
| Malayali | 151,949 |
| Melanau | 34,080 |
| Minangkabau | 538.826 |
| Nepali | 208,000 |
| Pashtuns | 5,065 |
| Penan , Batu | 50 |
| Punjabi | 101,299 |
| Sindhi | 25,325 |
| Sinhalese | 25,325 |
| Tagalog | 25,325 |
| Tamils from Jaffna | 23,000 |
| Tamils, others | 1,798,062 |
| Tausug | 192,957 |
| Telugu | 101,299 |
| Thai | 25,325 |
| Urdu | 12,662 |
| Vietnamese | 83,000 |
Ancestors named by Malay Malaysians
Malay Malaysians are of various origins. Up to 40% of the Malays in Malaysia have Arab ancestors, followed by ancestors from neighboring Indonesia (around 30%), South Asia and some Malays even have Chinese and European ancestors (Portuguese, Armenians).
Religions
Islam (see Islam in Malaysia ), Buddhism , Daoism , Hinduism , Christianity , Sikhs ; Note - Addition: Shamanism is practiced in eastern Malaysia.
languages
Malaysian (official), English , Chinese dialects ( Mandarin , Cantonese , Hakka , Hokkien , Teochew , Hainan , Foochow ), Tamil , Telugu , Malayalam , Thai .
Note, addition: Various indigenous languages are spoken in East Malaysia, the most widely used are Iban and Kadazan .
The English language in official correspondence and exams is based on British English , although there is also an American influence as a result of television. Anyway, the English spoken in Malaysia has changed and is called "Manglish". "Manglish" is very similar to "Singlish", the English spoken in Singapore , although some slang terms differ.
Literacy
- Definition: 15 year olds and older people can read and write.
- Total population: 88.7%
- Men: 92%
- Women: 85.4% (2002)
literature
- Compilation of the linguistic-anthrophological source literature on the indigenous peoples of Sabah: Hans JB Combrink, Craig Soderberg, Michael E. Boutin, and Alanna Y. Boutin: INDIGENOUS GROUPS OF SABAH: An Annotated Bibliography of Linguistic and Anthropological Sources
- Barbara Farkas: Chinese immigrants in Penang . Peter Lang, Frankfurt am Main 2009, ISBN 978-3-631-58327-2 .
- Owen Rutter: British North Borneo - An Account of its History, Ressources and Native Tribes , Constable & Company Ltd, London, 1922
- LW Jones: The population of Borneo - A Study of the peoples of Sarawak, Sabah and Brunei , 1966; Reprint: Opus Publications 2007; ISBN 978-983-3987-08-5
Individual evidence
- ^ Text of the Malaysian constitution on Wikisource
- ↑ Malaysian Higher Education Ministry: Buku Panduan Kemasukan ke Institusi Pengajian Tinggi Awam, Program Pengajian Lepasan SPM / Setaraf Sesi Akademik 2007/2008 (Guidebook for entry into public higher learning institutions for SPM / equivalent graduates for academic year 2007/2008)
- ↑ a b c CIA - The World Factbook , as of August 2012; Accessed August 12, 2012