Rotary transformer
A rotary transformer is a special design of three-phase transformer , which allows a continuously adjustable alternating voltage to be obtained in a three-phase system. It is one of the so-called variable transformers and is used, among other things, in some older electric locomotives such as the Badische A1 for control purposes and in electrotechnical high-voltage laboratories as a continuously variable voltage source.
construction

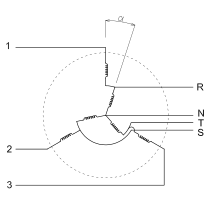
In contrast to conventional transformers , the rotary transformer consists of a double-fed asynchronous machine , the rotor of which is fixed in a certain position with a self-locking worm gear . Both the stator and the rotor of the machine consist of three windings each. The three stator windings, in the figure the connections 1, 2 and 3, are connected to the externally supplied three-phase system. The rotor windings are flexible cables to the terminals R , S and T led out, N represents the neutral point is. May be because only a finite angular positions between 0 and 2π is set via the worm gear on the rotor, in contrast to rotating machines no slip rings for the electrical Connection required.
The set rotor position in relation to the stator as a function of the angle α allows the coupling between stator and rotor to be changed, so that the voltage at R , S and T has an adjustable phase shift . Since the rotor windings are connected in series with the stator windings, the amount of the three-phase voltage at R , S and T is influenced by the vector addition , as shown in the phasor diagram below .
Due to the air gap between the rotor and stator, which is necessary for the design , rotary transformers have a comparatively high leakage flux , which limits the output. In addition, the technically possible insulation strength only allows operating voltage ranges up to approx. 20 kV. In this design, the rotary transformer has no galvanic isolation . Because of these disadvantages, the rotary transformer is only used in special applications.
A similar function, which avoids these disadvantages, can be achieved with three-phase transformers in combination with a step switch for power transformers , but with the disadvantage that the voltage cannot be adjusted continuously.
literature
- Germar Müller, Bernd Ponick: Fundamentals of electrical machines: Volume 1 . 9th edition. Wiley-VCH, 2005, ISBN 978-3-527-40524-4 , pp. 645-649 .